Essential Guide to Recognizing the Most Common Skin Rashes
Discover a comprehensive overview of common skin rashes, including psoriasis, hives, fungal, bacterial, and parasitic infections. Recognizing these skin conditions early can improve treatment outcomes. Visual references help, but professional diagnosis remains crucial for proper care.
Sponsored
Skin rashes appear as changes in skin color or areas of inflammation. While online images provide visual references, they can sometimes be misleading because the visual presentation may not match the actual condition. Understanding the characteristics of various skin rashes can help in early identification and treatment. Here are some of the prevalent types of skin rashes to be aware of:
Psoriasis: A condition where skin cells multiply rapidly, about ten times faster than normal, leading to thick, scaly patches often found on elbows, knees, and scalp.
Hives: Red, swollen bumps that cause itching and burning; often triggered by allergies or histamine release, lasting from hours to days.
Drug-Related Rash: Quickly identifiable, these rashes may resemble hives or form blisters and bumps following medication exposure.
Heat Rash: Occurs in hot, humid conditions when sweat pores get blocked, causing tiny red spots across the body.
Fungal Infections: Rashes caused by yeast or fungal overgrowth, usually appearing as itchy, ring-shaped spots.
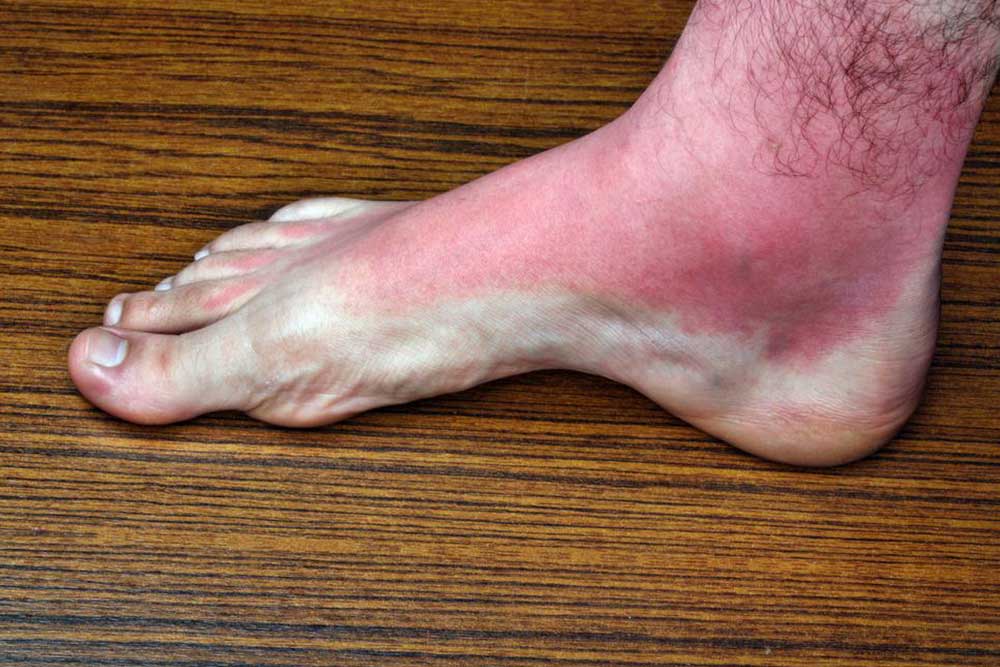
Bacterial Rashes: Such as cellulitis, characterized by painful, red, swollen areas requiring medical attention.
Parasite-Induced Rashes: For example, scabies caused by human itch mites, presenting as intense itching and rash.
Tinea (Ringworm): A fungal infection resulting in ring-shaped rashes with scaly edges.
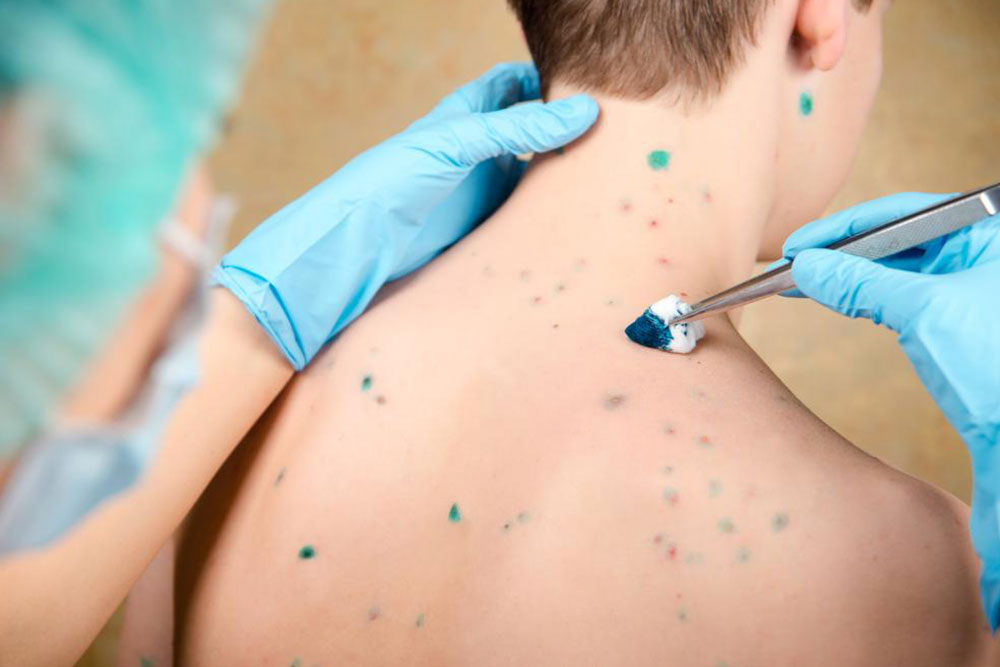
Chickenpox: Highly contagious, marked by red blister-like bumps that evolve into itchy vesicles.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: Features ulcers and rashes around the mouth, hands, and feet, often accompanied by fever.
Photographs of skin conditions can assist in identifying illnesses, but consulting a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.