Recognizing the Key Indicators of Cystic Fibrosis
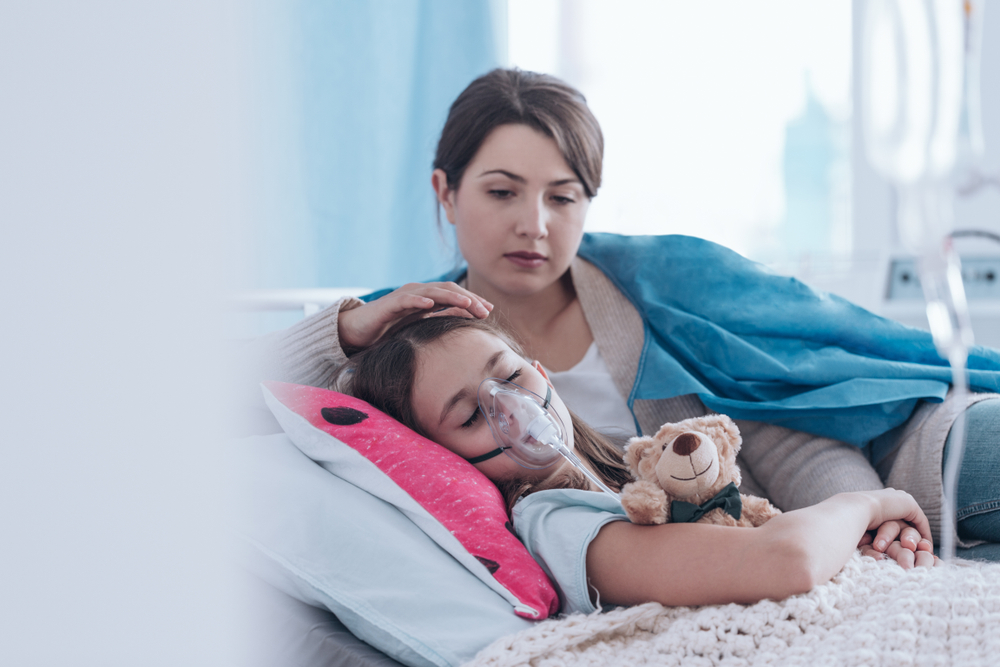
Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disease impacting the lungs and digestive system, characterized by thick mucus that causes cough, breathing issues, digestive problems, delayed growth, and other symptoms. Early detection is key to managing this life-threatening condition effectively.
Sponsored

Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary condition impacting both the respiratory and digestive systems. It results from defects in cells responsible for mucus, sweat, and digestive juices, causing these fluids to become thick and sticky. This thickened mucus can block airways, affect the pancreas, and lead to various health issues. The disease can be life-threatening and tends to shorten lifespan. Understanding its symptoms is crucial for early detection and management.
The common signs of cystic fibrosis include:
Persistent Cough - Due to mucus buildup, chronic coughing with phlegm or blood may occur.
Breathing Difficulties - Lung obstructions can cause shortness of breath, wheezing, pulmonary hypertension, or sinus infections.
Stomach Discomfort - Abdominal pain can stem from bacterial overgrowth, malabsorption, and constipation.
Digestive Problems - Thick pancreatic fluids may cause heartburn, diarrhea, or greasy stools.
Delayed Growth - Children and teenagers might experience slowed development and delayed puberty.
Exhaustion - Reduced oxygen intake and lung function can lead to fatigue, even after adequate rest.
Nasal Polyps - Growths in the sinuses can block airways, causing loss of smell and sinus issues.
Weight Loss - Despite high appetite, individuals often become underweight due to malnutrition.
Male Infertility - Especially common in men, it typically doesn’t affect sexual activity or children.
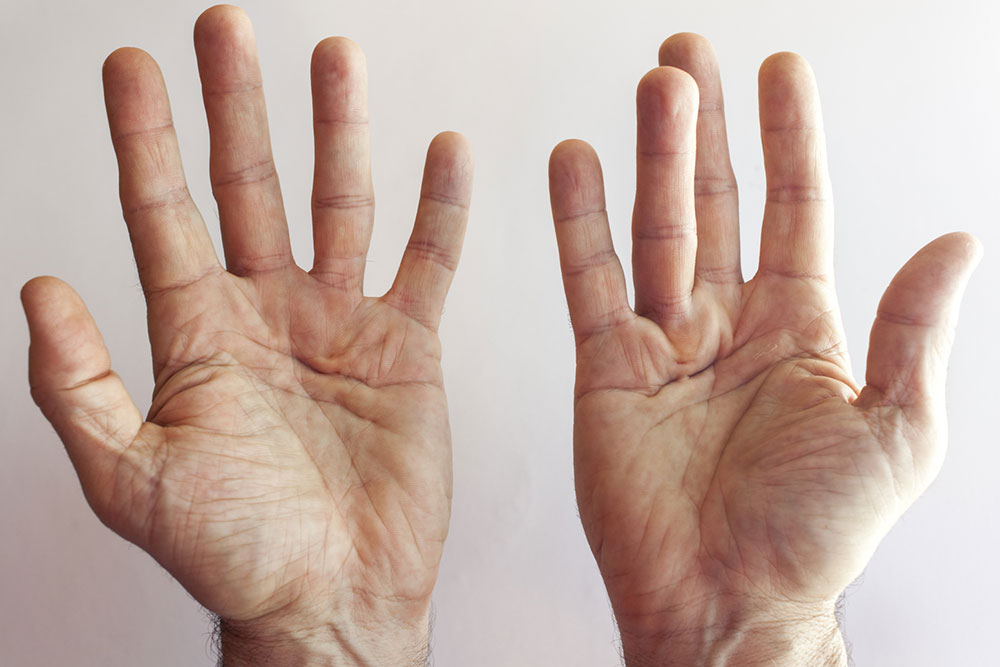
Nail Abnormalities - Clubbed fingertips and curved nails signal low oxygen levels in the blood.