Top 10 Causes of Skin Hives and How to Deal with Them
Discover the top causes of skin hives, from allergens and food sensitivities to infections and environmental triggers. Learn how to identify and manage outbreaks effectively, and when to seek medical attention for persistent symptoms.
Sponsored
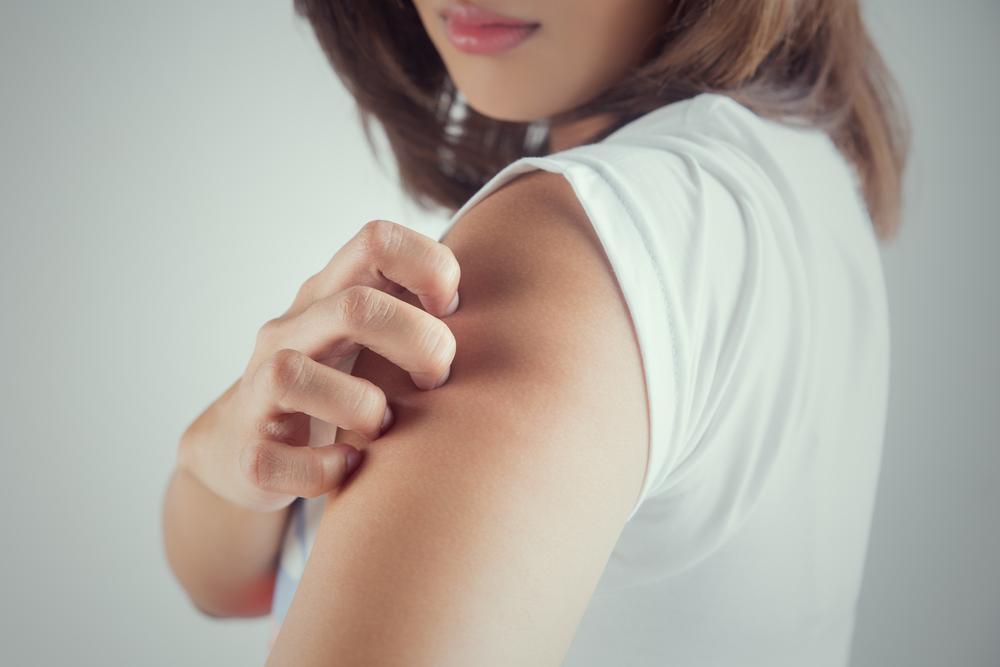

Top 10 Causes of Skin Hives and How to Manage Them
Skin hives, known medically as urticaria, are sudden, raised, red, and itchy bumps that can appear unexpectedly on any part of the body. Typically lasting between 6 to 12 hours, these bumps often fade without lingering effects. They vary in size and may merge into larger patches called plaques. Hives are commonly triggered by allergic reactions to various substances, prompting your immune system to react by forming rashes across your skin.
Locations can include lips, ears, face, shoulders, chest, and back. The discomfort is often accompanied by burning or stinging sensations, which can be embarrassing and inconvenient.
Understanding the causes of hives is essential for prevention and treatment. Here are crucial factors that can lead to their development:
External Triggers
Hives often result when skin cells release histamine in response to external substances. Common triggers include dust, pollen, pet dander, or insect bites and stings. Identification of the specific allergen can help in managing outbreaks.
Food Sensitivities
Many people develop hives after consuming certain foods. Common allergens include nuts, dairy, eggs, shellfish, berries, or foods with artificial colors and flavors. Reactions may occur immediately or after contact with these foods.
Infections
Viral and bacterial infections can cause hives, often accompanied by other symptoms like fever. These viral hives typically appear before or during the onset of illness and tend to resolve as the infection clears.
Clothing Choices
Tight-fitting clothes can increase friction on the skin, aggravating or triggering hives. Wearing loose, breathable clothing can help prevent irritation, especially during hot weather.
Medications
Allergic reactions to drugs such as antibiotics, aspirin, or certain medications can lead to hives. If you suspect medication as a trigger, consult your doctor for alternative options.
Stress and Anxiety
Psychological stress can worsen skin conditions, including hives. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Sun Exposure
Some individuals develop sun-induced hives, known as solar urticaria. These red, itchy bumps appear upon direct sunlight exposure and may resist relief even with sunblock.
Temperature Extremes
Heat or cold sensitivities can cause hives. Heat hives occur in hot conditions or after physical exertion, while cold hives develop due to exposure to cold air or water.
Sweating
Intense physical activity leading to sweating can trigger hives in some individuals. The body’s chemical response post-exercise or from hot water showers may contribute to outbreaks.
Underlying Health Issues
Persistent or recurrent hives can be symptoms of underlying conditions such as lupus, thyroid disorders, or hepatitis. Medical evaluation is recommended if hives persist or worsen, to rule out serious health concerns.
In most cases, hives are temporary and resolve on their own without the need for medical intervention. Recognizing triggers and avoiding known allergens can help prevent future outbreaks.