Recognizing the Key Indicators of Thyroid Eye Disorder
Thyroid eye disease presents various signs such as protruding eyes, swelling, dryness, double vision, and eye discomfort. Recognizing these symptoms early helps in timely diagnosis and tailored treatment to maintain eye health and comfort.
Sponsored

Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy, also known as Graves' orbitopathy, refers to autoimmune conditions affecting the eyes and surrounding tissues. These conditions manifest through various signs that can help in early diagnosis and management. Recognizing these symptoms allows healthcare providers to tailor treatments that support eye health and reduce discomfort.
Exophthalmos
Protrusion of the eyeballs, or exophthalmos, is a prominent symptom of thyroid eye disease. It involves swelling or bulging of the eyes out of their sockets, making it a highly noticeable and urgent sign that warrants medical attention.
Protruding eyes can lead to dryness, irritation, and increased discomfort due to inflammation.
Periorbital swelling
Swelling or redness around the eyes, especially in the eyelids and surrounding tissues, is common in thyroid eye disease. Fluid buildup from immune attacks makes closing the eyes difficult, causing pain and irritation.
Gritty or Foreign Body Sensation
Patients often describe a feeling of grit or sand in their eyes, which stems from dryness and irritation. Increased dryness worsens the sensation, especially when blinking, moving, or rubbing the eyes.
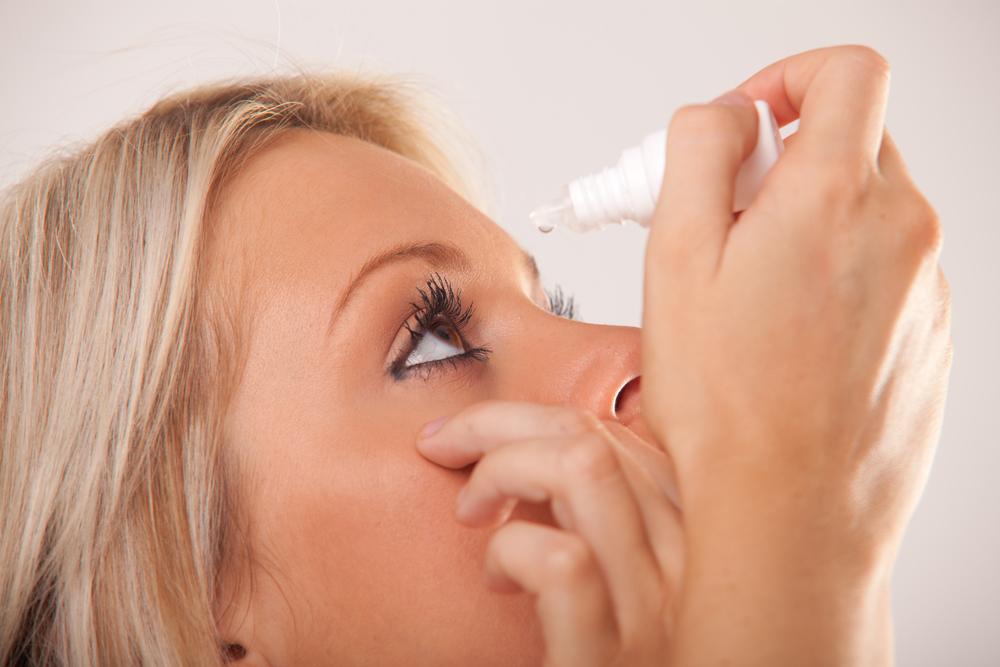
The autoimmune response impairs tear production, leading to dry eyes, irritation, blurred vision, and discomfort. Worsening environmental factors can exacerbate these symptoms.
Reduced Tear Production
Thyroid eye disease impairs tear glands, resulting in dry eyes or keratoconjunctivitis sicca. This causes red, irritated eyes, blurred vision, and discomfort that may intensify in windy or extreme environments.
Double Vision (Diplopia)
Difficulty aligning both eyes causes double vision, where objects appear as separate images. Inflammation or muscle issues interfere with eye coordination, affecting daily activities like reading and driving. Prompt medical evaluation is essential.
Eye Pain and Pressure
Inflammation and swelling often cause dull ache or stabbing pain in the eyes, along with pressure sensations. These symptoms may worsen with prolonged eye movements or activity.
Lagophthalmos
This condition prevents full eyelid closure due to eyelid retraction or bulging, risking dryness, corneal damage, and irritation. Medical care is vital to prevent complications.
Light Sensitivity (Photophobia)
Sensitivity to light often results from corneal dryness and irritation, causing discomfort and squinting. Patients tend to avoid bright environments to reduce symptoms.
Visual Changes
Thyroid eye disease can impair clarity and focus, leading to blurry or fluctuating vision. Muscle and nerve involvement cause difficulty in everyday activities, emphasizing the need for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Eyelid Retraction
Overly raised eyelids produce a staring or wide-eyed look, characteristic of thyroid eye disease. This can cause dryness, irritation, and altered facial aesthetics, prompting medical evaluation.