Top 11 Strategies to Manage and Treat GERD Effectively
Discover effective strategies for managing GERD, including medications, lifestyle changes, and surgical options. Understanding triggers and maintaining a healthy weight are key to reducing symptoms and preventing complications. Learn how dietary modifications and quitting smoking can significantly improve quality of life with GERD.
Sponsored
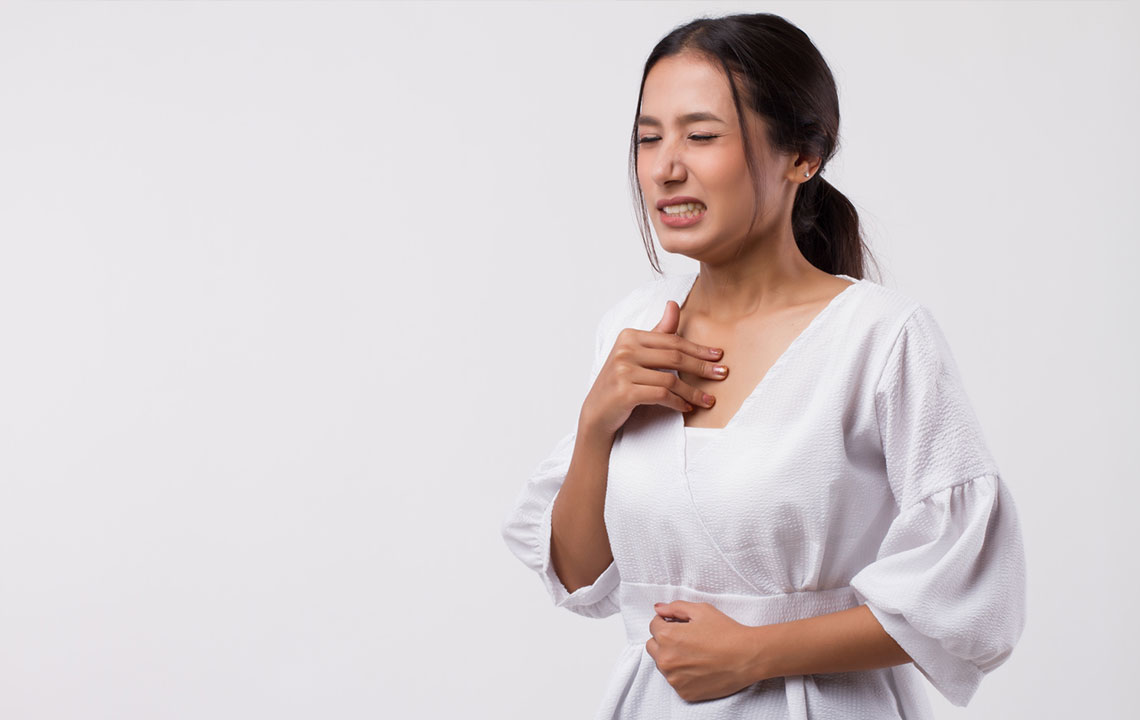

Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) affects roughly 20% of people, as reported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. It occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort. Symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, and coughing are common. While over-the-counter treatments help initially, lifestyle and dietary modifications are essential for complete relief. Untreated GERD can cause lasting esophageal damage. Effective options include prescription medications, surgical interventions, weight management, and dietary adjustments. Quitting smoking also plays a crucial role in symptom control.
H-2 Receptor Blockers: Available by prescription, these include drugs like famotidine and ranitidine, which reduce acid production. Long-term use may slightly increase risks of vitamin B-12 deficiency and bone fractures.
Medications to Enhance Esophageal Sphincter Function: Drugs like Baclofen help tighten the lower esophageal sphincter, reducing reflux episodes. Side effects such as fatigue or nausea are common.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Prescription-strength PPIs like Nexium 24HR significantly decrease stomach acid by blocking enzymes in stomach lining. Taking them prior to meals offers optimal results. Over-the-counter options like omeprazole are also available, and discounts may be accessible.
Antacids: Neutralize stomach acid fast but don't promote healing of existing esophageal damage. Overuse can cause diarrhea or kidney issues.
Acid Suppression Medications: Such as H-2 blockers, these manage symptoms for up to 12 hours by lowering acid levels with longer relief than antacids. Prescription options are stronger.
Surgical Options - Fundoplication: When medication isn't enough, a minimally invasive surgery wraps part of the stomach around the lower esophagus to prevent reflux.
LINX Device: Tiny magnetic beads form a ring around the junction of stomach and esophagus, allowing food to pass while blocking acid reflux. Placement is via minimally invasive surgery.
Healthy Weight Maintenance: Excess abdominal weight increases pressure on the stomach, prompting acid reflux. Losing weight can significantly reduce symptoms.
Dietary Changes: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods like spicy, fried, or high-fat foods, citrus, caffeine, and alcohol helps control symptoms. Keeping a food journal can be helpful.
Quit Smoking: Smoking damages the lower esophageal sphincter, exacerbating GERD. Quitting improves reflux symptoms and overall health.