Essential Insights into Common Stomach Disorders
Learn about three common stomach conditions—gastritis, peptic ulcers, and hiatal hernia—and their symptoms, causes, and risk factors. Recognizing these issues early can lead to better management and treatment, ensuring overall digestive health.
Sponsored
Stomach disorders encompass a variety of illnesses that impact the digestive organ, often resulting in abdominal pain and discomfort. While occasional stomach aches are frequent and often ignored, persistent or severe pain may indicate underlying health issues requiring medical attention. Here are three prevalent stomach conditions to be aware of:
Gastritis
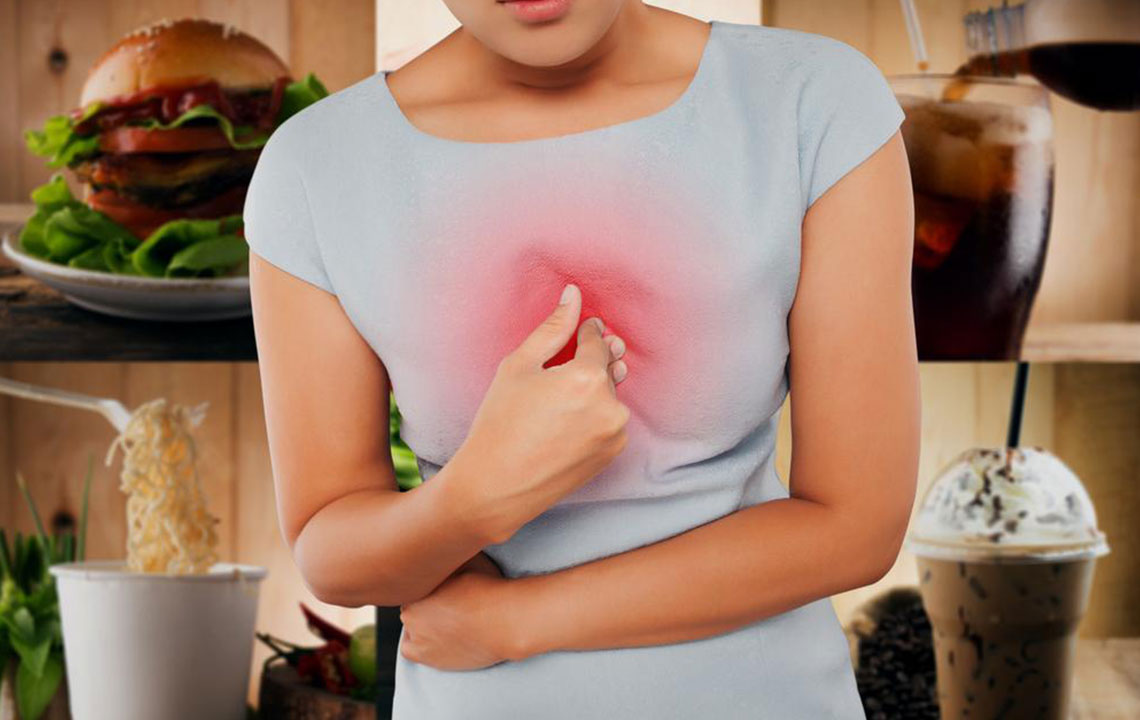
This condition involves irritation or inflammation of the stomach lining, which can develop suddenly or gradually. Chronic gastritis develops over time, presenting symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, heartburn, and decreased appetite.
Sometimes, gastritis may show no symptoms at all. The primary causes include bacterial or viral infections, bile reflux, or prolonged use of irritants such as certain medications. Risk factors are high stress levels, regular use of painkillers like aspirin, excessive alcohol intake, and chronic vomiting. Older adults often have a higher prevalence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, linked to gastritis.
Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers are lesions that develop on the stomach's mucosal lining caused by erosion from stomach acids or H. pylori infection. If untreated, ulcers can penetrate deeper, leading to perforation, which requires urgent care. Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, reduced appetite, belching, and early satiety. Fatigue and exhaustion can also accompany this condition.
Risk factors for peptic ulcers include smoking, alcohol abuse, spicy foods, and unmanaged stress. These factors can weaken the stomach lining and increase acid production, making the stomach more vulnerable to erosion.
Hiatal Hernia
This condition occurs when part of the stomach pushes through a gap (hiatus) in the diaphragm muscle between the chest and abdomen. Symptoms may include bloating, belching, persistent heartburn, and hiccups. Its exact cause is unknown but can be related to injury or age-related changes in the diaphragm. Overweight or obese individuals and those over 50 are at higher risk for developing a hiatal hernia.