Essential Overview of the Top 3 Lung Cancer Types
This article covers the three major types of lung cancer—Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Small Cell Lung Cancer, and Mesothelioma—highlighting their characteristics, origins, and importance of early detection for effective treatment.
Sponsored

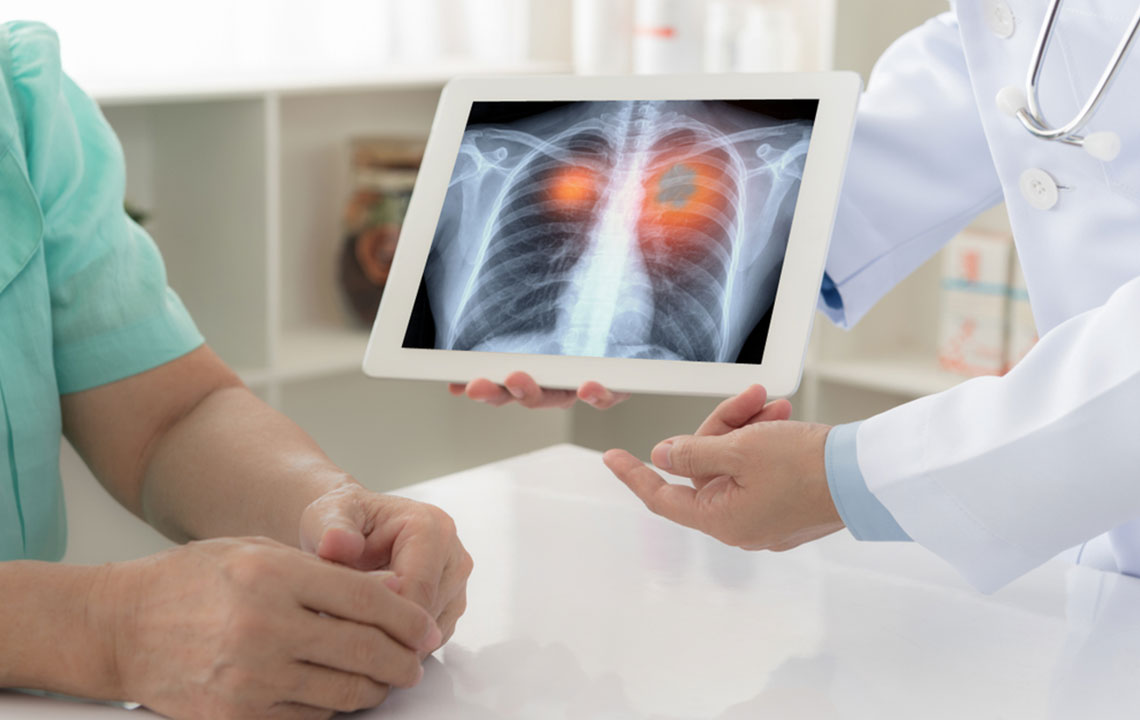
Lung health is vital for overall well-being, as our lungs facilitate the essential process of breathing. Lung cancer occurs when healthy lung cells mutate and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors. Understanding the main types of lung cancer can aid in early detection and treatment.
The primary categories include:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common form, progressing slowly over time. Subtypes include:
Adenocarcinoma: Arises in the lung lining with gland-like features, accounting for about 30% of cases.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Develops in flat respiratory tract cells.
Large Cell Carcinoma: Makes up approximately 9% of cases and grows rapidly, often hard to distinguish from other types.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): Known for rapid spreading throughout the body, this neuroendocrine tumor involves small-sized cells. It is classified as limited or extensive based on disease progression.
Mesothelioma: Strongly linked to asbestos exposure, this cancer can originate in the lungs (primary) or metastasize from elsewhere (secondary). Despite different origins, treatment approaches are similar.
Additional types include carcinoid tumors, which start in the small intestine but can spread to lungs. Early diagnosis enhances treatment success.