Effective Strategies to Eliminate Chalazion
Learn effective, safe methods to treat chalazion, including warm compresses, eyelid massages, and when surgery is necessary. Early intervention prevents complications and provides relief from discomfort. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice to manage this common eyelid condition promptly.
Sponsored
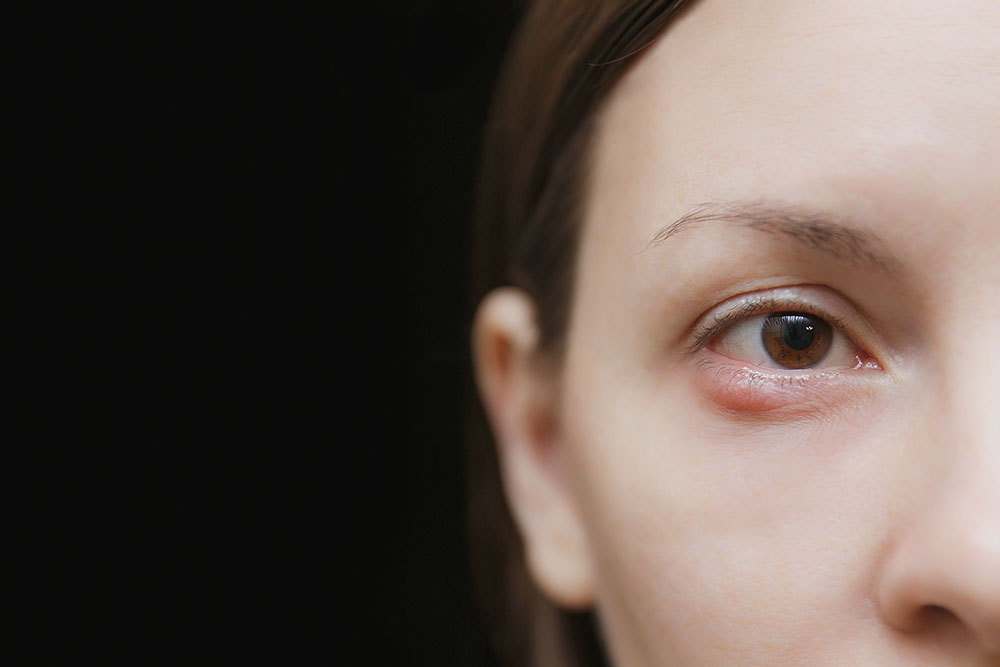
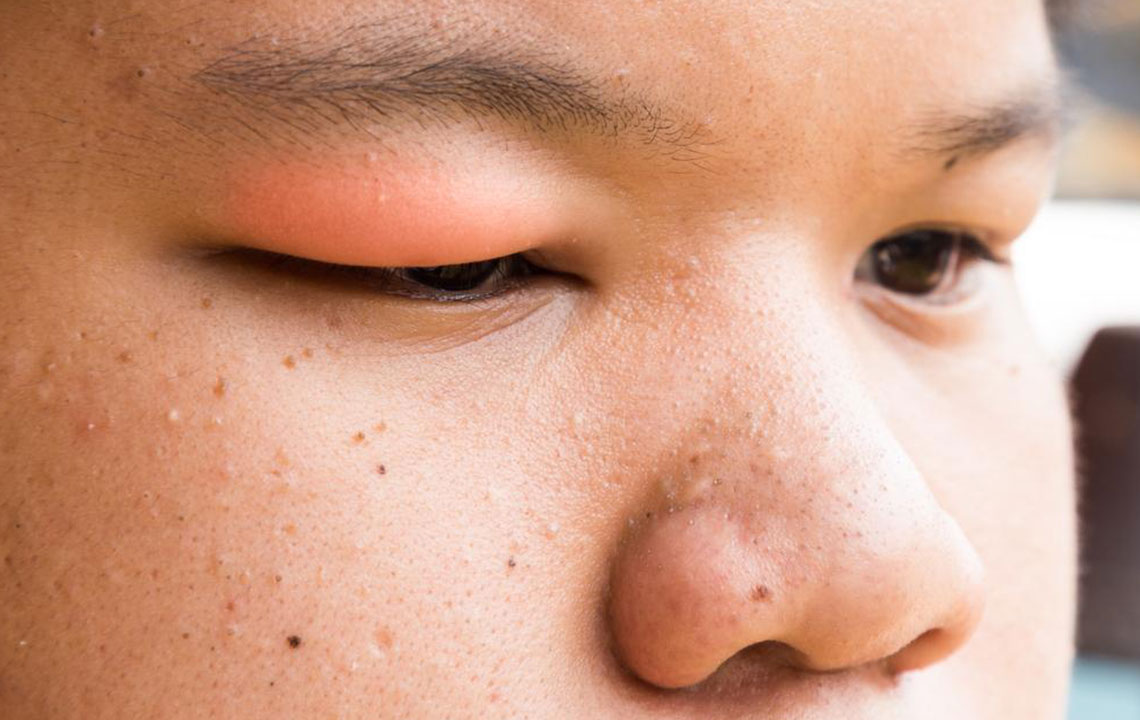
A chalazion is a small, painless bump that appears on the eyelid due to blocked oil glands called meibomian glands. When these glands become clogged, the buildup causes swelling and inflammation. While not the most serious eye condition, chalazion can be uncomfortable and tend to recur. Many individuals seek help from healthcare providers to eliminate this condition effectively.
Recognizing Chalazion Symptoms:
Swelling on the eyelid, which may be multiple lumps
Swelling around the eye area
Discomfort and sensitivity
Warmth, heaviness, and increased pressure on the affected eyelid
Itching and possible pus discharge
How to Treat Chalazion?
Applying Heat:
Applying gentle heat to the affected eyelid helps open the blocked gland. Use a warm, damp cloth or a heat pack for 1-2 minutes, wrapped with a thick cloth like muslin for prolonged warmth. Hold it close to the eyelid to soften the oil and facilitate drainage. Reheat as needed to maintain warmth.
Massaging the Eyelid:
Gentle massage aids in breaking down the blockage. For upper eyelid chalazion, massage upward; for lower eyelid, downward. This encourages pus drainage, reducing swelling. If painful, take paracetamol to ease discomfort during massage.
Medication and Medical Advice:
If signs of infection appear, such as spreading redness or fever, consult a doctor. Antibiotics may be necessary, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying conditions. Remember, heating and massaging are also essential components of treatment.
Importance of Prompt Treatment in Children:
Children with eyelid infections should be evaluated early, as their developing eyelid septum allows infections to spread rapidly into deeper tissues, risking more serious complications.
Surgical Removal:
Large, painful, or persistent chalazion may require surgical removal. The procedure involves local anesthesia, a small incision, and removal of the gland’s contents. Recovery is quick, though swelling, bruising, and discomfort are common initially. Most individuals return to normal activities within days.
Summary:
While chalazion can leave minor scars or a small bump, early and appropriate treatment prevents complications. Non-surgical methods like warm compresses, eyelid massage, and medication are preferred initially. Surgery remains an option for stubborn cases, with generally positive outcomes.