Top Strategies for Effective Acne Treatment
Discover effective acne treatments including OTC options, steroid injections, light therapy, and retinoids. Learn how each method works to combat pimples, cysts, and skin inflammation, ensuring healthier skin through personalized approaches. Consult a dermatologist to determine the best plan for your skin type and severity.
Sponsored
Acne, also known as "Acne Vulgaris," is a persistent skin condition that can result in pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, or even cyst formation. Human skin contains tiny, invisible pores called hair follicles, which include oil-producing sebaceous glands. These glands secrete sebum, helping to keep skin hydrated and hair healthy.
Sometimes, excess sebum and dead skin cells clog these pores, leading to blockages. This buildup causes sebum to accumulate while the glands continue to produce oil. Bacterial growth on these blocked follicles can cause redness and swelling, resulting in acne formation.
Effective acne management includes various options. Here are some of the best treatments available:
Over-the-Counter Products: Many brands offer creams, gels, soaps, and lotions containing active ingredients like Benzoyl Peroxide, Salicylic Acid, Azelaic Acid, and Sulfur. These help diminish bacteria, clear blocked pores, and reduce inflammation. Benzoyl Peroxide kills P. acnes bacteria and exfoliates skin, but it may cause skin bleaching. Salicylic Acid aids in peeling away layers of dead skin and unclogs pores. Azelaic Acid has anti-inflammatory benefits, suitable for mild cases. Sulfur dries excess oil and cleanses bacteria but can have a strong odor.
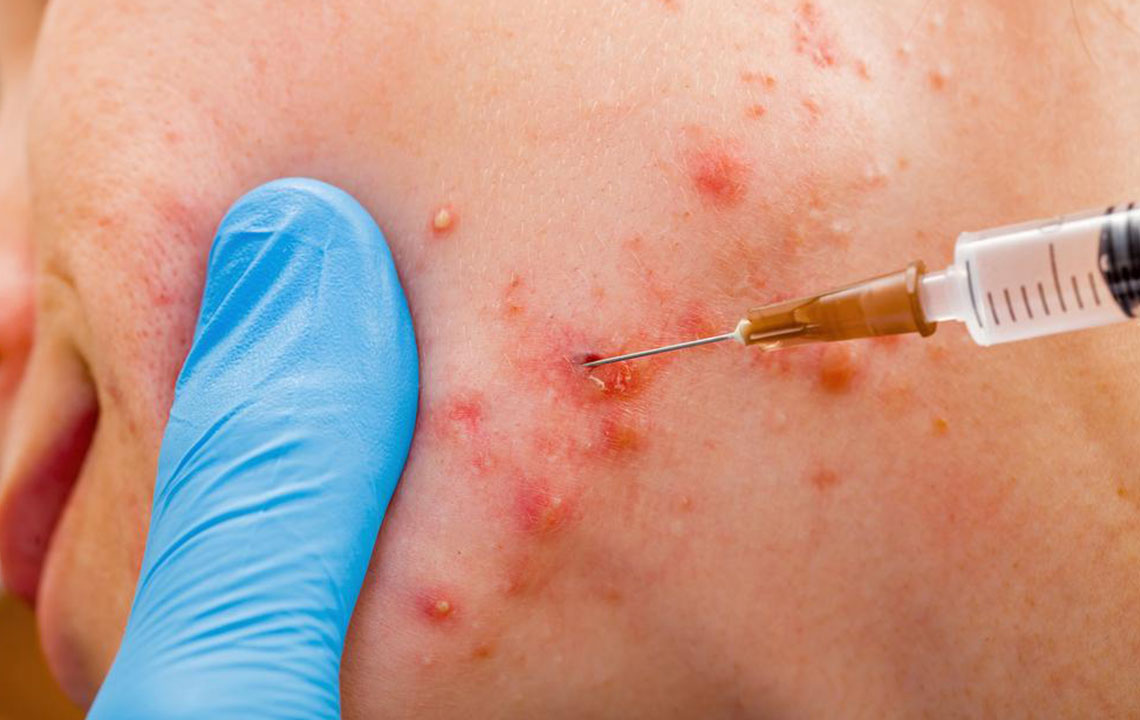
Corticosteroid Injections: For severe cystic acne, steroid shots provide rapid relief by reducing swelling and inflammation. While effective for cysts, they do not eliminate bacteria and typically show results within a few hours.
Photodynamic Therapy: This minimally invasive procedure uses blue light along with a special solution like Levulan to target and destroy acne-causing tissues. It involves applying the solution, waiting for activation, then exposing the skin to the light source, effectively reducing acne.
Retinoids and Vitamin A Derivatives: Topical retinoids such as Tretinoin, Differin, and Retinol help to open clogged pores and reduce sebum production. Oral options like Isotretinoin are reserved for severe or resistant acne, but carry risks like skin dryness, sensitivity, and for pregnant women, birth defects or mood changes.
The selection of treatment depends on acne severity and skin type, so consulting a dermatologist is recommended for personalized care.