Top 4 Causes of Elevated Bilirubin Levels
High bilirubin levels can be caused by liver diseases, bile duct blockages, hemolytic anemia, or medication side effects. Recognizing these causes is vital for diagnosis and treatment of related conditions. This article highlights four primary reasons behind elevated bilirubin, emphasizing the importance of liver and blood health for overall well-being.
Sponsored

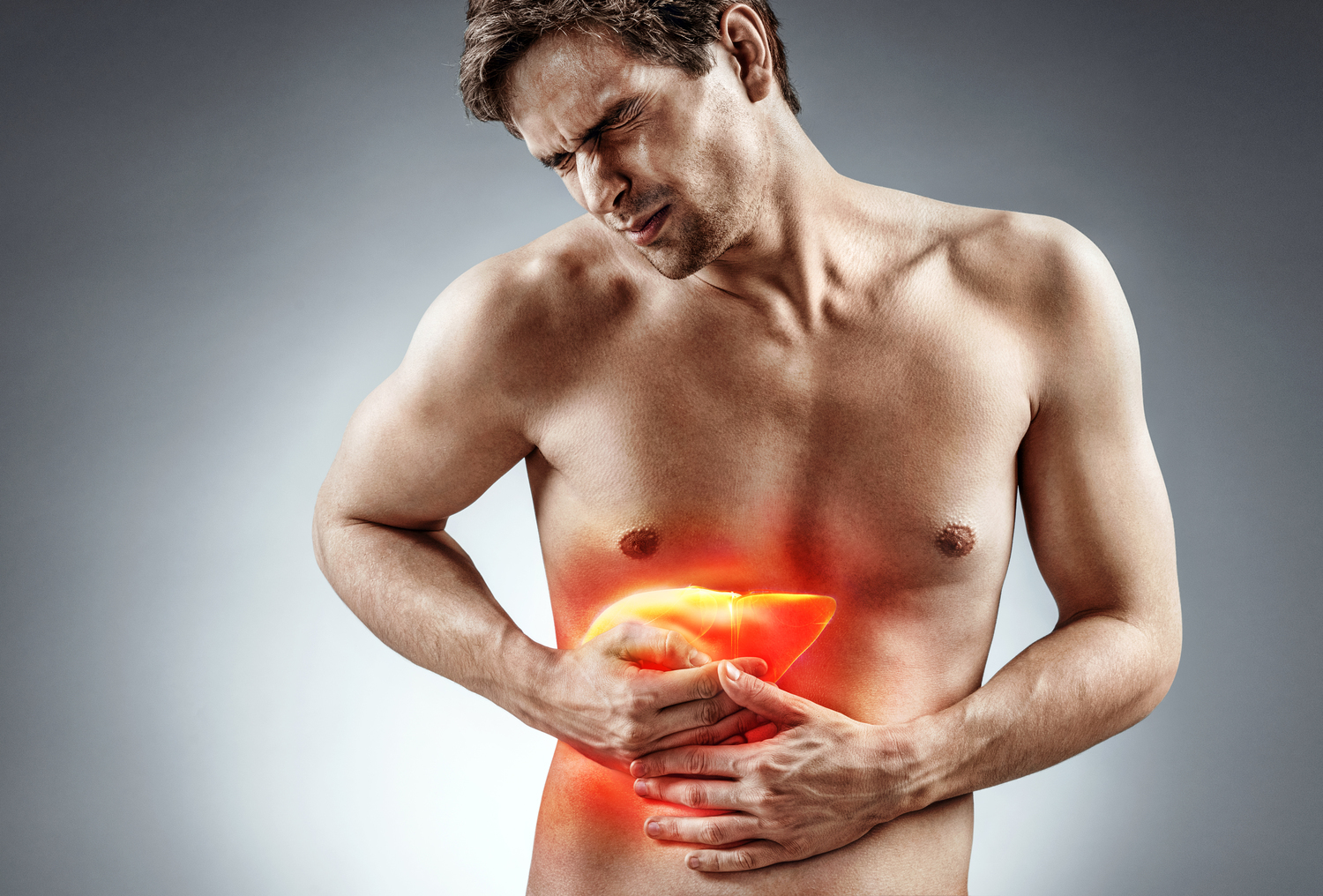
Bilirubin, a yellow-brown pigment found in bile, results from the breakdown of aged red blood cells processed by the liver. Hemoglobin in these cells converts into bilirubin, which is expelled through stool. Normally, small bilirubin amounts circulate in the blood without issues, but excessive levels can signal health problems. Conditions affecting the liver, red blood cells, or gallbladder can elevate bilirubin, leading to jaundice and yellow-tinted skin or eyes.
This article outlines four primary reasons behind high bilirubin levels:
Gallbladder and Bile Duct Disorders: Damage or blockages in bile ducts, caused by cholestasis or gallstones, hinder bile flow and raise bilirubin levels.
Liver Conditions: Diseases like hepatitis and cirrhosis impair the liver's ability to convert bilirubin into a soluble form, causing accumulation.
Hemolytic Anemia: Premature destruction of red blood cells boosts bilirubin production. Autoimmune diseases such as lupus and certain cancers can trigger this condition.
Medication Effects: Some drugs, including antibiotics for gout, psychiatric medications, estrogen, and steroids, can damage the liver or disrupt bilirubin processing, leading to elevated levels.