Top 5 Reasons for Discomfort Behind the Knee
Discover the top five common causes of pain behind the knee, including muscle cramps, tendon injuries, hamstring strains, Baker’s cysts, and arthritis. Recognize symptoms and seek proper medical care to maintain knee health and mobility.
Sponsored
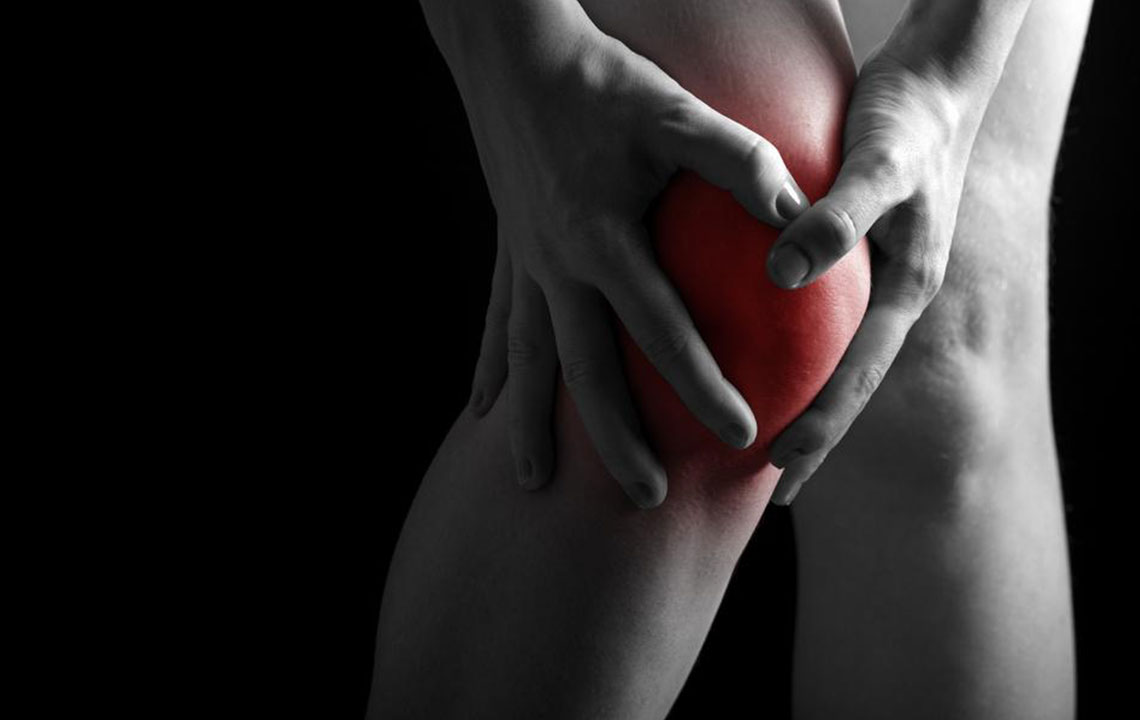
The knee joint is one of the largest and most intricate joints in the human body, composed of bones such as the shinbone (tibia), the smaller fibula, the thighbone (femur), and the kneecap (patella). It also consists of various tendons, muscles, cartilage, and ligaments, all working together to facilitate movement. Due to its complexity, the knee is highly susceptible to injuries, often leading to pain behind the knee at some point in life.
Activities like sports and exercise can sometimes strain muscles, cause fractures, or damage cartilage and ligaments. While some injuries heal naturally, others may require medical interventions or surgery. If knee pain is hindering your daily activities, it's crucial not to ignore it. Below are the primary causes of pain behind the knee:
Muscle Cramps
Sudden, intense contractions of muscles, especially in the calves or the back of the thigh, can cause pain behind the knee. These cramps often occur during physical activity or exercise. Factors such as pregnancy, dehydration, nerve issues, toxins, or liver problems can trigger cramps. The pain lasts from seconds to minutes, with possible swelling afterward.
Jumping-Related Tendon Injury
Patellar tendinitis, or jumper’s knee, involves small tears in the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone. Common in athletes engaging in jumping or rapid directional changes, it causes pain below the kneecap, stiffness, and muscle weakness if untreated.
Hamstring Strain
The hamstring comprises three muscles at the back of the thigh that assist in bending the knee. Excessive stretching can tear these muscles, resulting in sudden pain behind the knee. Symptoms include swelling, bruising, and weakness in the affected leg.
Baker’s Cyst
This condition features a fluid-filled sac forming behind the knee due to excess synovial fluid. It often results from knee injuries or arthritis, leading to swelling, stiffness, and discomfort. While sometimes resolving on its own, proper rest and therapy are recommended.
Arthritis
Arthritis involves the progressive breakdown of knee cartilage, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. Various types such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and psoriatic arthritis can impact the knee, sometimes necessitating surgical intervention.
If experiencing persistent or severe knee pain, consulting a healthcare professional is essential to prevent worsening of the condition.