Effective Nutritional Strategies for Managing Diabetes
Discover effective dietary strategies to manage and prevent diabetes. This article explores various meal plans, including Mediterranean, DASH, Paleo, and plant-based diets, along with foods to include or avoid. Combining proper nutrition with regular exercise can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce health risks associated with diabetes.
Sponsored

Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a metabolic disorder that impacts how the body manages insulin production. When insulin function is disrupted, carbohydrate metabolism is affected, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Key Facts About Diabetes
• Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood glucose levels.
• Type 1 Diabetes involves an inability to produce insulin, accounting for about 10% of cases.
• Type 2 Diabetes occurs when the body doesn't produce enough insulin or uses it inefficiently.
Many individuals are affected by type 2 diabetes.
• Symptoms include frequent urination, intense thirst, unexplained weight changes, fatigue, slow-healing cuts, numbness, male sexual issues, and tingling sensations.
• Those with Type 1 diabetes should adhere to a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and take insulin as prescribed.
• Type 2 patients benefit from physical activity, healthy eating, and regular blood sugar monitoring. Medications, including insulin or oral drugs, may be necessary.
• Monitoring cholesterol and blood pressure is vital, as diabetics are at higher risk for cardiovascular complications.
• Smokers with diabetes should quit immediately to reduce health risks.
Optimal Diet Plans for Diabetes ManagementPeople living with diabetes face nearly double the risk of heart disease and mental health issues such as depression. Fortunately, many cases of type 2 diabetes can be prevented or reversed by adopting proper dietary habits.
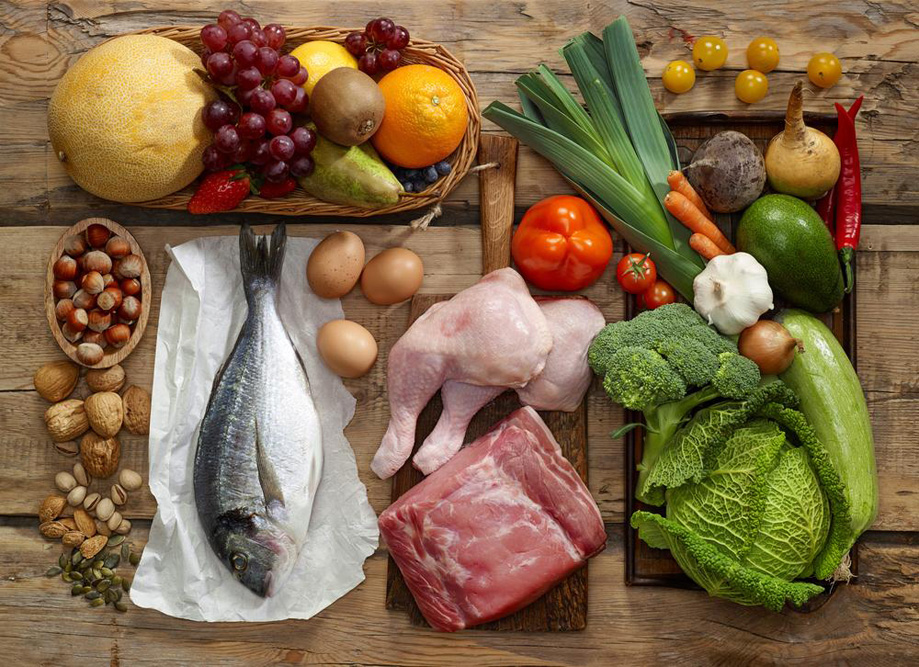
Incorporating lean proteins, high-fiber foods, fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy, and healthy fats like olive and canola oil is recommended. Limiting carbohydrate intake and focusing on complex carbs helps maintain blood sugar levels.
Foods to Limit for Better ControlDiabetics should restrict foods that elevate cholesterol and blood sugar, including:
• Refined grains like pasta and white rice
• Sweetened fruits such as jams and canned fruits
• Full-fat dairy products
• Foods containing trans fats or unhealthy unsaturated fats
• Refined flour-based foods
• High-glycemic foods with rapid sugar release
The DASH Diet for Blood Pressure and DiabetesThe Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) plan, initially designed to combat high blood pressure, also benefits diabetics. It emphasizes lean proteins, fresh produce, low-fat dairy, and whole grains, while limiting sweets, sugar-sweetened beverages, and red meats.
The Mediterranean DietThis diet reflects traditional Mediterranean eating habits, rich in healthy fats like olive oil and foods high in oleic acid. It can improve blood glucose control, support weight loss, and lower the risk of metabolic issues. Foods include seafood, poultry, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and moderate wine consumption.
The Paleolithic (Paleo) DietThis diet mimics ancient hunter-gatherer diets, emphasizing unprocessed foods like meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, seeds, and nuts. It avoids grains, dairy, and processed foods, potentially aiding blood sugar regulation and weight management.
The Gluten-Free DietThis diet eliminates gluten, a protein in wheat, rye, and barley, mainly required for those with celiac disease. It's not necessarily low-carb but can be beneficial when medically necessary. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting.
Vegan and Vegetarian Eating PlansVegetarian diets exclude meat but may include dairy and eggs, while vegan diets restrict all animal products. Suitable plant-based foods for diabetics include beans, soy, dark leafy greens, nuts, legumes, fruits, and whole grains. Combining diet with regular exercise helps maintain blood sugar levels and overall health.