Top 5 Health Conditions That Elevate Osteoporosis and Bone Density Decline Risks
Discover the top five health conditions that significantly increase the risk of developing osteoporosis and bone loss. From hyperthyroidism to celiac disease, learn how these ailments impact bone health and how to mitigate these risks through proper management and lifestyle choices.
Sponsored

Top 5 Health Factors Contributing to Osteoporosis and Bone Weakening
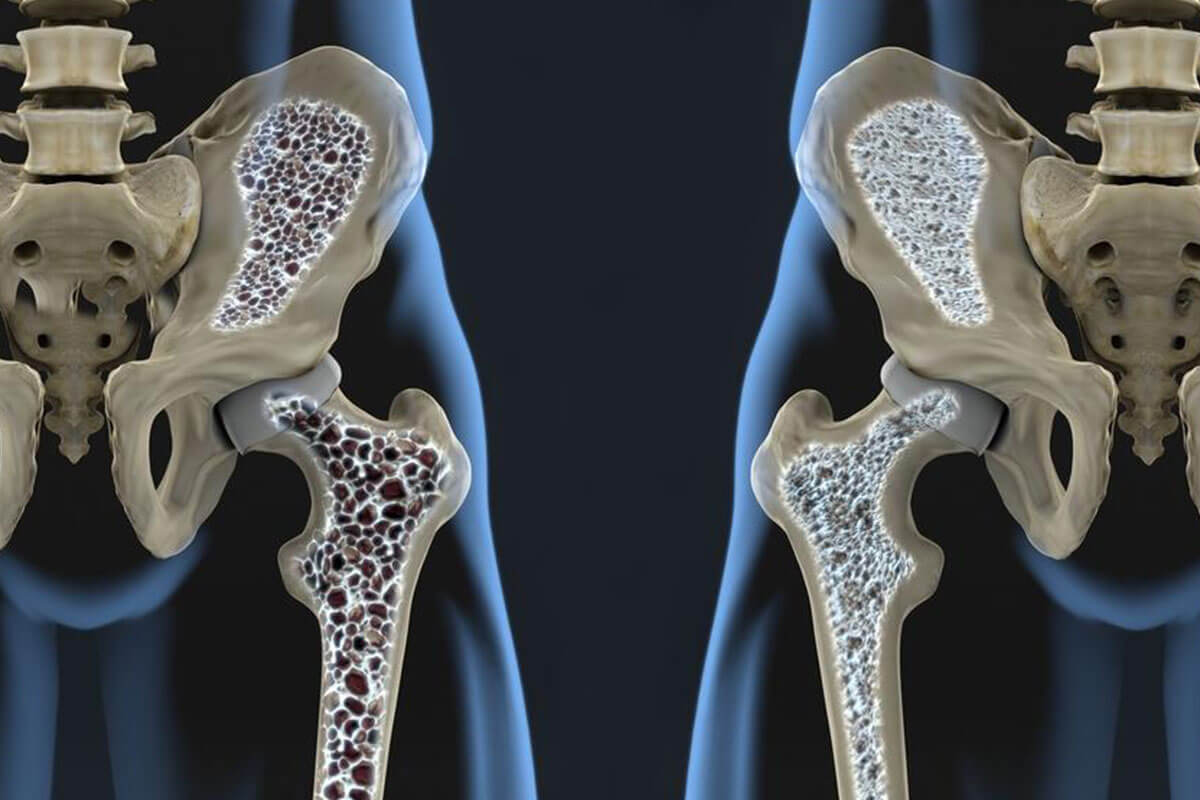
Osteoporosis, characterized by fragile bones, is a common age-related health concern worldwide. Over half of women and a significant portion of men over 50 are vulnerable. It occurs when bone density decreases, making bones susceptible to fractures from minor injuries like falls or even coughing. Certain health issues heighten this risk, including:
Hyperthyroidism
This condition involves an overactive thyroid gland, which accelerates the process of bone remodeling and leads to increased bone loss. Monitoring thyroid function is crucial to mitigate this risk.
Arthritis
Various arthritis forms, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can weaken bones. Inflammation and joint damage, combined with treatments that suppress bone-forming cells, escalate osteoporosis risk. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help prevent arthritis and its complications.
Diabetes
Ongoing research suggests that high blood sugar levels in diabetes may hinder bone formation, increasing vulnerability to fractures and delayed healing.
Asthma
Although asthma doesn't directly cause bone loss, medications used for symptom control, like corticosteroids, can contribute to weakened bones. Additionally, limited physical activity due to breathing difficulties reduces overall bone strength.
Celiac Disease
This autoimmune disorder caused by gluten intolerance damages intestinal lining, impairing calcium and vitamin D absorption vital for healthy bones, leading to a higher osteoporosis risk.