Top Birth Control Options for Nursing Mothers
Explore the best birth control options for breastfeeding mothers, including natural, hormonal, and device-based methods. This guide offers insights into effectiveness, safety, and considerations for each method, helping new mothers make informed decisions post-childbirth.
Sponsored

Managing pregnancy while caring for a newborn can be challenging. Experts often recommend waiting at least a year after childbirth before considering another pregnancy, ensuring the mother's recovery and minimizing risks. Once couples resume intimacy post-delivery, choosing effective contraception is essential. Keep reading to discover the most suitable birth control methods for breastfeeding women.
Lactational Amenorrhea
Breastfeeding acts as a natural contraceptive, often called lactational amenorrhea, due to elevated prolactin hormone levels that suppress ovulation. This method is most reliable within the first six months of exclusive breastfeeding. However, once menstruation resumes or breastfeeding frequency decreases, the probability of pregnancy increases.
Condoms
For those avoiding hormonal methods, condoms offer a reliable, affordable, and safe option. They are approximately 98% effective and also protect against sexually transmitted infections. Both male and female condoms are suitable during breastfeeding.
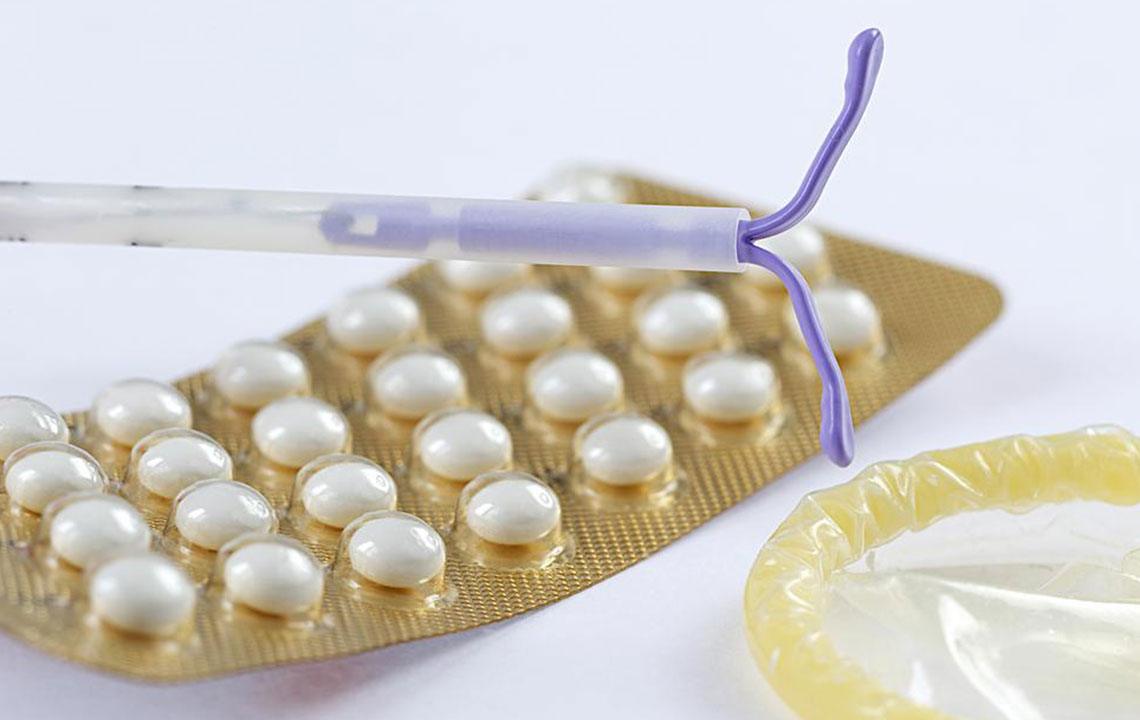
Progestin-Only Pills
Unlike combined pills, progestin-only pills, or mini pills, contain only progestin and must be taken daily at the same time to prevent pregnancy.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
There are hormonal and copper IUDs. The hormonal type releases progestin to block fertilization, while copper IUDs create an inflammatory environment to prevent conception. Both are highly effective and long-lasting, lasting several years.
Contraceptive Implants
A small, flexible rod inserted under the upper arm releases progestin to prevent pregnancy. This method is a good alternative for those concerned about IUD placement.
Birth Control Shots
Administered every three months, these injections contain progestin to suppress ovulation. They are about 94% effective, although some studies suggest a temporary reduction in milk supply. Fertility typically takes over 10 months to return after discontinuation.
Before choosing a method, consulting a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure safety and suitability, especially during breastfeeding.