Effective Strategies for Managing Long-Term Bronchitis
Learn comprehensive strategies for managing long-term bronchitis, including medication, lifestyle changes, and advanced interventions. Early diagnosis and proper care are vital to prevent worsening symptoms and improve breathing health.
Sponsored

Chronic bronchitis involves persistent inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to increased mucus production that hampers airflow. This causes symptoms like a lingering cough, chest heaviness, and difficulty breathing. When these symptoms last over three months, the condition is classified as chronic bronchitis. It commonly results from smoking, air pollution, infections, or irritants, especially in individuals with existing respiratory issues such as asthma or weakened immunity.
Identifying Chronic Bronchitis
Major signs include a prolonged cough lasting more than three months, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Diagnosis starts with clinical assessments, lung function tests, blood evaluations, and chest X-rays to evaluate lung health and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Long-Term Bronchitis
Early diagnosis enables various treatment methods. These include:
Cough Suppressants: Used when coughing is persistent and unproductive, aiding in airway clearance.
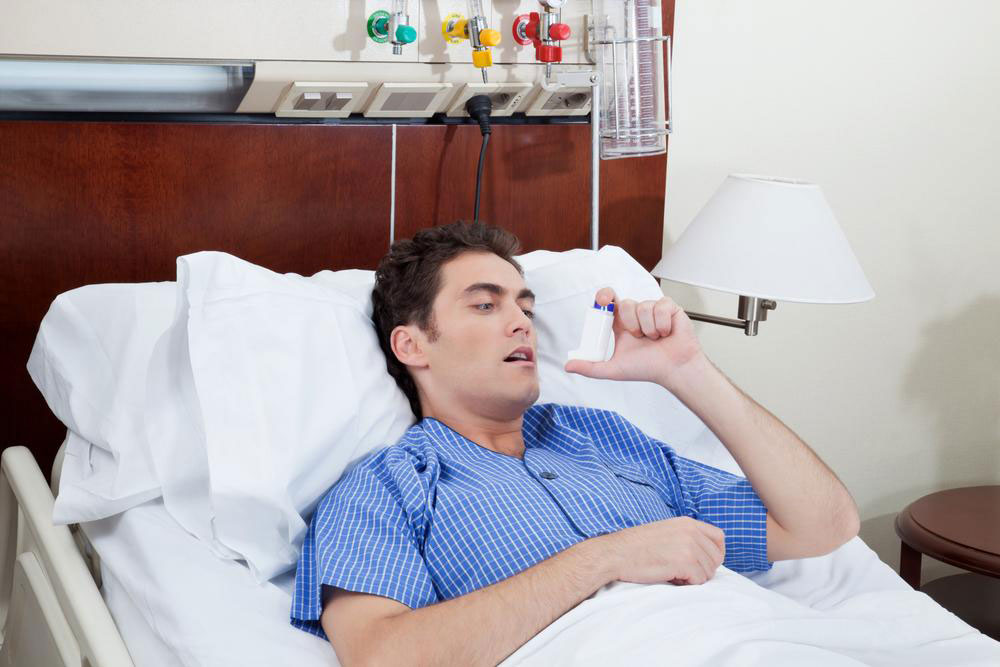
Inhalation Therapy: In severe cases, inhalers dilate airways, making breathing easier.
Oxygen Supplementation: For advanced cases with low oxygen levels, oxygen therapy enhances lung function and alleviates breathlessness.
Home Care Practices: Protect yourself from cold air, pollution, and dust by using masks. Breathing exercises and yoga can strengthen lung capacity.
Vaccinations: Specific vaccines help prevent respiratory infections that can worsen bronchitis symptoms.
Pulmonary Rehab: Programs focusing on breathing techniques, smoking cessation, nutritional guidance, and education facilitate recovery.
Surgical Intervention: When other treatments are ineffective, surgery can repair damaged lung tissues to reduce symptoms.
Preventing disease progression emphasizes avoiding irritants, quitting smoking, and maintaining good respiratory health. Prompt consultation with healthcare providers upon symptoms is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life.