Effective Strategies to Reduce Spasticity Symptoms
Discover comprehensive strategies to manage spasticity effectively. This guide outlines collaboration with healthcare specialists, therapy options, assistive devices, medications, and surgical procedures designed to improve mobility, speech, and daily living for those affected by muscle spasticity. Stay informed about emerging treatments and personalized approaches to enhance quality of life.
Sponsored

Neurological conditions can manifest in diverse ways, impacting individuals due to factors like age, genetics, or specific treatments. One common complication is spasticity, where certain muscles involuntarily tighten. The severity varies among patients and can influence movement and speech. Although a cure remains elusive, managing symptoms effectively can enhance quality of life.
Collaborating with Healthcare Experts
Managing spasticity typically involves multiple therapies, often combined for the best results. A multidisciplinary team, including physiatrists, neurologists, advanced care clinicians, occupational and physical therapists, and sometimes surgeons or speech specialists, develops personalized treatment plans.
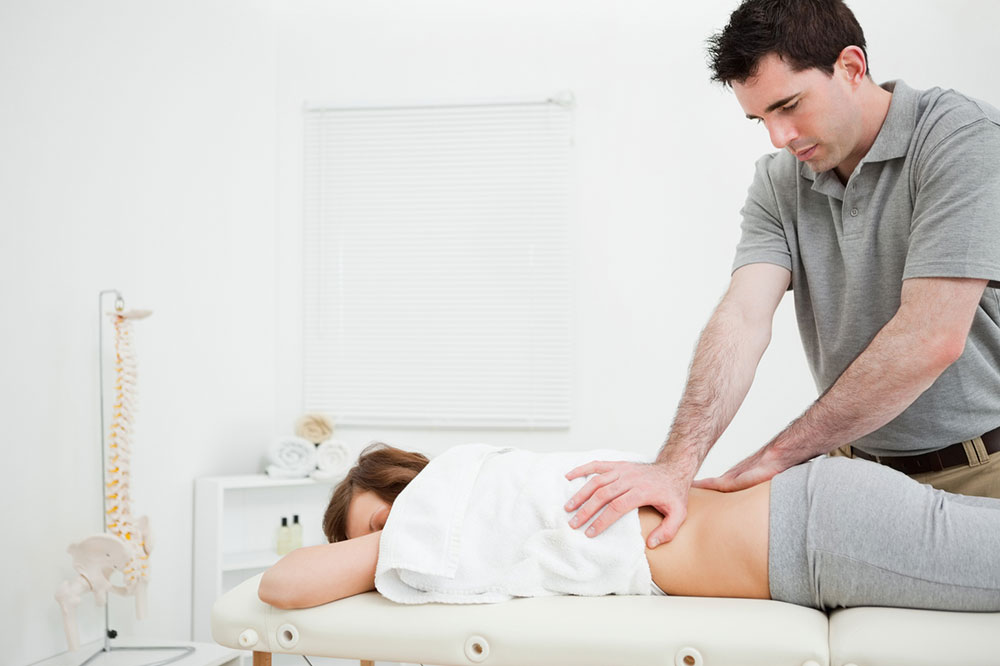
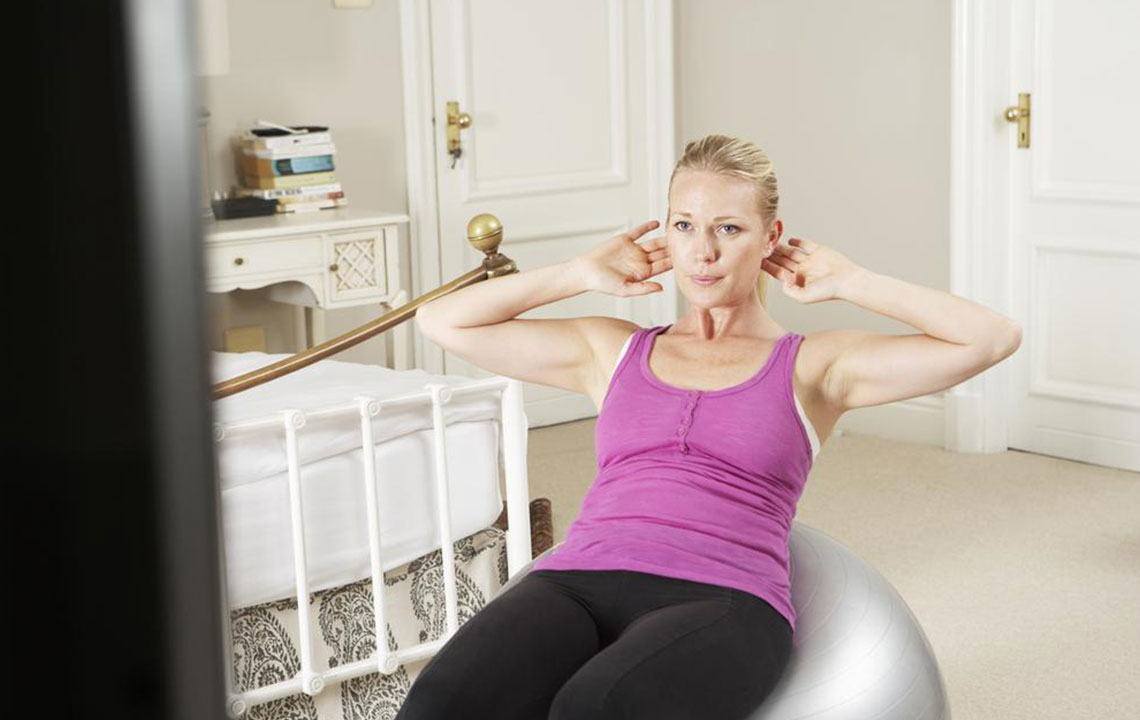
Physical and Occupational Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy often emphasizes gentle stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises like walking, swimming, cycling, and treadmill work. These can provide short-term relief from spasticity and help prevent long-term issues like stiffness and muscle pain. Occupational therapy focuses on upper limb movements, aiding daily routines such as dressing or grooming.
Speech and Communication Therapy
When spasticity affects speech, speech therapy can be beneficial. For children, it may involve games and language activities, while adults might work on facial exercises, mouth movements, reading aloud, or word association tasks to improve communication skills and quality of life.
Assistive Devices for Better Mobility
Professionals may recommend devices to support movement and daily tasks, including:
Supportive braces or casts help stabilize limbs, reduce involuntary spasms, and enhance range of motion.
Splints assist in maintaining joint positions, especially for hand or leg spasticity.
Canes provide partial weight support, easing movement without overburdening muscles.
Walkers assist in walking stability, bearing more weight and aiding balance.
Wheelchairs accommodate those with significant mobility challenges, available in various styles and sizes.
Additional devices like hearing aids and specialized utensils can also improve daily functioning.
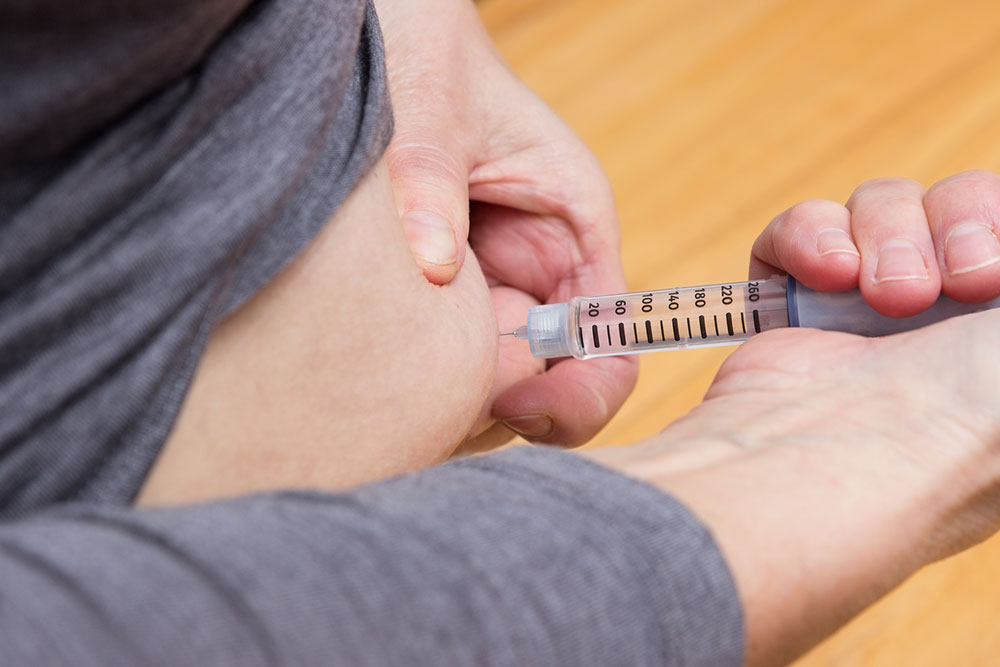
Medication Prescriptions
Medicines may be prescribed to relieve muscle tightness, pain, and improve sleep disrupted by spasticity. These are usually part of an overall treatment plan, with tailored dosage instructions.
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgery might be recommended, including intrathecal baclofen pumps, dorsal rhizotomy procedures, or orthopedic interventions. The choice depends on the patient's overall health and specific affected areas.
Emerging Treatments for Spasticity
Innovative approaches like deep brain stimulation are currently under investigation. Patients can discuss novel options, including new oral or intravenous medications, with their healthcare providers for comprehensive management.