Signs You Might Be Consuming Too Much Sugar
This article highlights key signs of excessive sugar intake, including mood swings, weight gain, skin issues, and health risks like high blood pressure and joint pain. Recognizing these symptoms can help in managing and reducing sugar consumption to improve overall health.
Sponsored

Indicators of Excessive Sugar Consumption
Sugar, a common carbohydrate found in many foods, is responsible for the sweetness in treats like cookies, chocolates, and baked goods. While enjoyable, high sugar intake can negatively impact health, contributing to fatigue, accumulation of visceral fat, diabetes, and cardiovascular issues. Recognizing the symptoms of excessive sugar consumption is essential for maintaining overall well-being.
Mood Swings and Irritability
Consuming too much sugar can lead to emotional changes, including irritability and stress, due to rapid blood sugar fluctuations. These spikes are caused by foods low in protein and healthy fats, which cause the body to respond aggressively.

Decreased Sweetness Sensation
If sweet foods no longer taste as sugary, it may be a sign you're consuming too much sugar. Additionally, you might find less satisfaction from foods with lower sugar, indicating tolerance build-up.
Accumulation of Abdominal Fat
Excess sugar affects hormones like leptin, which signals fullness. High sugar intake, especially from processed snacks lacking protein and fiber, contributes to visceral fat and insulin resistance.
Acne Outbreaks
An increase in breakouts could be linked to high sugar consumption. Sugary beverages can elevate androgen and insulin-like growth factors, promoting oily skin and acne formation.
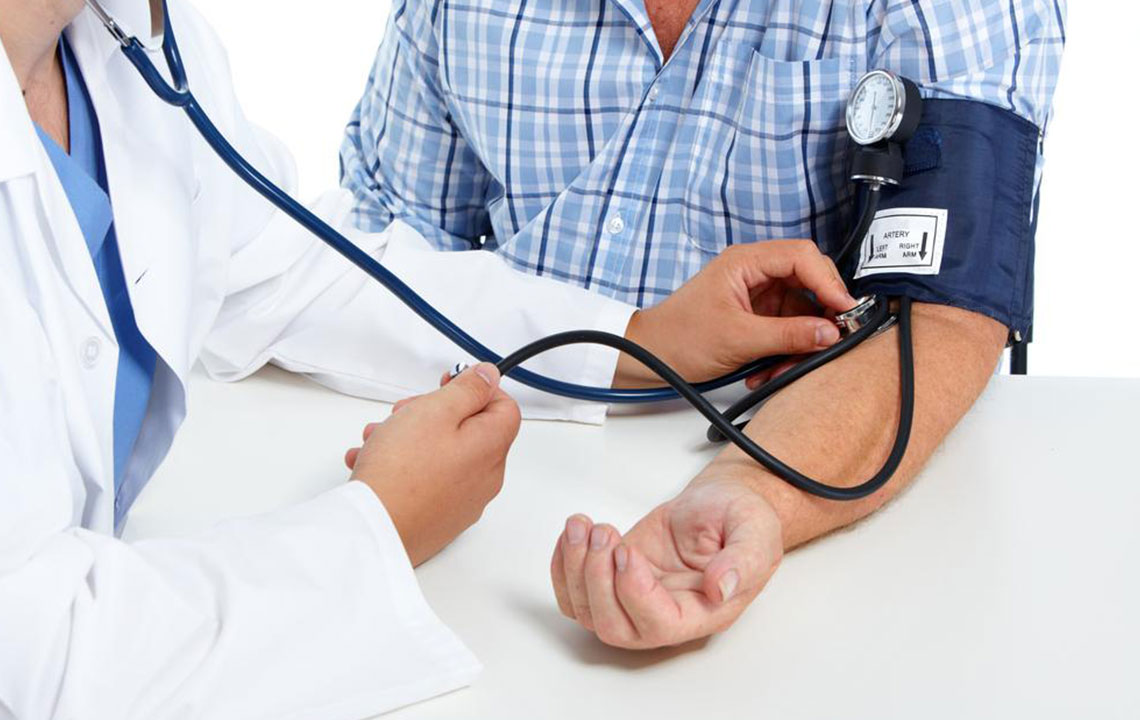
Elevated Blood Pressure
Consuming too much sugar can damage blood vessel linings, leading to lipid buildup and vessel hardening, which raises blood pressure levels.
Joint Discomfort
Increased joint pain, especially after eating sugary foods, may indicate high sugar intake. Research shows that sugar-rich diets can worsen symptoms in inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Sleep Disruptions
High sugar intake may interfere with sleep quality, affecting the circadian rhythm and making it harder to fall asleep due to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Digestive Issues
Overeating sugar can irritate the gut, causing symptoms like stomach cramps, diarrhea, or bloating.