Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Sciatic Nerve Pain
This comprehensive guide details effective treatments for sciatic nerve pain, including medications, physical therapies, and surgical options. It emphasizes early management strategies, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive measures to reduce discomfort and avoid long-term issues.
Sponsored
Effective Approaches to Alleviate Sciatic Nerve Discomfort
Sciatic nerve pain occurs when the nerve extending from the lower back down to the legs becomes compressed, resulting in severe discomfort. This condition often stems from issues like herniated discs, spinal canal narrowing, muscle cramps in the buttocks, disc degeneration, or injuries.
Applying heat or cold packs can help reduce pain, especially during initial treatment stages. Use ice or heat for about 20 minutes, with a two-hour break, making sure not to place ice directly on the skin to prevent burns.
Medications play a vital role in pain relief. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Ibuprofen and Naproxen help diminish inflammation and pain signals but should be used cautiously due to potential side effects on the stomach, liver, or kidneys.
Muscle relaxants such as Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) and Tizanidine (Zanaflex) ease muscle spasms, promoting relaxation. However, prolonged use can reduce their effectiveness, necessitating alternative treatments. In severe cases, narcotics like Codeine, Morphine, or Vicodin may be prescribed temporarily to manage pain.
Certain antidepressants, including Desipramine and Doxepin, may increase pain perception chemicals, helping with chronic pain. Anti-seizure medications, typically used for epilepsy, can also calm nerve activity, offering relief.
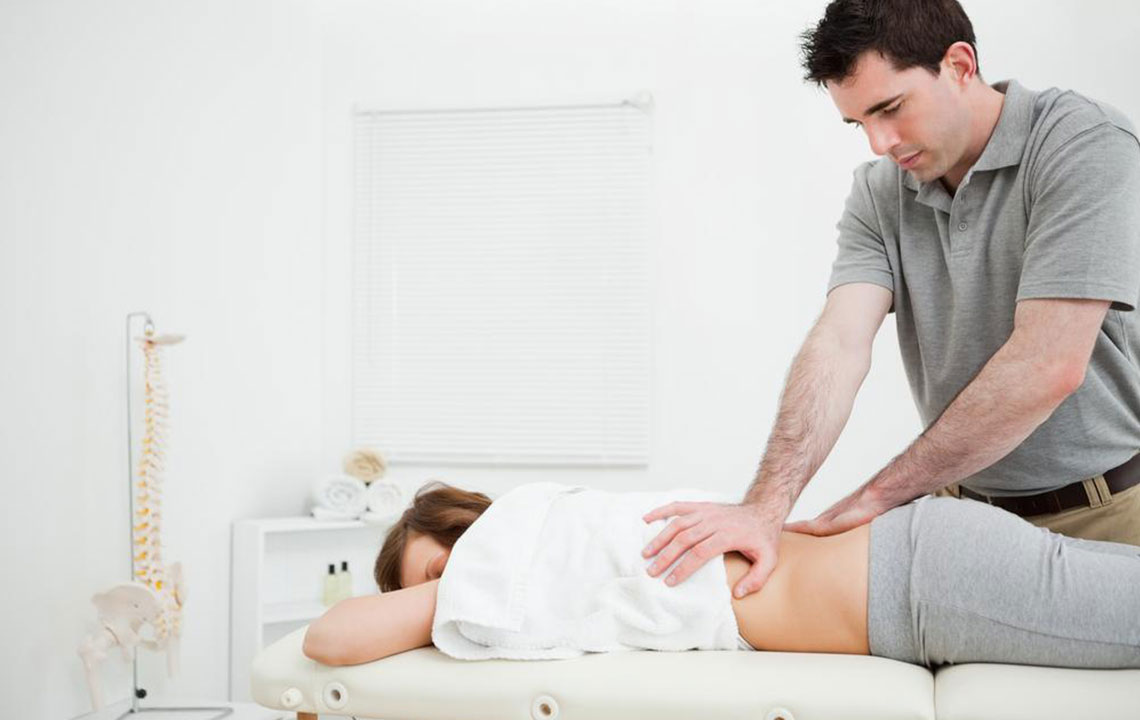
Physical methods like targeted exercises enhance hip and back flexibility, combatting stiffness. Yoga strengthens muscles and promotes spinal health, while acupuncture offers another alternative pain management technique. Chiropractic adjustments realign vertebrae, restoring movement.
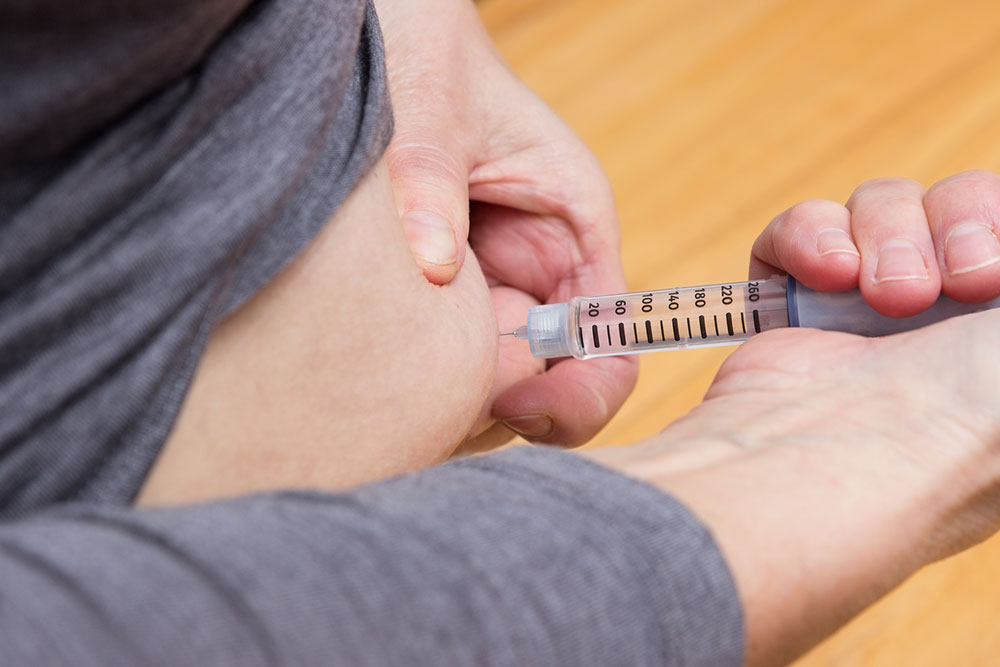
Ultrasound therapy employs sound waves to generate heat, relax muscles, and soothe nerves. Massage therapy alleviates muscle tightness around the sciatic nerve, reducing numbness and pain. Steroid injections, administered via X-ray guidance, can temporarily diminish inflammation but should be used sparingly due to side effects.
When conservative treatments fail, surgical options like microdiscectomy remove the herniated disc portion compressing the nerve. Surgery is typically considered after persistent pain lasting over four to six weeks.
Preventing further injury involves avoiding excessive strain, such as heavy lifting or prolonged sitting. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces spinal pressure, and staying active helps prevent worsening symptoms, promoting overall spinal health.






