Understanding Pink Eye: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Pink eye, or conjunctivitis, is a common, contagious eye condition caused by infections or allergies characterized by redness, swelling, and irritation. It often resolves within days but requires proper care to prevent spreading. Treatment includes eye drops, hygiene practices, and home remedies like warm or cold compresses. Early diagnosis and preventive measures are key to managing symptoms and avoiding contagion. Consulting an eye specialist ensures appropriate treatment, especially in persistent or severe cases, to maintain eye health and comfort.
Sponsored
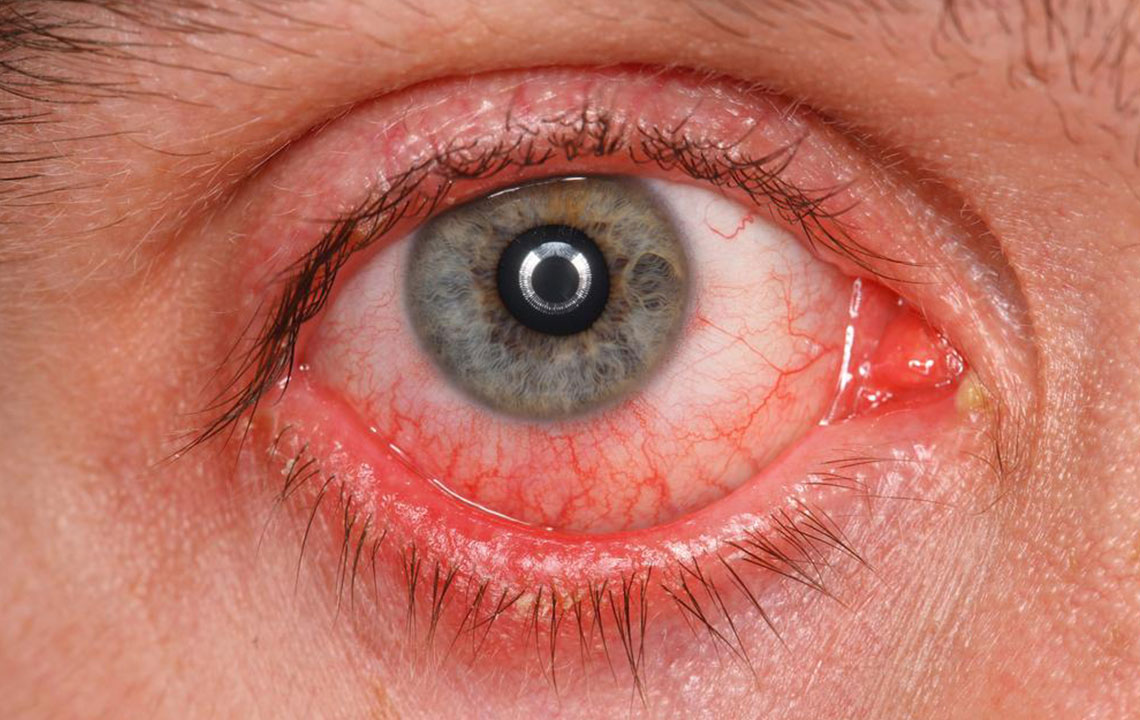
Pink eye, or conjunctivitis, is a common eye condition caused by infections or allergies. It results in redness, swelling, and irritation of the conjunctiva, the moist tissue covering the eyeball and eyelids' inner surface. Usually, vision remains unaffected, but the condition can cause discomfort and is highly contagious. Early diagnosis and proper care can ease symptoms and prevent spread. Over-the-counter eye drops may provide relief, but consulting an eye specialist is recommended for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Causes of Pink Eye
Infectious conjunctivitis often clears within a week to ten days. Eye drops can help alleviate symptoms during this period.
Pink eye can occur due to bacterial or viral infections. Environmental factors like smoke, chemicals, and fumes can also trigger conjunctivitis. Allergies and dry eyes caused by wind or sunlight are additional contributors.
Types
The condition is classified as viral or bacterial pink eye, depending on the cause.
Viral Pink Eye
Caused by adenoviruses or herpes viruses, symptoms usually last 3 to 5 days but can persist up to three weeks in some cases. It typically resolves without medication, though good hygiene is vital to prevent spreading. In herpes-related cases, antiviral drugs are prescribed.
Symptoms include:
Excess tearing
Redness in the white part of the eye
Swollen eyelids
Itching and burning sensations
Discharge from the eyes, clear or sticky
Swelling near the ears
Home treatment involves maintaining hand hygiene, using separate towels, and avoiding contact with others. Viral pink eye typically heals on its own, but viral or herpes cases may require medication.
Bacterial Pink Eye
Bacterial infections such as gonorrhea, staphylococcus, or Haemophilus influenzae can cause bacterial conjunctivitis. Symptoms include yellowish discharge, eyelid swelling, redness, mild pain, and eyelash adhesions, lasting around 7 to 10 days. Antibiotic eye drops are effective, with symptoms often improving in 2-3 days.
Consult a healthcare professional before use. Topical antibiotics help reduce itching, discomfort, and bacterial load, speeding recovery.
Home Care Tips
Discontinue contact lens use, opt for glasses, and apply warm compresses for relief. For allergy-induced conjunctivitis, cold compresses work well; for infections, warm compresses provide comfort. Use a clean cloth for each eye to avoid cross-infection. If symptoms persist beyond 3-5 days or worsen, seek prompt medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Preventive Strategies
Practice good hygiene, wash hands frequently, avoid sharing towels, pillows, or eye makeup, and disinfect makeup tools after use. Refrain from sharing eye drops or contact lenses during infection. Wearing protective glasses outdoors can prevent irritant exposure. Never share eye medicine, and always wash hands thoroughly when caring for an infected person.
Risks and Precautions
Though pink eye does not impair vision, its high contagiousness necessitates early detection to prevent outbreaks. Maintaining hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals are essential to control spread.