Comprehensive Overview of Epilepsy Management and Treatment Options
This article provides a detailed overview of epilepsy, including its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options like Topiramate (Topamax). It emphasizes the importance of medical supervision, proper medication adherence, and understanding potential side effects. The content also highlights the need for prompt medical attention during seizures and advises against self-medication. With available treatments worldwide, managing epilepsy effectively requires professional guidance and regular monitoring for better quality of life.
Sponsored
Epilepsy is a neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures, affecting individuals of all ages. Seizures can be unpredictable, causing temporary disruptions in mental, sensory, or motor functions. The frequency and severity differ among patients, mainly depending on the affected brain region. Triggers include head trauma, chemical imbalances, stroke, alcohol consumption, or birth injuries. It’s crucial to distinguish epilepsy from febrile seizures caused by high fever.
Diagnosis and treatment options are widely available in healthcare centers, though epilepsy may not always be fully curable, and seizures can recur. Medication adherence and medical supervision are essential. Topiramate, known as Topamax, is frequently prescribed to control seizures in both children and adults, without significant adverse effects when used correctly.
It’s vital to follow the prescribed dosage, as deviations can cause side effects. Common issues include nausea, dizziness, fatigue, diarrhea, depression, weight loss, and tingling sensations. Rare side effects may involve nasal or throat problems. Pregnant women should avoid this medication due to risks to the fetus. Taking the medication at night can help mitigate drowsiness. In case of missed doses, take the medication promptly. A thorough medical history is necessary before starting treatment.
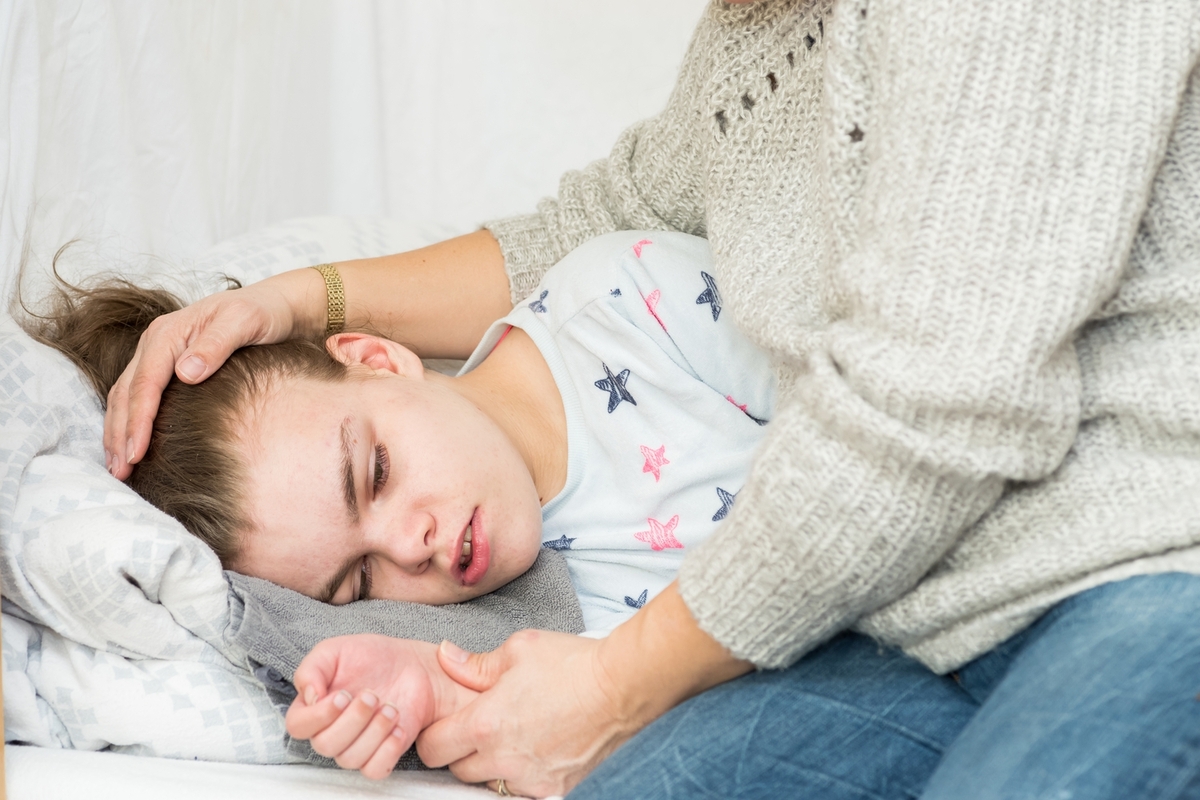
Topamax is a prescription drug and should not be obtained without medical guidance. Sudden seizures necessitate immediate hospital care and proper diagnosis. Not all seizures indicate epilepsy; self-medication without professional evaluation can be dangerous and possibly fatal.