Understanding and Managing Pollen Allergies
This guide explains pollen allergies, how pollen levels are measured, symptoms to watch for, and effective prevention strategies. Learn how to reduce exposure, understand pollen counts, and seek treatment options like allergy shots for better allergy management. An essential resource for allergy sufferers aiming to stay comfortable throughout allergy seasons.
Sponsored
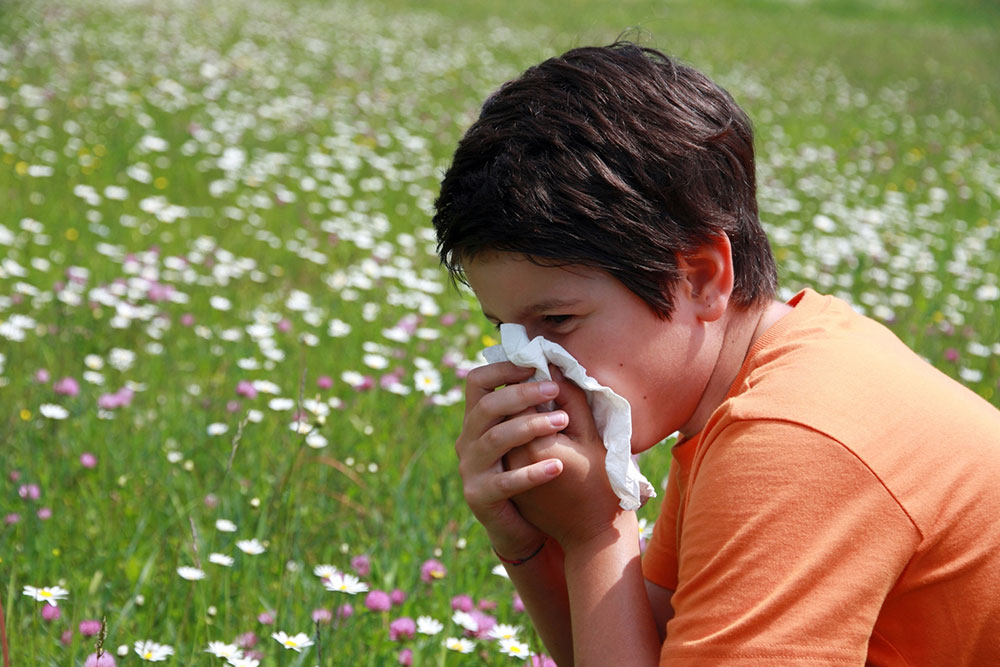

Pollen triggers allergies and hay fever, affecting many individuals nationwide. It is a fine powder produced by flowers, trees, and grasses. When inhaled, pollen can cause adverse reactions in some people. Normally, the immune system fights harmful entities like bacteria and viruses, but in allergic individuals, it mistakenly targets harmless pollen, leading to allergic responses. These reactions may occur year-round or during specific seasons, depending on local pollen levels. Recognizing these patterns helps manage allergy symptoms effectively.
Pollen Levels
Pollen level indicates the amount of pollen present in the air at a given location. Monitoring this helps allergy sufferers plan outdoor activities accordingly. An allergist measures pollen levels using specialized tests, which vary based on weather conditions and geographic area. Levels are typically categorized as low, medium, or high, and sometimes specify the types of pollen present. Being aware of pollen counts allows for better symptom management.
Measuring Pollen Concentration
To determine pollen levels, experts set up pollen counters on rooftops or high points. These devices collect air samples, and pollen grains stick to slides coated with a jelly-like substance. Under a microscope, professionals analyze the samples to estimate pollen concentrations. High pollen counts often correspond to increased allergic reactions, especially during dry and windy seasons such as winter.
Signs of Pollen Allergies
Symptoms vary but commonly include sinus pressure causing facial pain, nasal congestion, itchy and watery eyes, runny nose, coughing, sore throat, and swollen eyes. Severe reactions may trigger asthma attacks or loss of taste and smell. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent worsening conditions.
Preventive Strategies for Pollen Allergies
The best approach is minimizing exposure. During high pollen days, stay indoors whenever possible. Keep doors and windows closed, wear masks outdoors, and consult your doctor for appropriate medications. In severe cases, allergy shots may be recommended for relief and long-term management.
Home Care Tips
Use HEPA filters indoors for cleaner air. Change clothes after outdoor exposure to remove pollen. Avoid drying clothes outside; instead, use a dryer. Keep car windows closed and use air conditioning. If pollen enters your nose, sneeze to expel it, and regularly clean your home with a vacuum cleaner to reduce indoor pollen levels.
Paying attention to pollen counts is essential for allergy sufferers. When levels are low, simple precautions suffice. During high pollen periods, proactive measures prevent symptoms. Consulting an allergist can help identify specific pollen types in the air, enabling better protection. Staying informed and prepared allows for effective allergy management and improved quality of life.