Understanding IPO Valuation and Investment Strategies
This article provides a comprehensive overview of IPO valuation methods, the process of determining stock worth, and strategies for investing in IPOs. It explains how market demand, financial analysis, and regulatory considerations influence IPO pricing. Investors gain insights into evaluating IPOs and understanding the risks and opportunities associated with early trading. The content also highlights the significance of IPOs for companies seeking growth capital and offers guidance on how to participate in these offerings effectively.
Sponsored

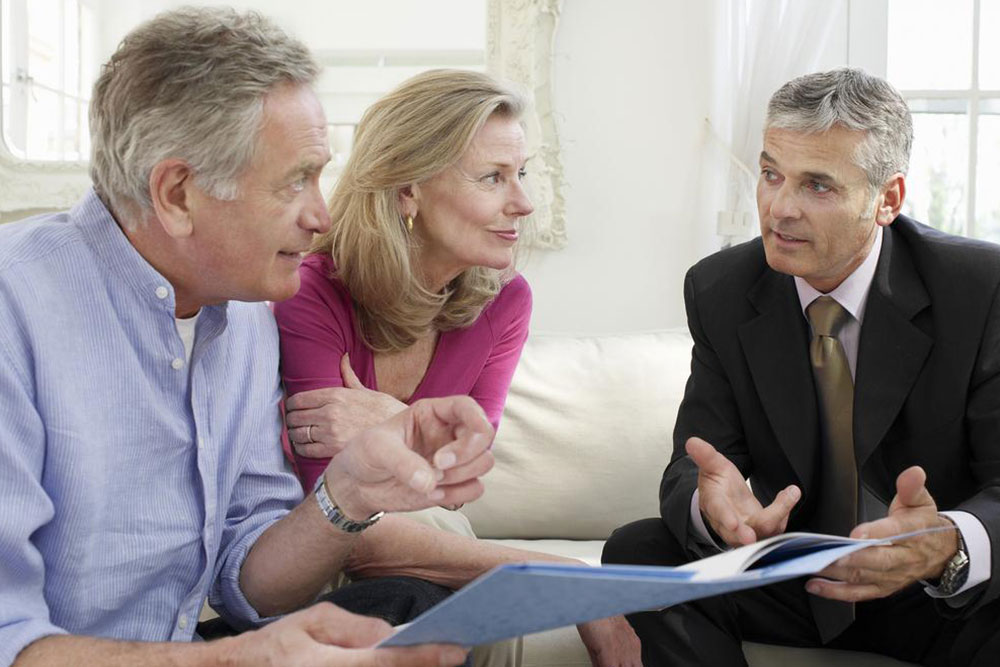
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) marks a company's first sale of stock to the public. Typically, smaller firms utilize IPOs to raise capital for growth or expansion. Investors who subscribe to an IPO become part-owners of the company. Every publicly traded company begins its journey with an IPO. Before listing, companies undergo a rigorous process that can last several months to a year, fulfilling numerous regulatory and preparatory requirements.
How is IPO worth determined?
IPO valuation hinges on market dynamics like supply and demand. Experts analyze various factors to set an appropriate price, avoiding overpricing or underpricing. Since historical data for new stocks are unavailable, methods such as financial modeling, comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions are used. An underpriced IPO may leave gains on the table, whereas an overpriced one might deter investors.
The valuation process involves collaboration among company executives, auditors, legal advisors, regulators like the SEC, and underwriters. They assess factors such as growth potential, market trends, and investor demand to determine the stock’s value. Absolute valuation techniques consider discounted cash flows, company assets, liabilities, and economic value, setting a baseline share price. Relative valuation compares the company with similar firms to gauge market positioning.
Before investing in an IPO, it’s vital to examine aspects including the purpose behind the offering, future growth prospects, and plans for the raised funds. Reviews of regulatory filings like the S-1 statement aid investors in making informed decisions.
What is the goal of the IPO?
What are the company's growth chances?
How will the company use the proceeds?
With thorough analysis, an investor can decide whether the IPO's valuation aligns with its potential for profit.
How to participate in an IPO?
Investors can partake via brokers or stock exchanges. Post-listing, demand can push prices above the initial fixed price, resulting in oversubscription. Funds from IPOs often support expansion, R&D, or debt repayment, and sometimes serve as exits for founders or private investors. Companies typically collaborate with investment banks to manage the process. Initial trading days usually see heightened volatility, marking a significant milestone as the firm transitions from private to public.