Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing and Treating Cellulitis
This article provides an in-depth overview of cellulitis, covering its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and effective treatment options. Recognizing early signs and understanding preventative measures are crucial for managing the infection and avoiding serious complications.
Sponsored

Understanding Cellulitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
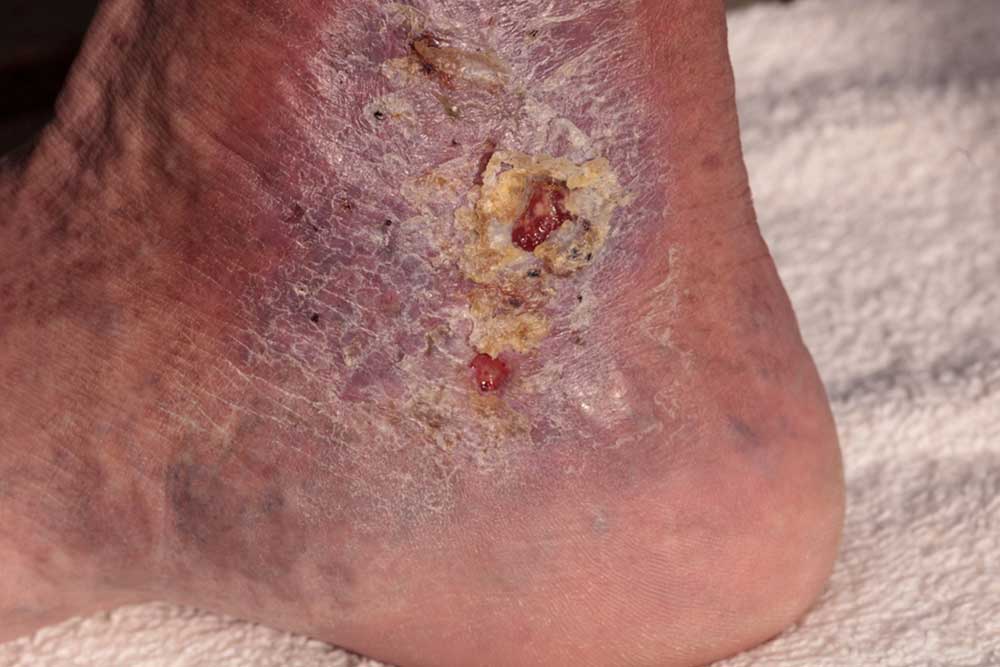
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection impacting skin layers and underlying soft tissues. Individuals with obesity, athlete's foot, or psoriasis are at higher risk of developing leg cellulitis. Prompt treatment is vital to prevent complications. Small cuts, dry or dirty wounds act as entry points for bacteria. Preventing injuries and managing skin issues significantly reduce infection chances. Risk factors include poor circulation from aging or mobility issues, weakened immune systems, diabetes, and post-chemotherapy recovery. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and pain, typically improving quickly with antibiotics.
Early intervention with oral antibiotics over 3-10 days is often effective. Completing the full course prevents recurrence. Warm compresses can ease pain and inflammation. For severe cases, IV antibiotics and surgical drainage may be necessary. Proper wound care, keeping skin moist, and avoiding further injury are essential. Penicillin is the main antibiotic used, with alternatives based on individual health history. Untreated cellulitis can escalate, risking systemic infection, limb loss, or life-threatening conditions.