Understanding Pet Allergies: Focus on Dogs
Learn about dog allergies, including symptoms, causes, risk factors, and effective treatment options. This guide offers insights for allergy sufferers and prospective pet owners to manage and prevent allergic reactions to dogs safely.
Sponsored

While dogs are cherished companions for many, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to them. Pet allergies are prevalent in the United States, affecting approximately 15% to 30% of the population. Reactions to cats and other pets are generally less severe than those triggered by dogs. People with asthma are particularly vulnerable to canine allergies. This article explores the common signs, causes, risk factors, and treatment approaches for dog allergies.
Signs of Dog Allergies in Humans
Exposure to dogs can lead to various allergic symptoms, which vary from mild to severe. Sensitivity levels differ; some may not notice symptoms immediately. Common signs include:
Itching and swelling around the eyes and nose
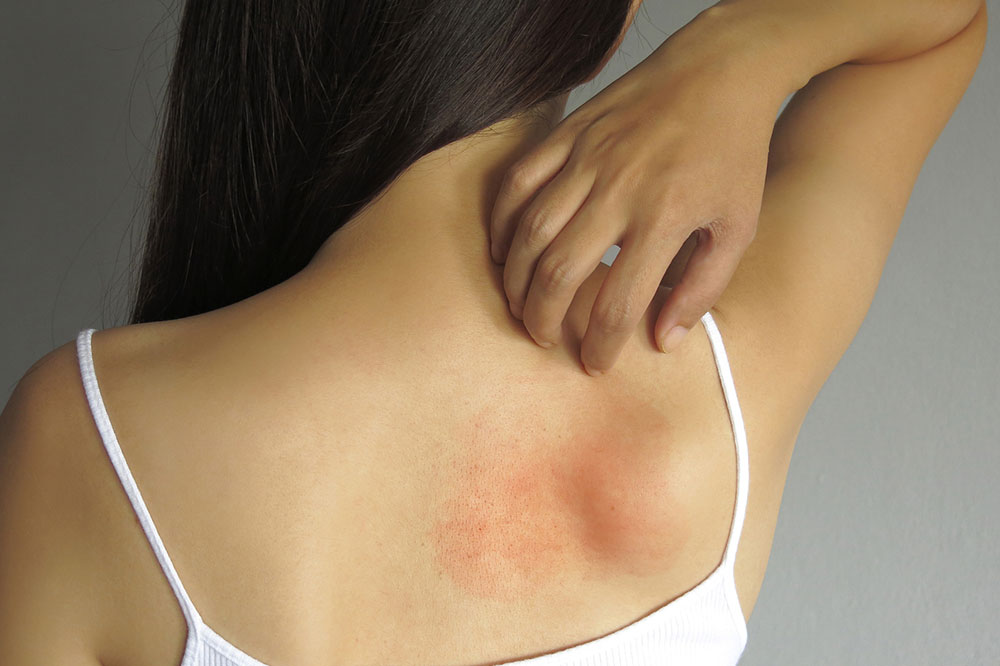
Redness of the skin after being licked by a dog
Wheezing, coughing, or shortness of breath within 10-30 minutes of contact
Skin rashes on the face, neck, and chest
Severe asthma attacks in asthmatic individuals
Sleep disturbances due to breathing issues
Facial pressure and discomfort
Nasal congestion
What Causes Dog Allergies?
Dog allergies stem from proteins in their dander, urine, and saliva. These proteins often cling to dead skin flakes, which can settle on carpets, furniture, clothing, and walls. When exposed, the immune system reacts abnormally. Different dog breeds produce varying amounts of dander, meaning some individuals may only be allergic to specific breeds. These allergens can linger in the air, settle on surfaces, and cause symptoms even without direct contact.
Factors Increasing Risk of Dog Allergies
Genetics play a role, with those having a family history of asthma being more susceptible. Early exposure to dogs may sometimes reduce allergy risk, especially for children who grow up around canines, possibly promoting tolerance. Conversely, lack of exposure might increase vulnerability later in life.
Potential Complications
Sinus infections: Inflammation in nasal tissues can obstruct sinus drainage, leading to bacterial sinusitis.
Asthma exacerbation: Individuals with pre-existing asthma may experience worsened symptoms, including severe attacks requiring urgent medical care.
When to Seek Medical Help?
Symptoms resembling a cold, such as sneezing, nasal congestion, or cough, can mask dog allergies. If these persist beyond a couple of weeks or worsen—especially with breathing difficulties or sleep disruption—consult a healthcare provider promptly. Immediate medical attention is critical if experiencing shortness of breath unrelated to activity.
Managing Dog Allergy Symptoms
Medical treatments include:
Medications: Doctors may prescribe antihistamines or other allergy medications for symptom relief.
Saline rinses: Nasal irrigation with saline solution can reduce allergens in the nasal passages.
Environmental adjustments: Keeping dogs outside or designating pet-free zones inside your home can minimize allergen exposure. Regular cleaning and air filtration are also beneficial.
Before adopting a dog, ensure you are not allergic. Asthma sufferers should consult their doctors before bringing a pet into their home to prevent complications.