Understanding Psoriasis: Causes, Types, and Treatment Options
This comprehensive article delves into psoriasis, exploring its causes, various types, and effective management strategies. It offers practical tips on treatments, natural remedies, and dietary considerations to help individuals control symptoms and improve their quality of life. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Sponsored

Comprehensive Guide to Psoriasis
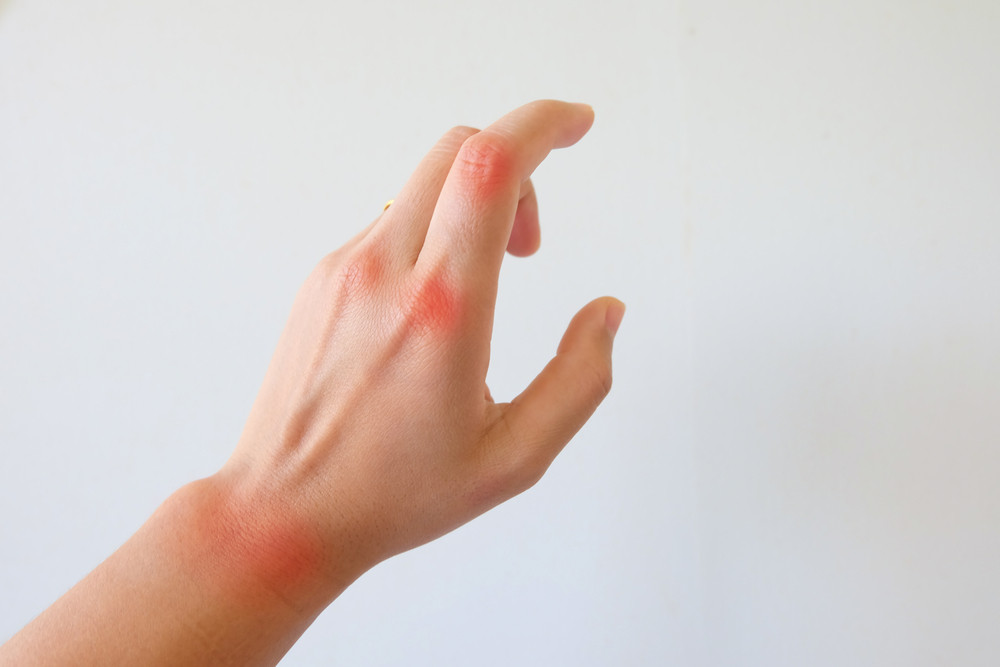
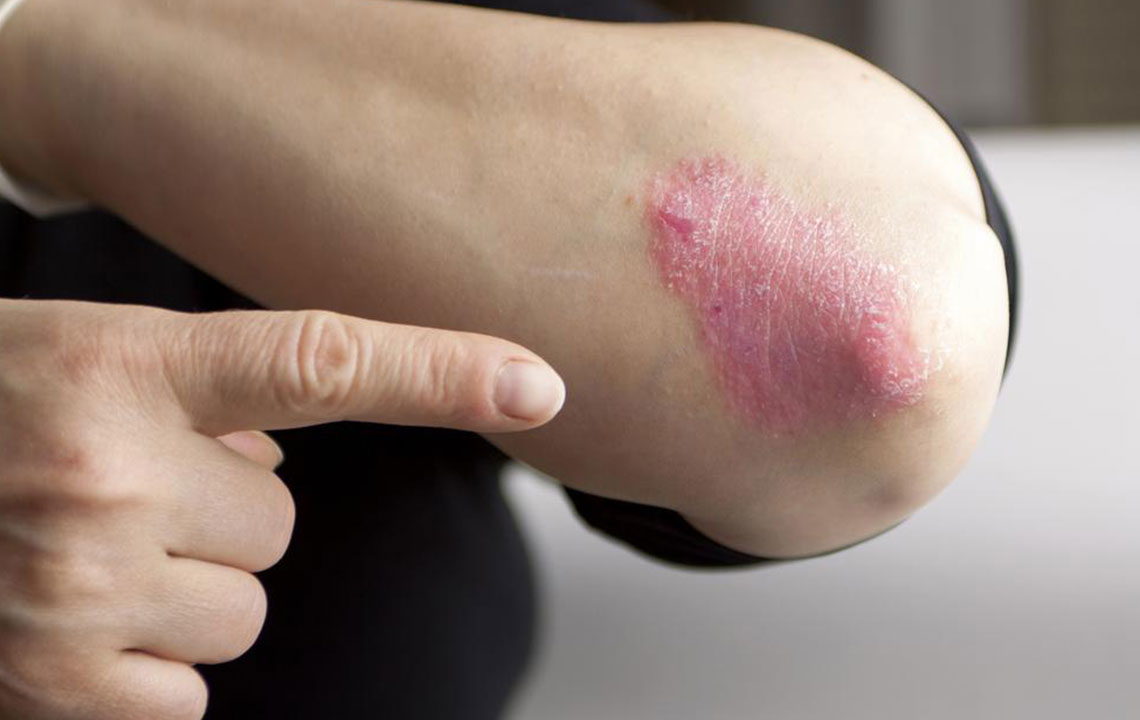
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder characterized by rapid skin cell growth, resulting in red, scaly patches. These typically appear on elbows, knees, scalp, or face, but can also show up on nails, mouth, or genitals. Although there's no cure, effective management strategies exist to control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Managing psoriasis involves lifestyle adjustments, medication, and diet to minimize triggers. Key causes include immune system dysfunction and genetics, especially if there's a family history. Types vary from plaque and erythrodermic to pustular and inverse psoriasis, each requiring tailored treatment plans.
Causes of Psoriasis
While the exact cause remains unknown, research indicates that immune system irregularities and genetic factors play significant roles. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to excessive production. A family history also increases risk.
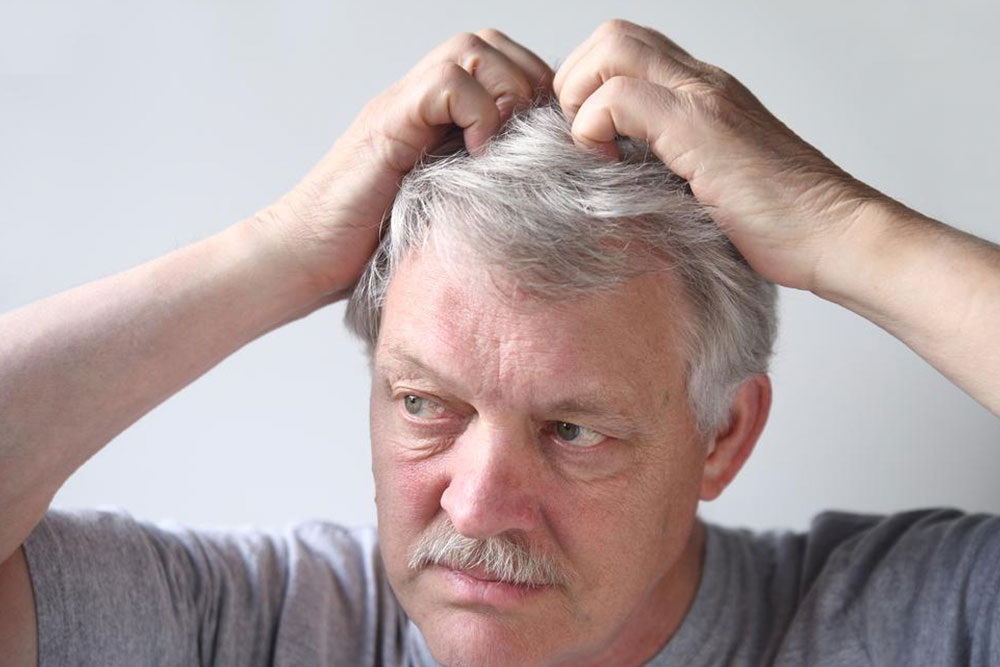
Types of Psoriasis
Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, with thick, red patches topped with silvery scales.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe emergency with widespread redness and skin peeling, requiring immediate medical attention.
Guttate Psoriasis: Small pinpoint lesions that can develop into larger plaques over time.
Pustular Psoriasis: White pustules on red skin, sometimes accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever.
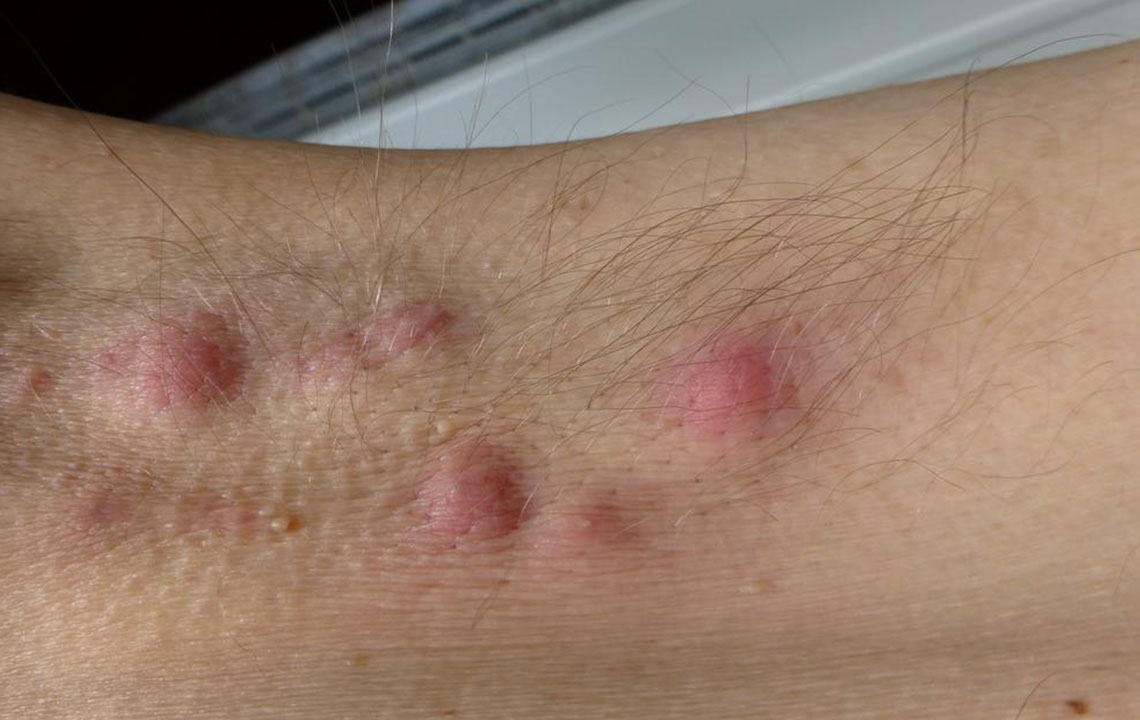
Inverse Psoriasis: Smooth, shiny patches in skin folds like armpits and groin, often causing discomfort.
Psoriatic Arthritis: Affects skin and joints, with skin issues typically appearing before joint pain.
Treatment Strategies
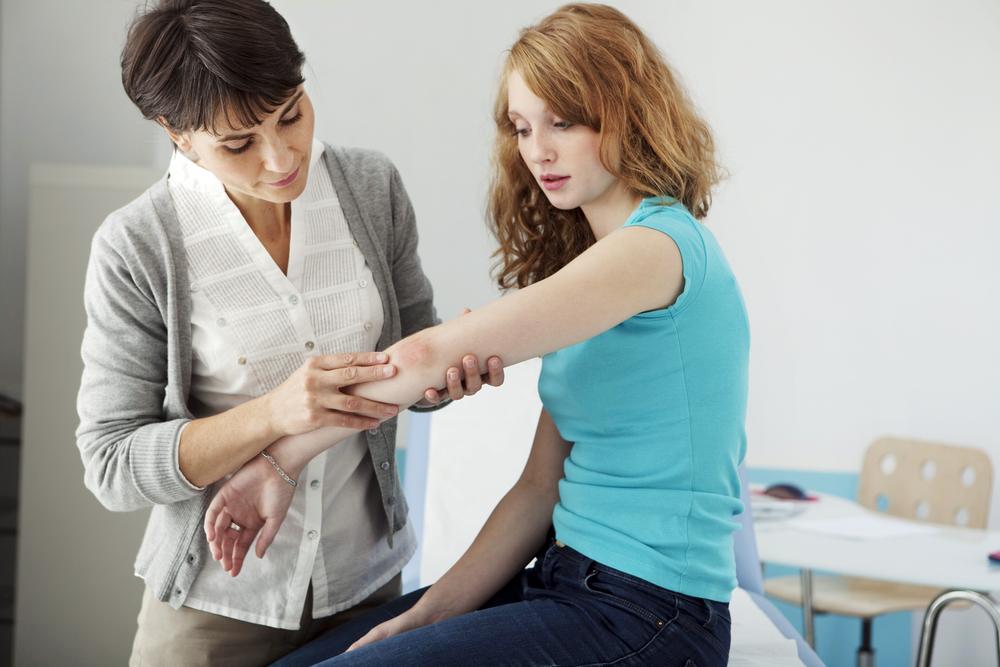
Treatment varies based on type and severity. Topical treatments, including creams and ointments, are effective for mild cases. Systemic medications, taken orally or via injection, are used for moderate to severe psoriasis under professional supervision. Light therapy with UV exposure can mitigate symptoms but requires clinical oversight. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
Natural remedies like Epsom salt baths, aloe vera, diluted apple cider vinegar, and turmeric may alleviate symptoms. Dietary choices play a vital role; consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts, along with leafy greens and berries, can reduce inflammation. Avoiding alcohol and smoking is highly recommended. Prior to making significant lifestyle changes, consult your doctor for personalized advice.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. Please seek professional medical guidance for diagnosis and treatment of psoriasis or any health concerns.