Comprehensive Guide to Shingles Vaccination for Older Adults
This article provides an in-depth overview of shingles vaccination, emphasizing the importance for seniors aged 60 and above. It covers symptoms, eligibility, side effects, and vaccination benefits, helping older adults prevent or manage shingles effectively.
Sponsored
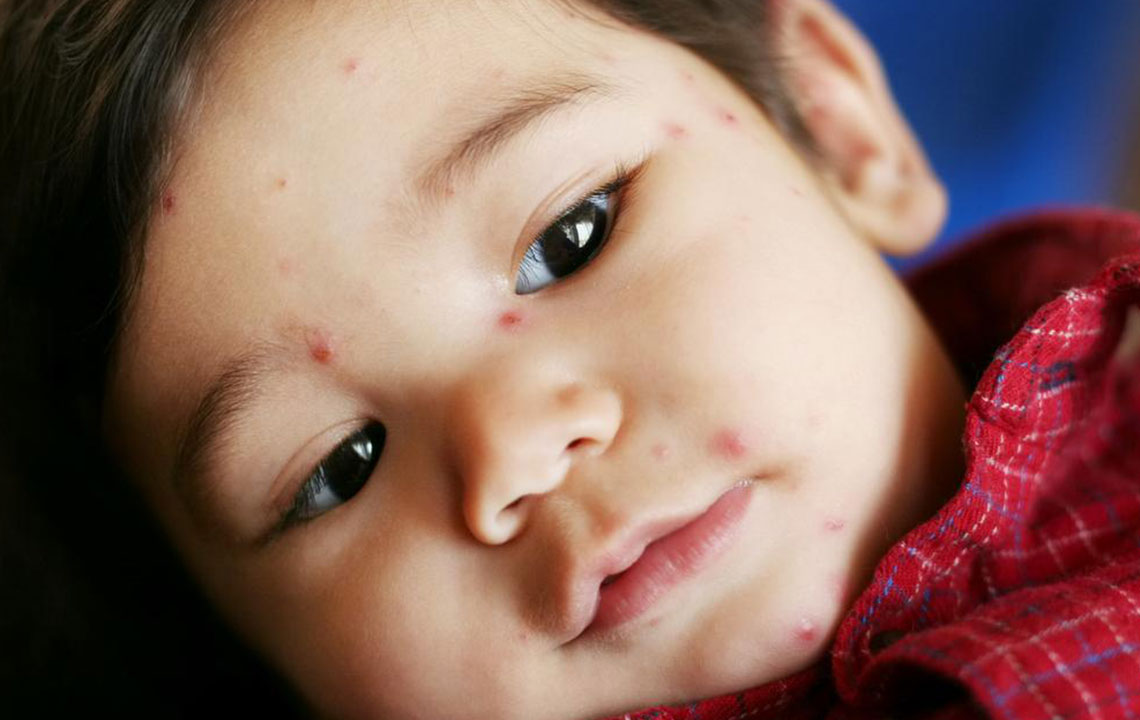
As individuals age, their immune defenses weaken, making them more susceptible to infections. One such illness affecting those aged 60 to 80 is shingles, caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, which also causes chickenpox. This disease manifests as painful red rashes and blisters on one side of the body. Even after chickenpox recovery, the virus can remain dormant and cause shingles later in life. Vaccination can significantly reduce the risk and severity of shingles.
Getting vaccinated against shingles can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing shingles symptoms early helps manage the disease effectively. Common signs include:
Persistent burning or stabbing pain
Red rashes and blisters
Soreness and numbness
Itchy sensations
Fever and chills
Headaches and fatigue
Muscle weakness
Who Should Consider the Shingles Vaccine?
The vaccine is recommended for individuals over 60, particularly those with a history of chickenpox. Vaccinating older adults can prevent disease onset or lessen severity if it occurs again. Even post-recovery, vaccination is advisable to prevent recurrence, although it’s rare.
Side effects are generally mild, such as headache, redness, or soreness at the injection site. Rare reactions like allergic responses, including difficulty breathing, swelling, or dizziness, require immediate medical attention. If adverse effects are noticed, visiting a healthcare provider is essential for proper care.