Understanding the Importance of Cord Blood Banking
Explore the essentials of cord blood banking, including collection methods, storage options, and its crucial role in medical treatments. Discover how cord blood stem cells can aid in healing and provide life-saving solutions for various diseases, making it an important aspect of modern healthcare.
Sponsored
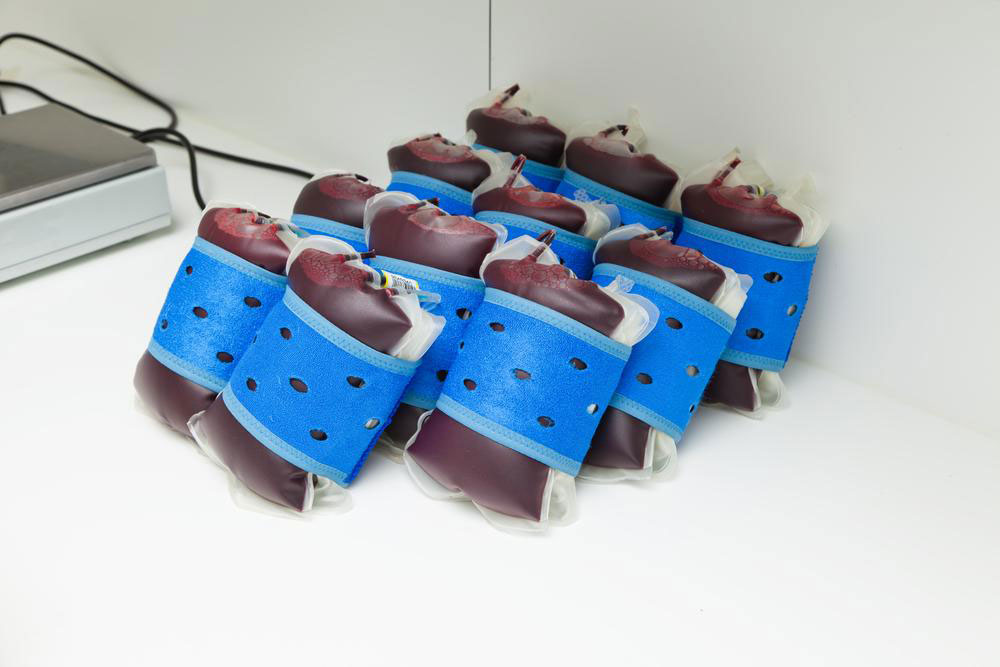
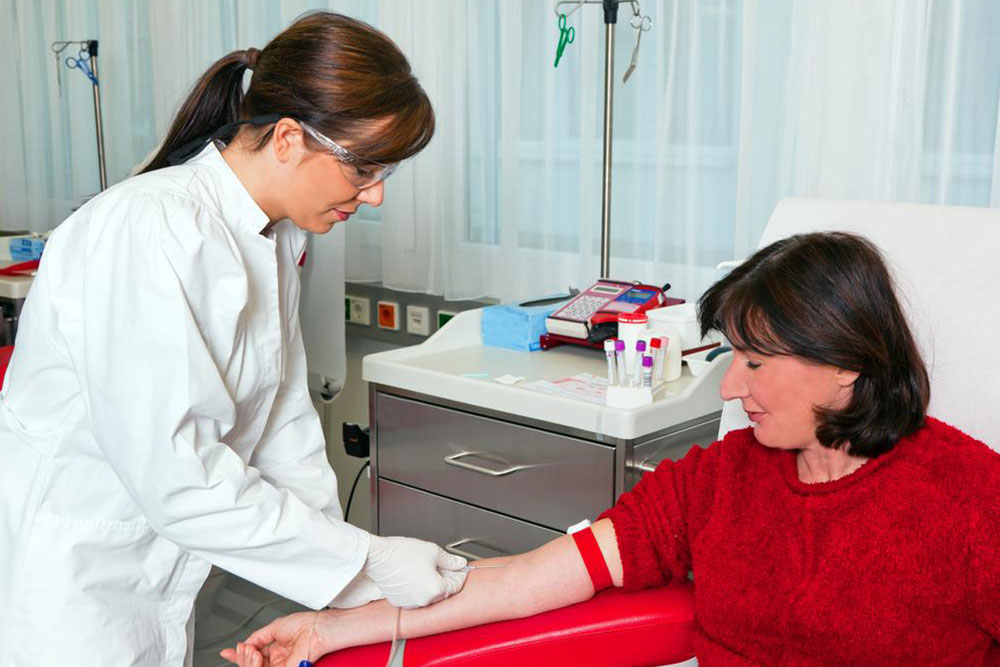
Cord blood, found in the umbilical cord of a newborn, is a valuable source of stem cells capable of regenerating blood vessels, organs, and tissues. Cord blood banking involves collecting this blood after birth and preserving it for potential future medical treatments. It contains vital stem cells that could be life-saving.
Parents can choose to donate their baby's cord blood to a public bank for communal use or store it privately for personal future needs.
The collection process is quick and painless, taking less than 10 minutes. It involves clamping the cord shortly after delivery, inserting a needle into the umbilical vein, and draining about 100-150 ml of blood into a sterile bag. The blood is then shipped to a cryogenic lab for testing and preservation. Some banks also offer collection of umbilical cord tissue, which contains different stem cells than blood.
Stem cells from cord blood play a critical role in treating serious diseases. They can develop into various cell types, helping repair tissues, organs, and blood vessels. Transplants using stem cells from cord blood or bone marrow often have less risk of rejection, making them vital options in regenerative medicine. When other treatments fail or diseases relapse, stem cell transplants can restore the patient's immune system, improving recovery prospects.