Comprehensive Guide to Effective Treatments for Toenail Fungal Infections
This guide covers effective treatments for toenail fungus, emphasizing early intervention, medical options, and preventive tips. It highlights the importance of maintaining foot hygiene, consulting healthcare professionals, and using home remedies as supplementary care. Early detection and proper treatment can prevent the infection's spread and long-term damage, ensuring healthier toenails and overall foot health.
Sponsored

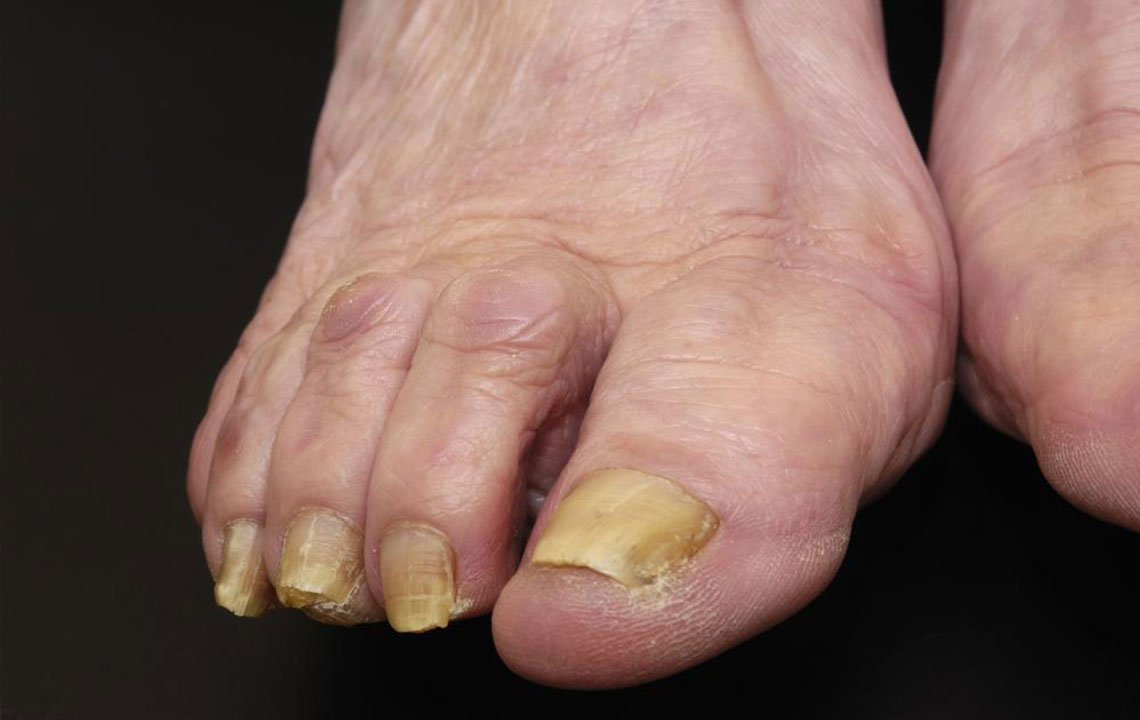
Toenail fungus is a common infection that infiltrates the cracks in the nails, sometimes reaching the surrounding skin. It causes thickening and discoloration of the toenails, often leading to pain and discomfort. The warm, moist environment of the toes promotes fungal growth. Various fungi and yeasts can infect nails, and if left untreated, the infection may spread to other areas. The affected nails become fragile, thickened, and discolored, potentially detaching from the nail bed and spreading to the skin.
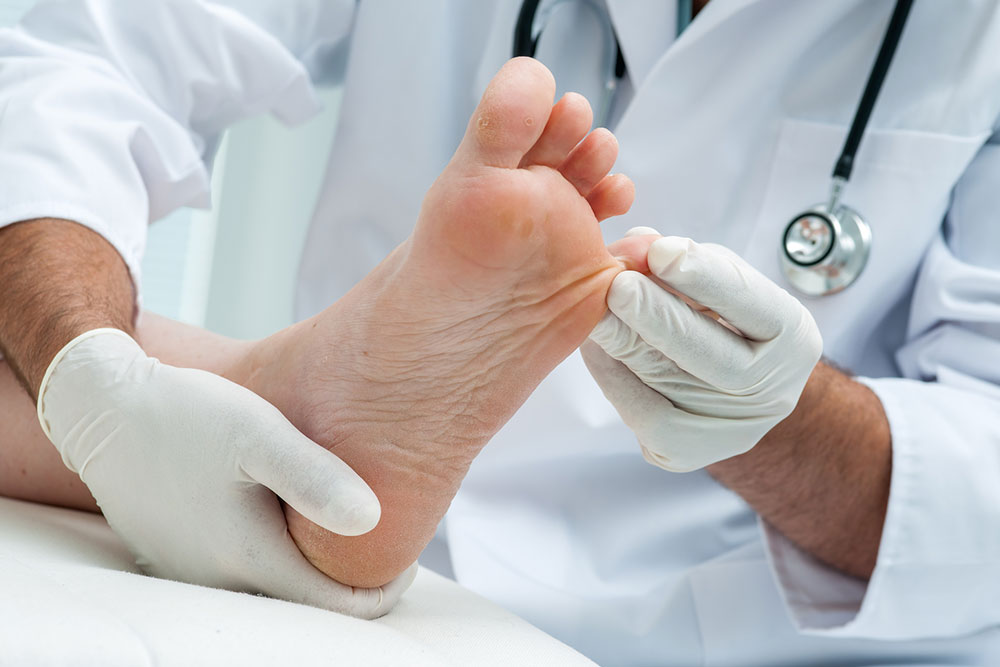
Men, older adults, and individuals with diabetes or weakened immune systems are at higher risk of developing toenail fungus. Those frequently exposed to water or who smoke also face increased susceptibility. If family members have this infection, others are more vulnerable. Early intervention by consulting a healthcare professional can effectively control the infection. A podiatrist or dermatologist may recommend lab tests, topical treatments, antifungal pills, or, in severe cases, nail removal. Maintaining foot hygiene, wearing breathable footwear, changing socks regularly, and keeping feet dry are essential preventive measures. Regularly inspecting nails for changes helps detect infections early and seek prompt treatment, minimizing long-term issues.
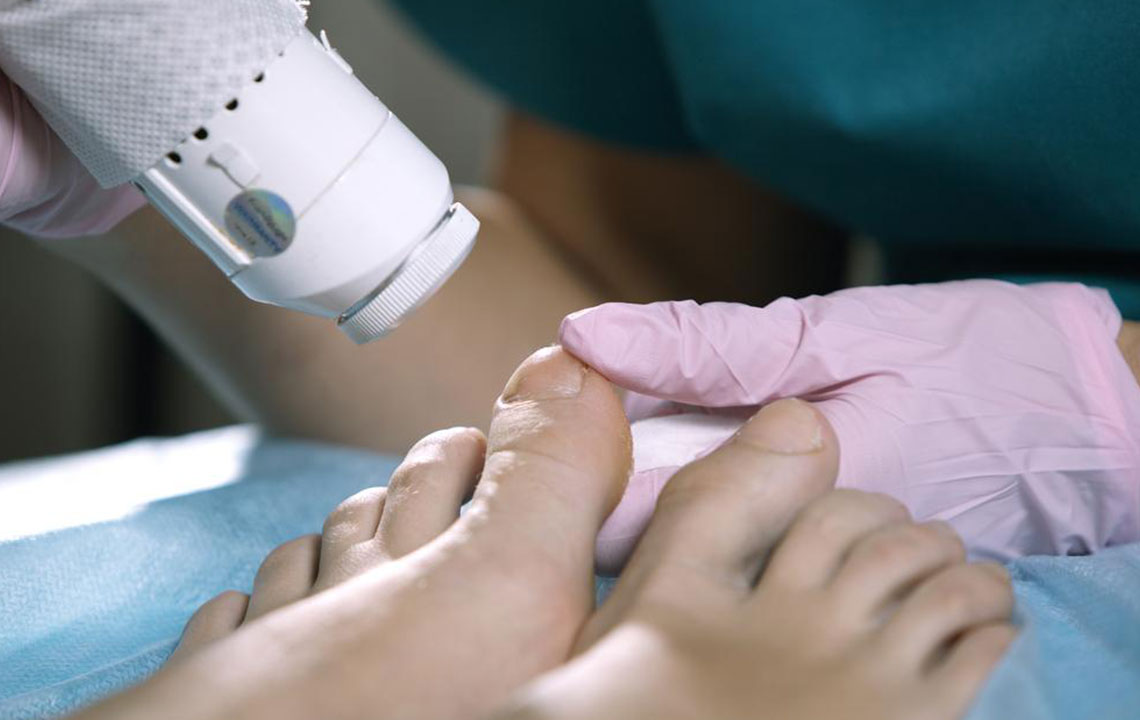
Oral antifungal medications are often prescribed to eradicate the infection efficiently, typically taken for 6-12 weeks. These are more effective in younger individuals with stronger immune systems but may have side effects like lung issues or skin rashes, necessitating monitoring through blood tests. Specialized antifungal nail polishes and creams are also available, applied directly to affected nails to reduce fungi and soften skin. In advanced cases, procedures like nail removal or surgical intervention may be necessary if medications are ineffective. Home remedies such as baking soda, vinegar soaks, and coconut oil can offer relief when used properly, especially before the infection worsens. Proper nail trimming and hygiene practices significantly reduce recurrence. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures appropriate treatment, especially when home remedies fail to deliver results.