Understanding Elevated Triglyceride Levels and Their Impact
Learn about high triglyceride levels, their causes, health risks, and effective strategies to manage and lower them through lifestyle changes and diet. Understanding these factors can help prevent serious cardiovascular issues.
Sponsored

Understanding high triglyceride levels
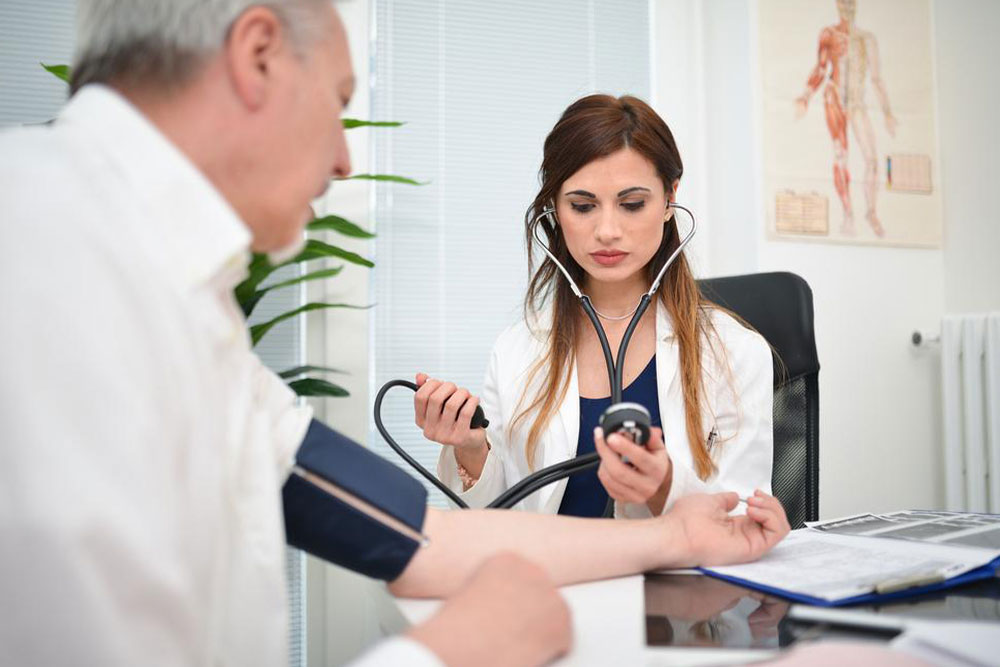
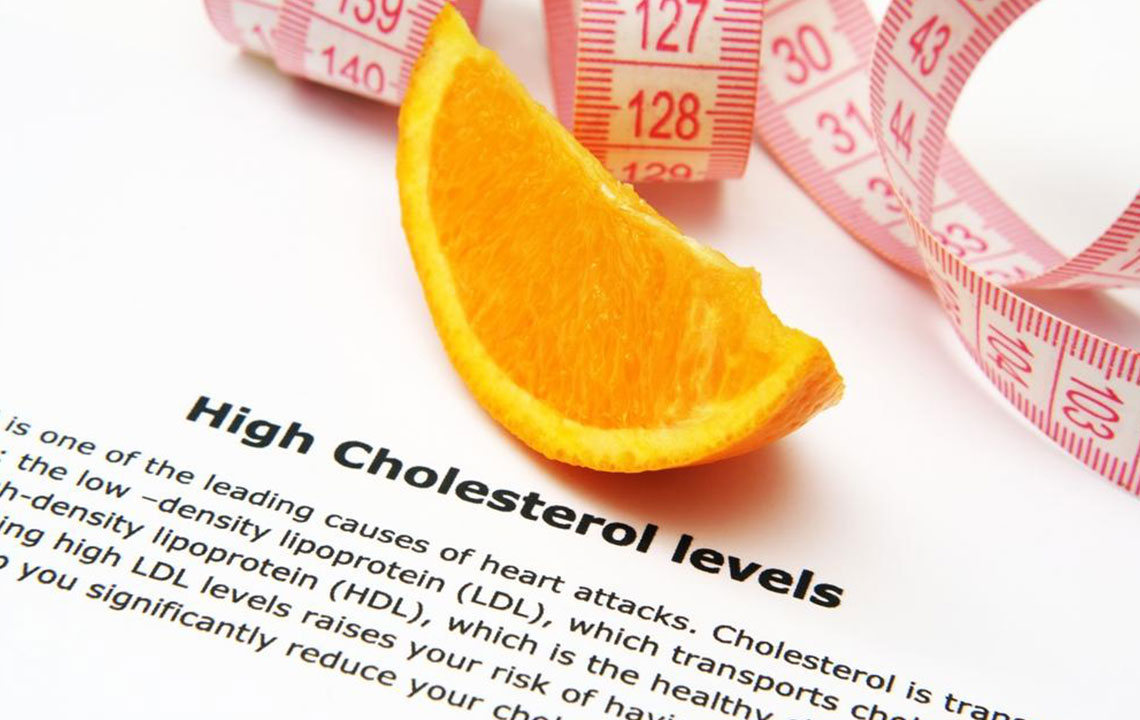
Triglycerides are fats present in our bloodstream, providing energy for bodily functions. While essential in moderation, excess triglycerides pose risks for heart disease, metabolic syndrome, high blood sugar, and abdominal obesity. Blood tests assess triglyceride and cholesterol levels, helping identify potential health issues. Causes include obesity, unmanaged diabetes, kidney issues, high-calorie diets, alcohol consumption, certain medications, and genetic factors. Lifestyle modifications like weight reduction, dietary changes, increased physical activity, quitting smoking, and medication can effectively lower triglyceride levels. The body produces triglycerides from food and liver activity, storing surplus as fat. Elevated levels can lead to artery blockages, increasing stroke and heart attack risks, and can cause pancreatitis. Dietary choices significantly influence triglyceride levels; avoiding sugary foods, saturated fats, and trans fats while consuming high-fiber and healthy fats, such as omega-3-rich fish, improve lipid profiles. Regular testing and a balanced diet are vital for maintaining healthy triglyceride levels, typically below 150 mg/dL.