Comprehensive Guide to Skin Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
This article offers a detailed overview of skin cancer, highlighting its causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and prevention strategies to reduce the risk of developing this potentially dangerous disease.
Sponsored

Understanding Skin Cancer
Skin cancer involves abnormal or malignant growths of skin cells and is classified into three main types based on affected cell types. The most prevalent form is basal cell carcinoma, followed by squamous cell carcinoma. The rarest yet most aggressive type is melanoma. Other less common variants include atypical fibroxanthoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, Kaposi sarcoma (related to blood vessel tumors), skin adnexal tumors, cutaneous lymphoma, and various sarcomas.
What Causes Skin Cancer? It results from genetic mutations within skin cells. Excessive UV radiation from sunlight or tanning beds damages the DNA, leading to cancer. Sometimes, skin carcinomas develop without UV exposure, often linked to a weakened immune system.
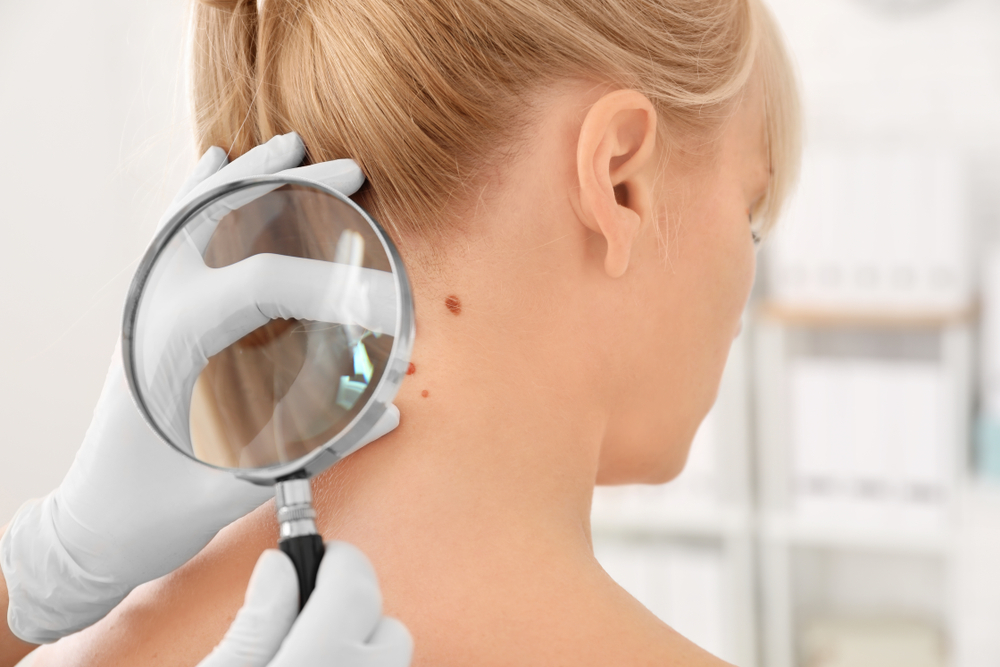
Risk Factors Factors increasing susceptibility include frequent severe sunburns, light skin with less melanin, red or blonde hair, blue eyes, freckles, high-altitude or warm climate residence, family history, exposure to arsenic or radiation, irregular moles, previous skin cancer, actinic keratoses, and certain viral infections.
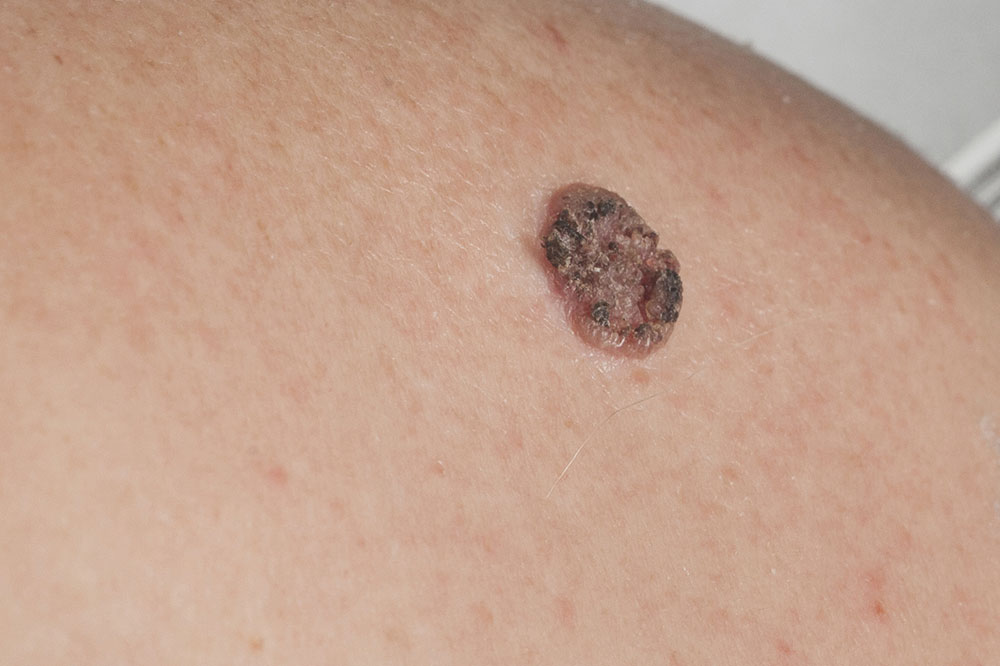
Signs and Symptoms Skin cancers present differently. Basal cell carcinoma may appear as shiny bumps or flat brown lesions. Squamous cell carcinoma manifests as scaly, red, or firm nodules. Melanoma often looks like large, irregular, multi-colored spots or changing moles. Kaposi sarcoma shows purple or red patches, while Merkel cell carcinoma appears as shiny bumps. Other types have distinct appearances, but any unusual skin growth warrants medical attention.
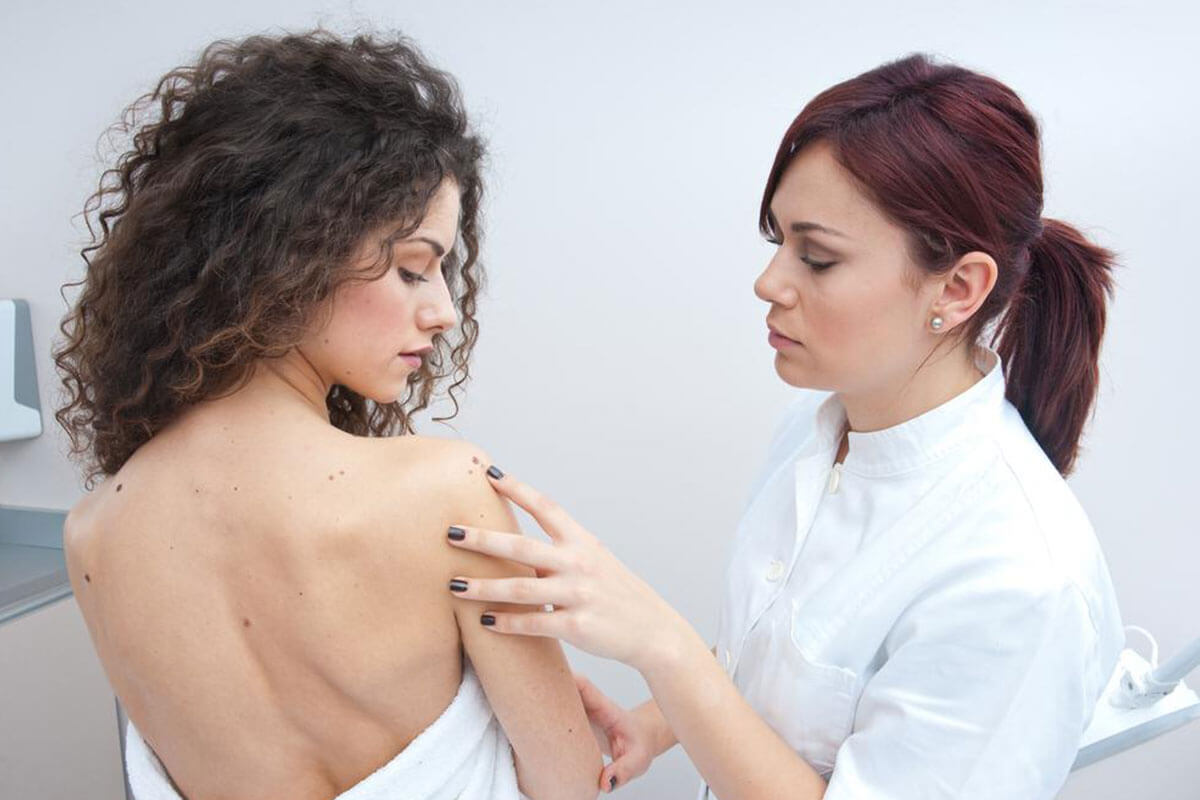
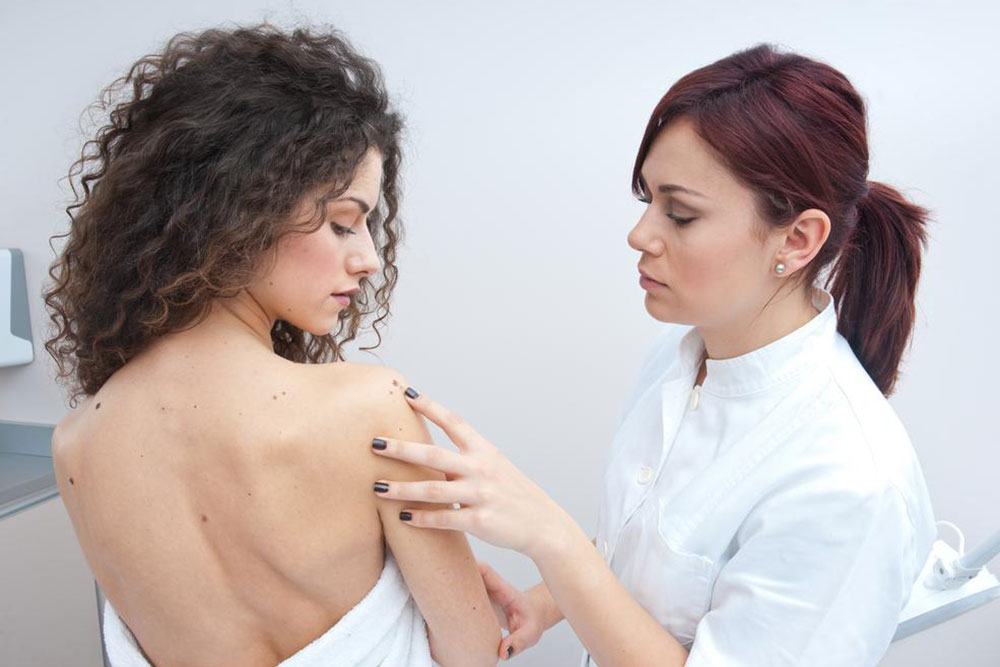
Available Treatments Treatment options include surgical removal, radiation therapy, topical medications, cryosurgery, laser treatments, and specialized medicines. Preventive measures like sun protection can significantly reduce the risk of developing skin cancer.