Understanding Tooth Discomfort and Available Treatment Methods
This article provides a detailed overview of tooth pain causes, risk factors, and treatment options, including modern dental procedures like root canals and implants. It emphasizes the importance of oral hygiene and regular dental visits to prevent dental discomfort and maintain healthy teeth.
Sponsored

Comprehensive guide to tooth discomfort and treatment options
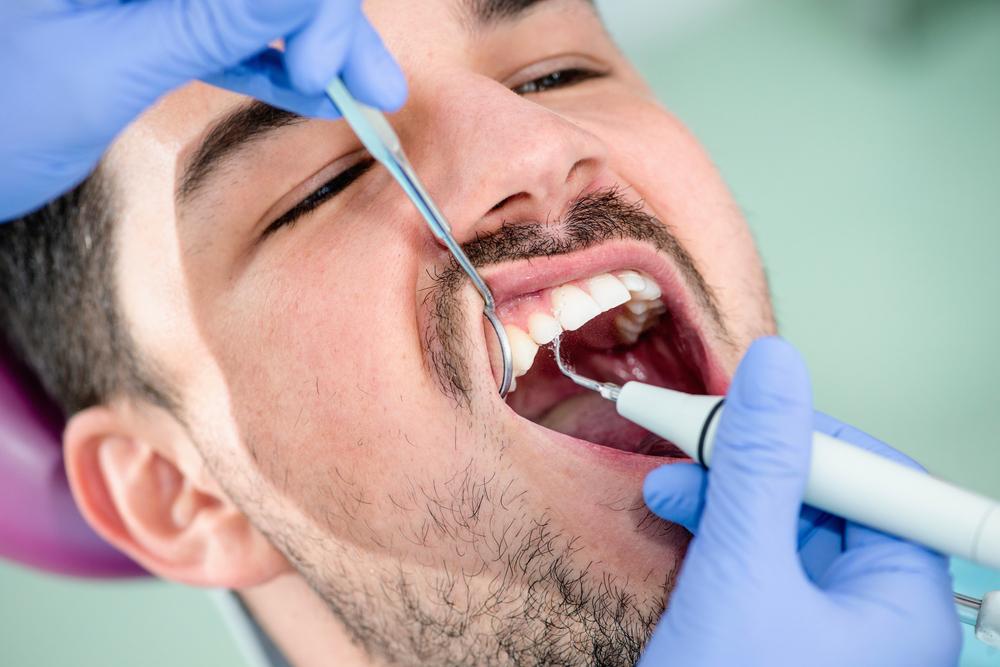
The main reason behind tooth pain often relates to neglecting regular dental visits. However, modern dentistry has advanced significantly, making checkups less intimidating. Today, except for the drilling noise, dental visits are quite manageable. Maintaining good oral hygiene through daily care, routine dental visits, and prompt treatment can prevent serious issues in the future.
Sometimes, toothache appears unexpectedly, leaving you distressed. Here's some essential information to help you understand the pain and options to alleviate it.
What causes tooth pain?
Early signs include mild pain indicating enamel damage and fluid infiltration into the pulp.
Not all toothaches are due to cavities; sometimes, pain is referred from other areas.
Sensitivity can often be an initial symptom of decay but isn't always definitive.
Initial steps to manage toothache
Visit your dentist promptly at the first sign of pain or sensitivity.
The dentist will examine your teeth and gums for issues.
A soft brown layer on the enamel suggests early decay, which can be cleaned and filled if necessary.
Usage of specialized toothpaste or fluoride coatings might be recommended for repair and protection.
Factors increasing the risk of tooth pain
Poor oral hygiene, such as neglecting brushing twice daily, especially after meals.
Skipping regular dental checkups and treatments.
Diets full of sugars and carbohydrates, fueling oral bacteria.
Insufficient fluoride intake; many regions add fluoride to water and food.
Lack of saliva, which aids in rinsing away acids and bacteria, increasing decay risk.
Medical conditions like diabetes.
Smoking and tobacco use contribute to decay and gum issues.
Infants are vulnerable due to underdeveloped teeth and exposure to bacteria via unclean feeding utensils.
How to diagnose and treat tooth pain
Initial exams include personal and family health history, providing insight into possible causes.
The dentist conducts an oral exam with probing tools and looks for sensitive or decayed areas.
Pain upon tapping or probing indicates possible cavities needing further investigation.
An X-ray may be used to assess the extent of decay.
Based on findings, treatment options include fillings, root canals, extractions, or gum surgery.
What is a root canal procedure?
Teeth are classified into incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, each with specific root structures.
During a root canal, the dentist opens the pulp chamber, removes infected tissue, and disinfects the space under local anesthesia.
The cleaned pulp chamber and roots are sealed with inert gutta-percha cones.
Advances now include placing implants into the jawbone and attaching artificial teeth for durability and function.