Comprehensive Guide to Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
This comprehensive guide offers essential insights into urinary tract infections (UTIs), covering symptoms, causes, risk factors, and effective prevention and home treatment options. Learn how to reduce your risk and manage symptoms effectively with expert advice on lifestyle and hygiene practices.
Sponsored
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections
Understanding urinary tract infections
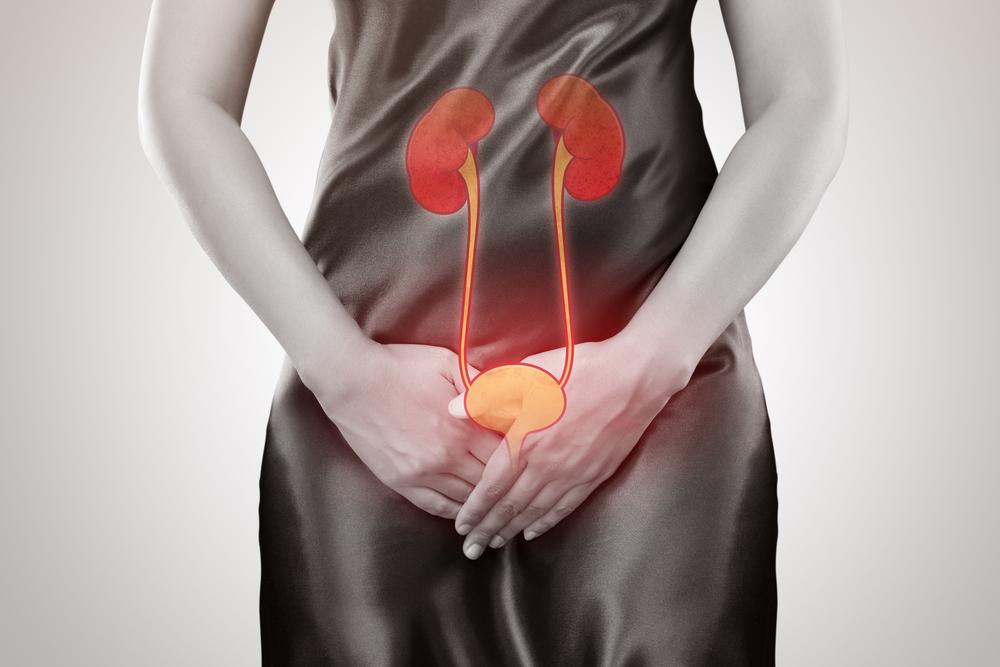
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that can affect any part of the urinary system, which includes the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract, primarily the bladder and urethra. Women are more susceptible to UTIs than men.
An infected bladder can cause discomfort and pain, but if the infection spreads to the kidneys, it can lead to serious health issues. Treatment typically involves antibiotics prescribed by healthcare professionals.
In addition to medical treatment, some home remedies may help soothe symptoms and prevent recurrence. Taking proactive steps can reduce your risk of developing UTIs. Below are details about symptoms, causes, and prevention strategies.
Common symptoms of UTIs include:
Persistent urge to urinate
Passing small amounts of urine frequently
A burning sensation during urination
Cloudy urine
Red or pink urine indicating blood
Strong foul-smelling urine
Pelvic pain, especially around the pubic area in women
What leads to UTIs?
Infection is usually caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, which normally resists such invasion. When this defense fails, bacteria can colonize, causing infection. Women are especially prone, often affected in the bladder and urethra, due to anatomy and other factors. Common causes include:
Urethritis: An infection of the urethra, often due to bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract spreading to the urethra, or STIs like herpes or gonorrhea in women.
Cystitis: An infection of the bladder, frequently caused by E. coli bacteria found in the gut. Sexual activity can sometimes trigger cystitis, but it’s not necessary for it to occur. Women’s anatomy makes them more susceptible.
Who is at higher risk?
Women face a greater risk, often experiencing at least one UTI during their lifetime. Key risk factors include:
Postmenopausal changes due to decreased estrogen levels
Frequent sexual activity, especially with new partners
Having a shorter urethra, facilitating bacterial entry
Use of certain birth control methods like diaphragms
Urinary tract abnormalities, catheter use, immune suppression, or recent urinary procedures
Effective home remedies for UTIs
While antibiotics are the primary treatment, certain home strategies can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future infections. These include:
Maintaining proper hydration
Boosting vitamin C intake
Drinking unsweetened cranberry juice
Consuming probiotics
Practicing good hygiene habits
Taking natural supplements