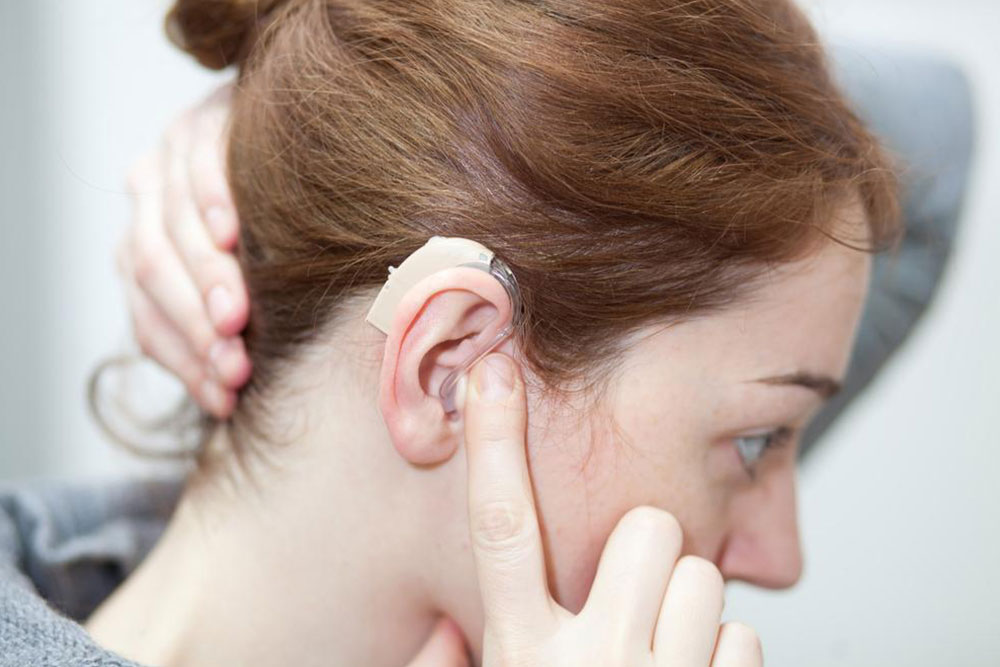
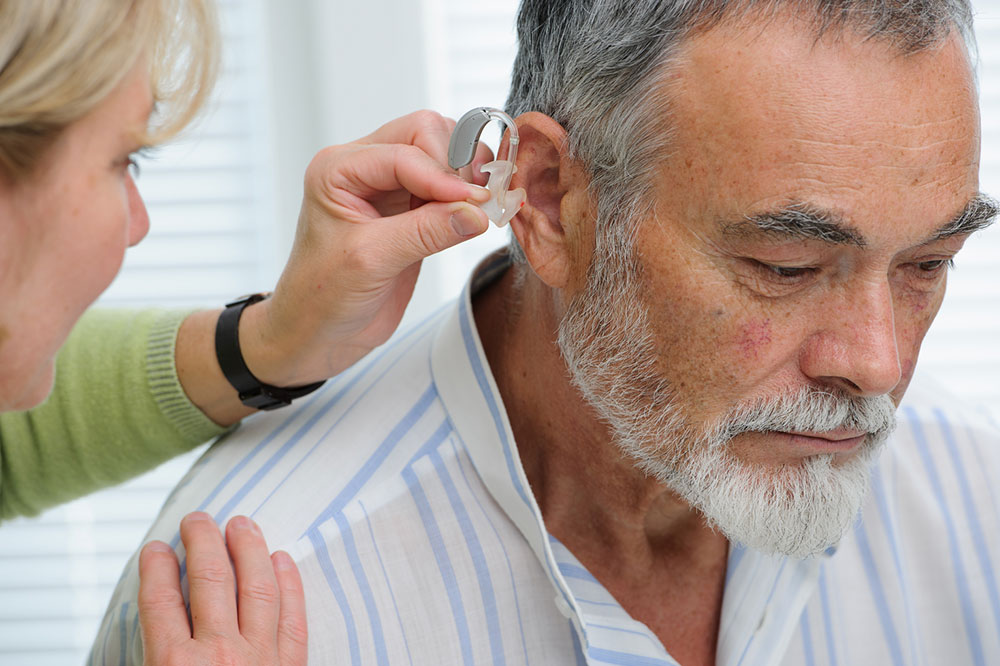
Signs and Preventive Measures for Hearing Loss
Early detection of hearing loss is vital for effective management. Recognize signs such as muffled sounds and difficulty understanding speech. Risk factors include age, noise exposure, genetics, medication, and illnesses. Treatments like hearing aids, surgery, and implants can significantly improve quality of life. Regular hearing assessments are recommended, especially for those in noisy environments or with hereditary risks.
Sponsored
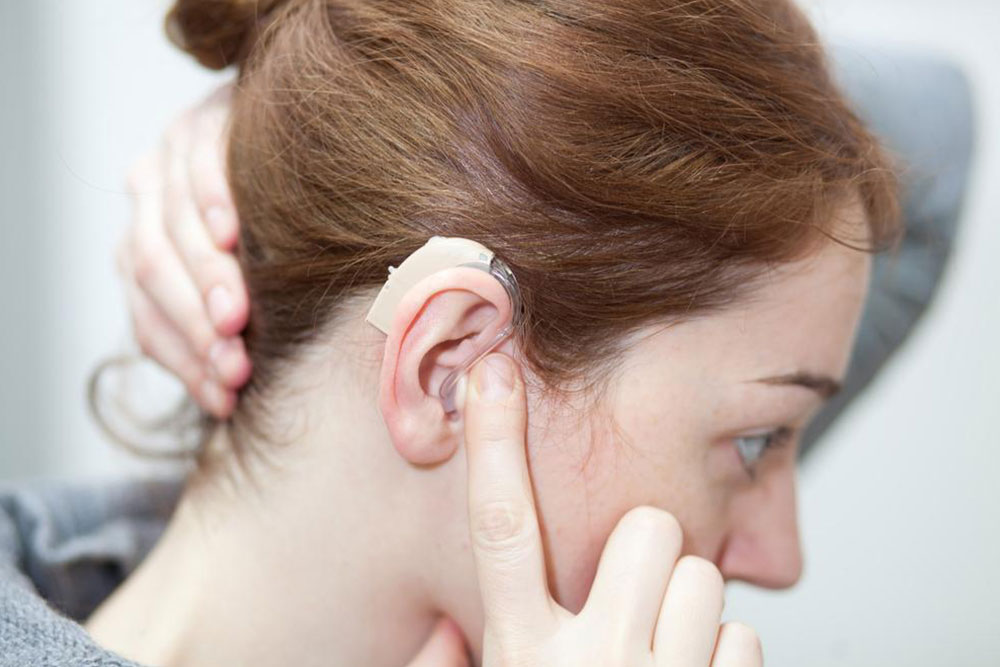
Signs and Preventive Strategies for Hearing Impairment
Hearing ability can decline over time, even if you start with perfect hearing. Recognizing early signs of hearing impairment is essential for timely intervention. Hearing loss, often permanent, can be managed effectively with devices like hearing aids that enhance sound clarity.
Several factors influence the risk of hearing loss, including:
Age – The deterioration of inner ear components with age can lead to declining hearing.
Loud noise exposure – Continuous exposure to loud environments (80-110 decibels) can harm inner ear cells.
Sudden loud sounds, such as explosions, can cause immediate hearing damage. If working in noisy settings, always use ear protection. Other risk factors include:
Genetics – Hearing issues can be inherited from parents.
Medications – Certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, high-dose pain relievers, and aspirin may impact ear health.
Illnesses – Conditions like meningitis can harm auditory organs, leading to hearing impairment.
Detection of early symptoms is crucial for diagnosis and treatment. Watch for signs like muffled sounds, difficulty distinguishing speech from background noise, trouble understanding words, needing louder volumes, or difficulty maintaining conversations. Ignoring these signs can result in social withdrawal and psychological issues like depression. Hearing aids, surgical options, and cochlear implants are common treatments to restore hearing or improve auditory function.