Managing Atopic Dermatitis: Foods to Include and Avoid
This article explores dietary strategies for atopic dermatitis, highlighting foods to incorporate for anti-inflammatory benefits and foods to avoid that may trigger flare-ups. It emphasizes early symptoms and offers practical tips for managing this common skin condition effectively through nutrition.
Sponsored
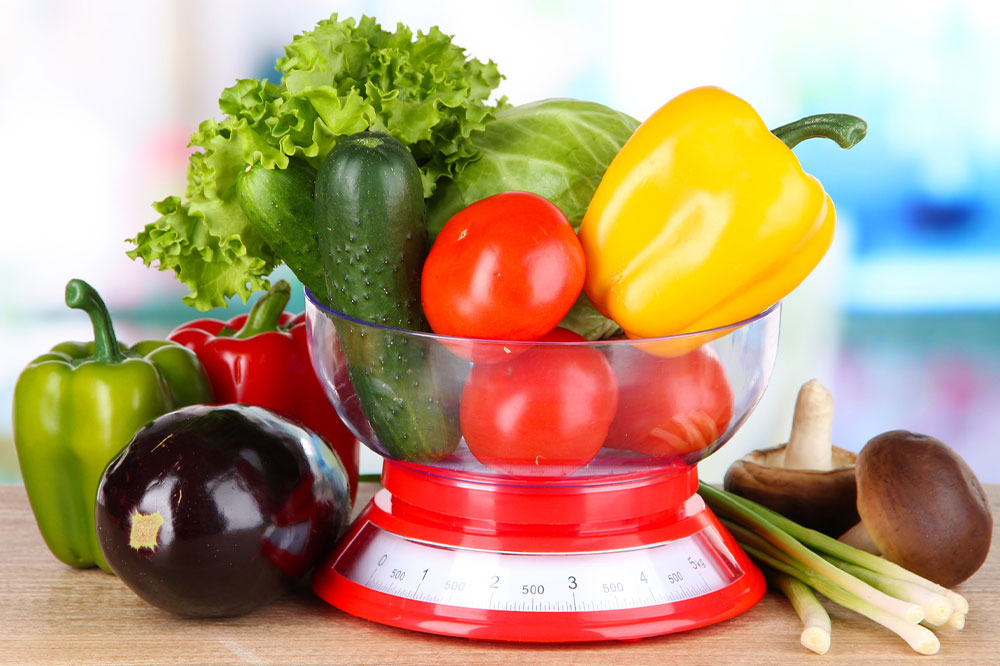

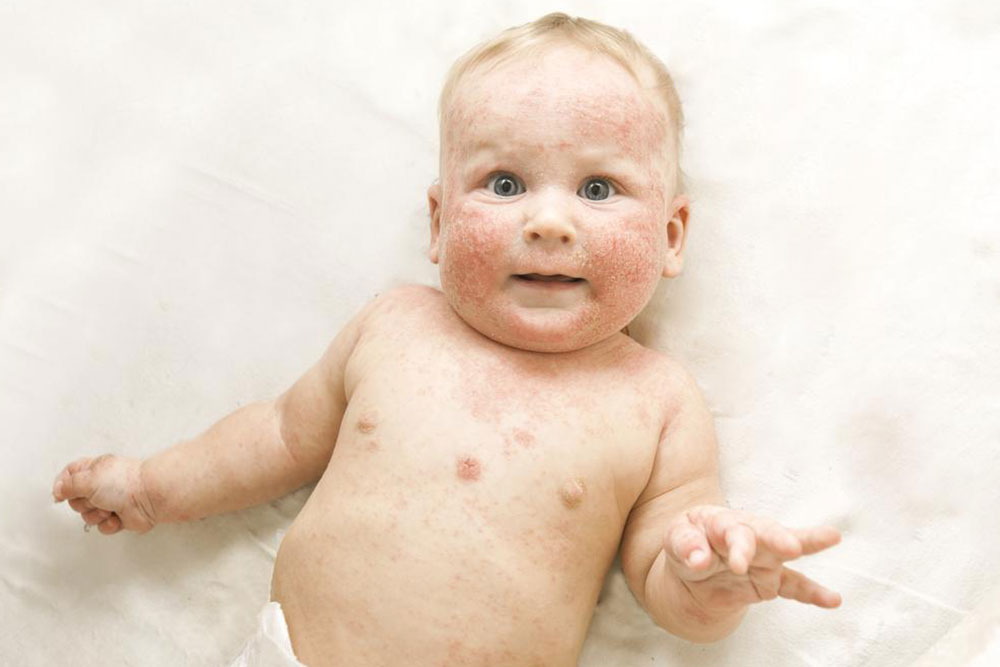
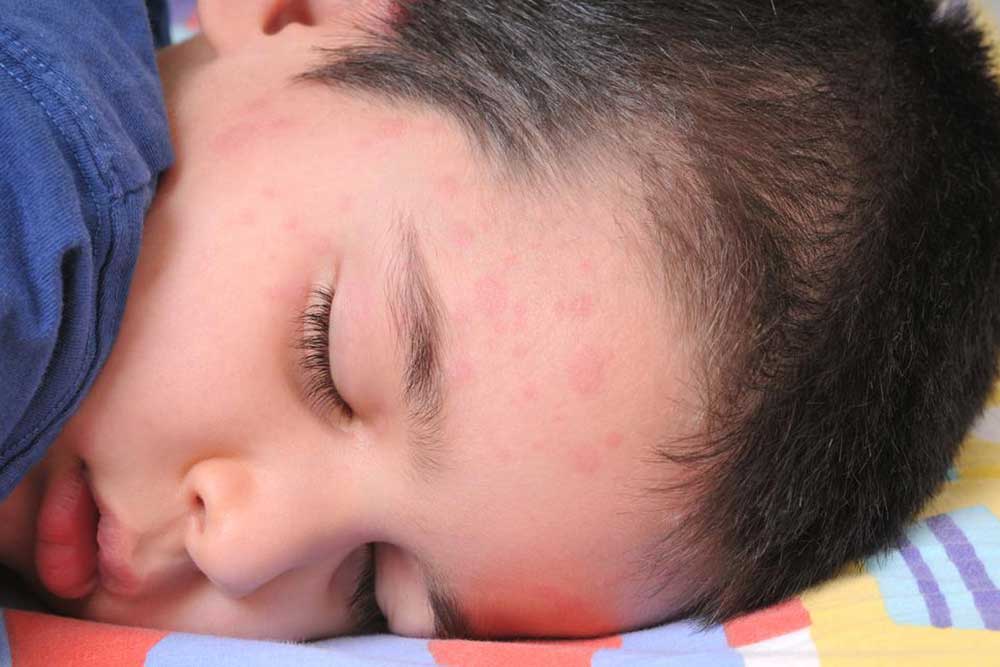
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a skin condition marked by inflammation that can affect individuals of all ages, although it is most prevalent in young children. Since inflammation plays a key role, consuming anti-inflammatory foods while reducing intake of trigger foods can help manage symptoms. Early signs often appear before age five and include dry, itchy skin, tiny bumps, and red to grayish patches, especially on limbs and the face. Incorporating omega-3 rich fish like salmon, probiotic foods such as yogurt, and antioxidant-rich blueberries may provide relief. Conversely, limiting cow's milk, citrus fruits, and eggs can prevent flare-ups. Proper diet management alongside medical advice can improve quality of life for those with atopic dermatitis.