Understanding Atopic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
This article provides comprehensive insights into atopic dermatitis, explaining its causes, symptoms, and management approaches. It emphasizes the importance of recognizing triggers, proper skincare routines, and medical guidance to effectively control eczema and improve skin health.
Sponsored
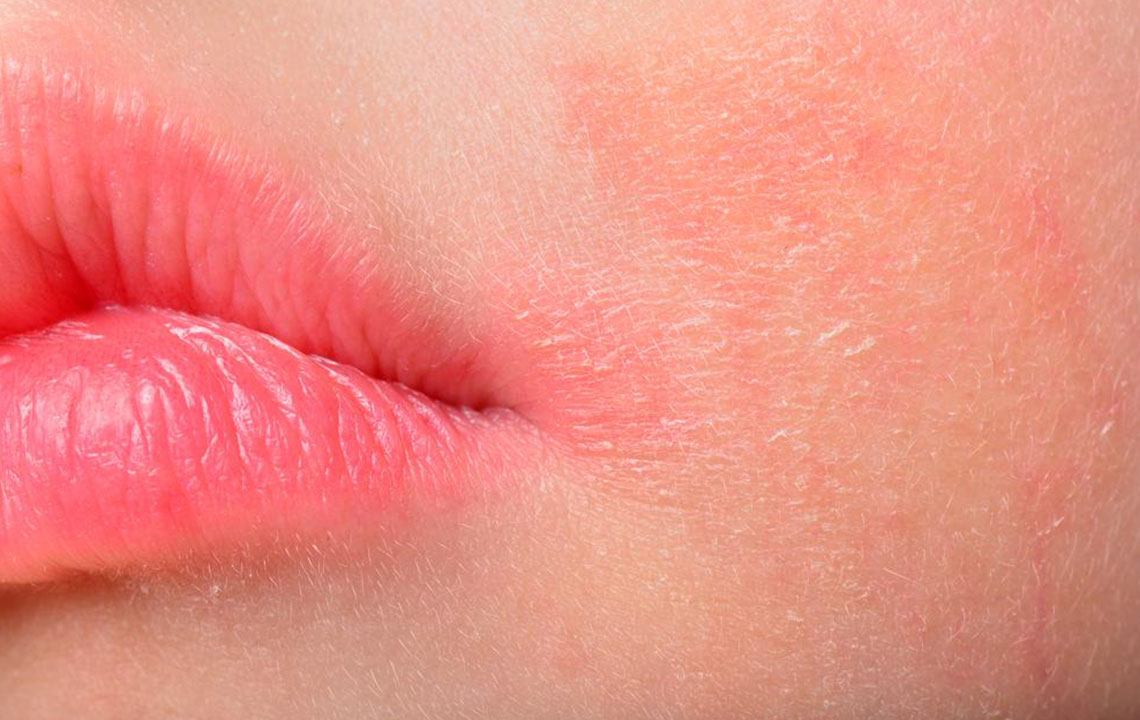
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin disorder characterized by redness, dryness, and intense itching. While it frequently affects children, adults are also susceptible. The exact cause remains unknown; however, it often persists in episodes. The condition impairs the skin's natural moisture barrier, leading to dryness and susceptibility to irritants. It is often associated with other allergic conditions like hay fever and asthma.
Individuals with a family history of allergies are at higher risk. Several factors can worsen eczema symptoms, including harsh soaps, food allergies (peanuts, dairy, soy, fish, wheat), weather changes (cold, dry, humid), skin infections, pet dander, stress, and depression.
Recognizing the triggers of eczema is crucial for effective management. Healthy skin retains moisture effectively, shielding against irritants and pathogens. In eczema-affected skin, moisture retention is compromised, causing dryness and increased vulnerability.
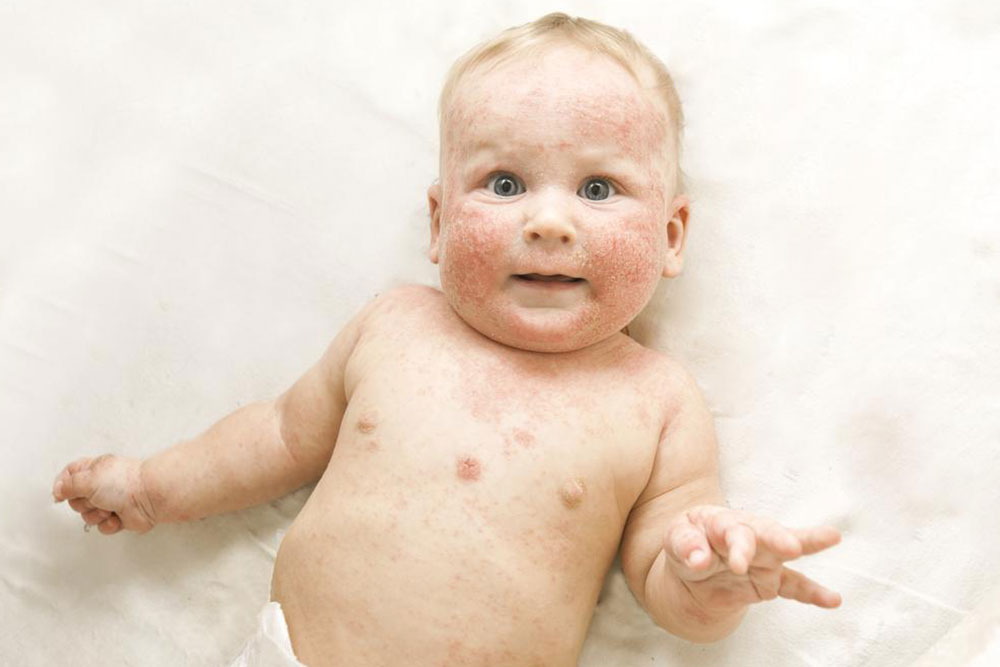
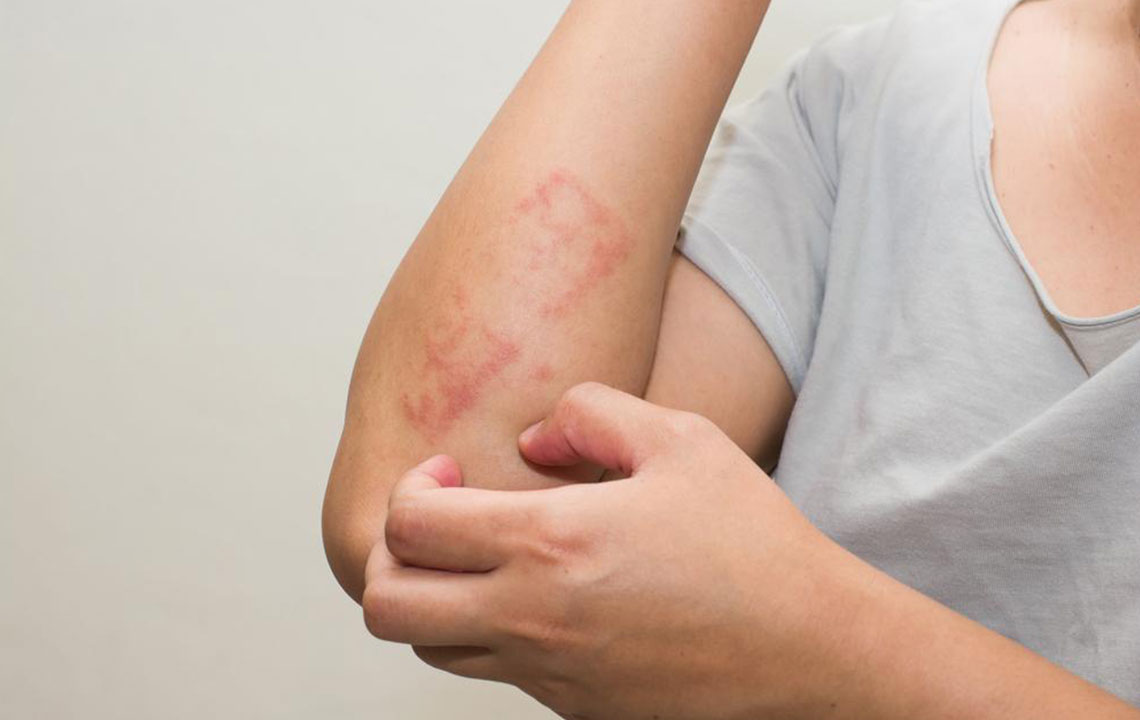
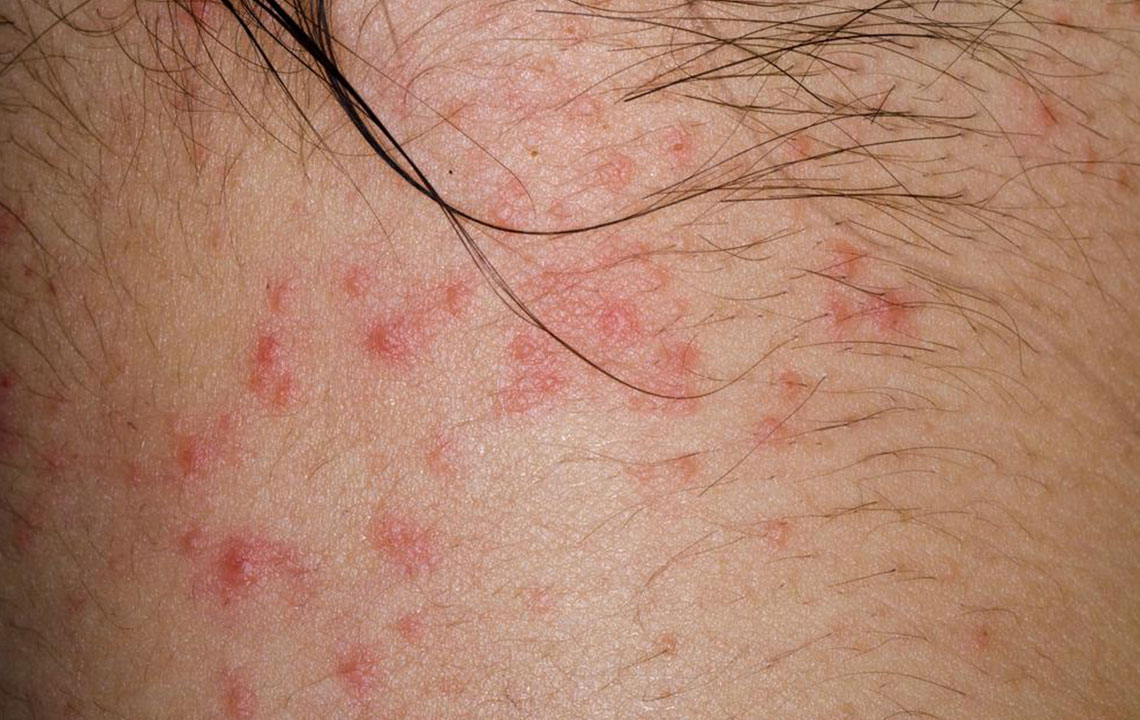
Symptoms typically start with dry, itchy patches that can lead to skin inflammation. Small bumps or blisters may develop, sometimes oozing fluid. Symptoms tend to fluctuate, with episodes of flare-ups causing rough, thickened skin. Eczema can be classified into mild and severe forms, with mild cases affecting small areas and manageable through moisturizers. Severe cases involve larger areas, intense itching, and notable inflammation.
The condition can appear in various body parts depending on age. Infants often have rashes on cheeks, scalp, and back of elbows. Children might experience rashes on legs, knees, wrists, and ankles, while adults frequently develop symptoms on the neck, elbows, and knees.
Managing eczema involves lifestyle modifications and medical treatment. Daily moisturizing, anti-itch creams, prescribed oral medications, and protective bandages can help. Warm baths and humidifiers are also beneficial. Immediate treatment of flare-ups and avoiding known triggers are key to controlling symptoms. Consulting a dermatologist ensures personalized care and effective management.
If you notice persistent skin rashes or itching, it is essential to identify the cause promptly. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve quality of life.