Understanding Heartburn: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Learn about heartburn, its causes, symptoms, and lifestyle-based prevention strategies. This article explains how the condition affects many, especially during pregnancy and obesity, and offers tips for managing and reducing symptoms effectively.
Sponsored

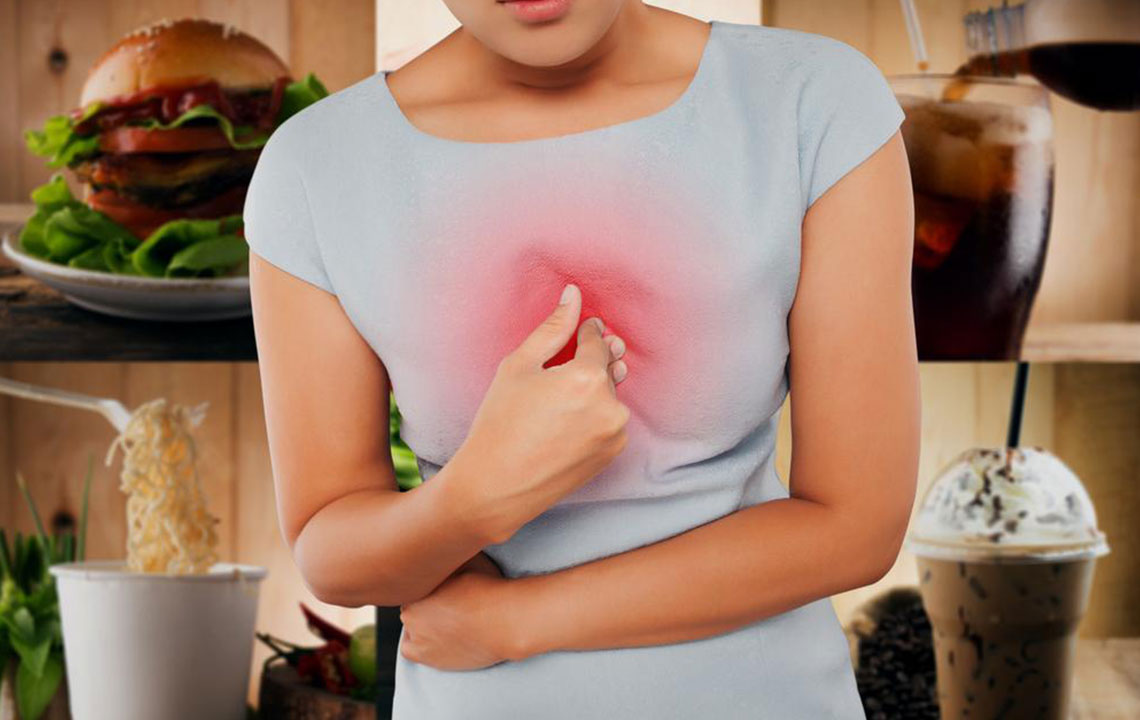
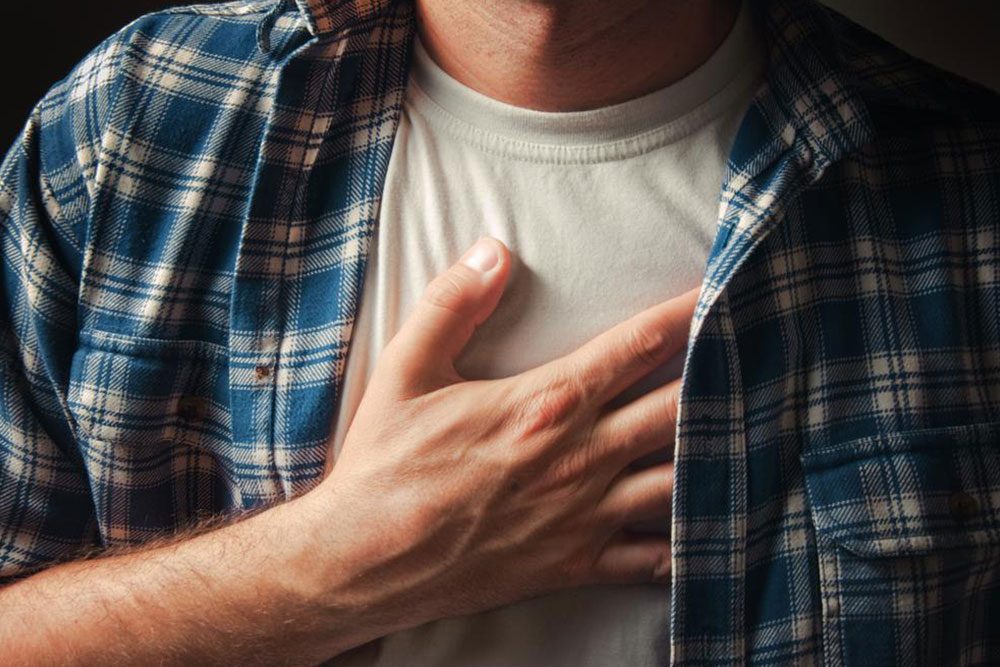
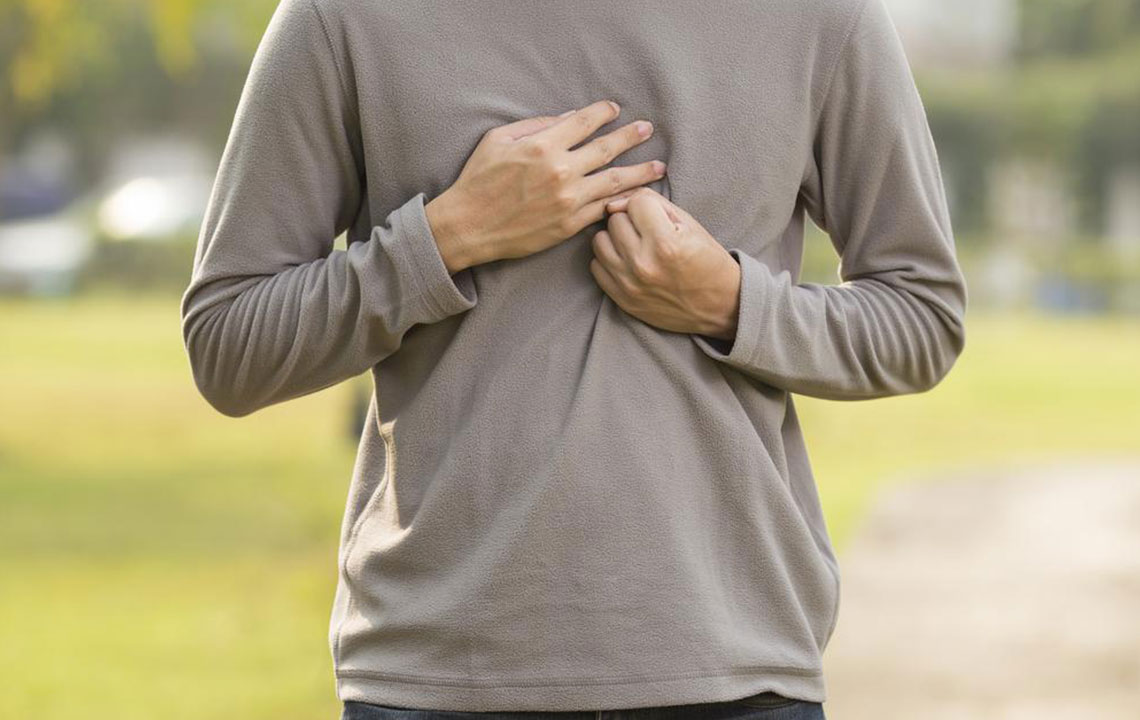
Despite its name, heartburn has no connection to the heart. It is a common digestive issue caused by stomach acidity. Symptoms such as burning pain in the chest or upper abdomen can resemble heart problems, but it is a different condition. Heartburn occurs when stomach acids and contents flow back into the esophagus, leading to discomfort. Persistent episodes, more than twice weekly, may indicate GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease). Typical signs include a burning sensation, difficulty swallowing, cough, and chest pain.
Causes
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) acts as a valve between the esophagus and stomach, preventing acid reflux. When the LES weakens or opens frequently, stomach acids can escape into the esophagus, causing heartburn. Factors like heavy meals, lifting heavy objects, obesity, pregnancy, and smoking can weaken this barrier, increasing reflux chances. Lifestyle habits play a crucial role, with about 20% of Americans experiencing weekly heartburn episodes. Managing weight, avoiding large meals, and quitting smoking can significantly reduce symptoms.
Diagnosis & Prevention
Doctors may perform tests such as endoscopy, upper GI series, or pH monitoring to diagnose persistent heartburn. Preventive measures include eating smaller, more frequent meals, avoiding exercise immediately after eating, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. These habits help minimize acid reflux episodes and improve overall digestive health.