Effective Strategies for Managing Peripheral Nerve Damage
Discover comprehensive approaches to treat and manage peripheral neuropathy. This article covers types, symptoms, diagnosis, therapies, alternative methods, and lifestyle tips to alleviate nerve damage. Tailored treatment plans and expert advice are vital for effective relief and nerve health improvement.
Sponsored
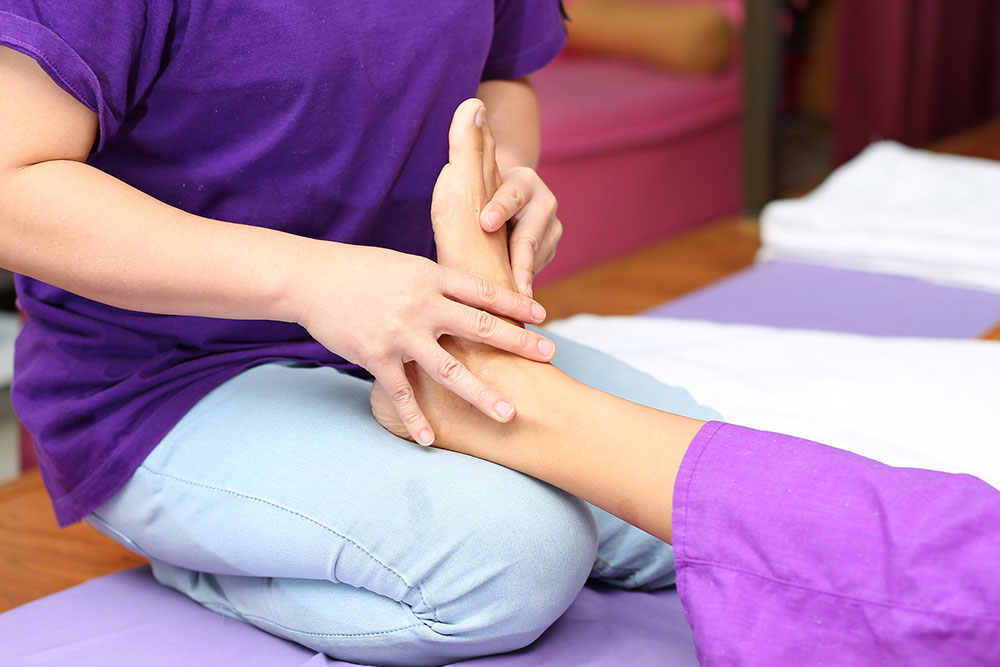

The peripheral nervous system connects the brain and spinal cord to various parts of the body, including limbs, facial muscles, and internal organs. These nerves transmit sensory information back to the brain. Neuropathy, or peripheral nerve disorder, occurs when these nerves become damaged, leading to incorrect signals—such as pain without cause or numbness where sensation should exist. Causes include injuries, infections, genetic factors, or systemic illnesses.
Though uncomfortable, neuropathy can be managed effectively with proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Identifying the root cause is crucial, as treatments vary based on individual circumstances.
Types and Symptoms of Neuropathy
With over 100 types, neuropathy presents diverse symptoms and treatments. It’s classified into two categories based on the nerve damage—sensory nerves, motor nerves, and autonomic nerves—each affecting different body functions. Conditions may involve a single nerve (mononeuropathy) or multiple nerves (polyneuropathy). Symptoms include tingling, numbness, shooting pains, dizziness, sexual dysfunction, skin thinning, digestive issues, and excess sweating. Accurate diagnosis and symptom reporting are essential for effective treatment.
Diagnosis Procedures
Medical History Review: Doctors assess past health, lifestyle, toxin exposure, and family history of neurological issues.
Neurological Exam: Tests evaluate reflexes, muscle strength, sensation, posture, and coordination.
Blood Tests: Detect underlying conditions such as diabetes, immune disorders, or vitamin deficiencies.
Imaging: MRI or CT scans help identify structural issues like herniated disks or tumors.
Nerve Function Tests: Electrical conduction tests and sensory assessments evaluate nerve health.
Skin Biopsy: Small skin samples reveal nerve ending density and damage.
Management and Treatment
The goal is symptom relief through targeted treatments based on the cause. Continuous medical supervision ensures progress and adjustment of therapies.
Medications can be beneficial but may cause side effects. Alternative therapies and lifestyle modifications are also valuable.
Therapeutic Approaches
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Electrodes deliver gentle current to reduce discomfort, typically for a month.
Immune-based Treatments: Plasma exchange and IV immune globulin help address inflammatory neuropathies by removing or supplementing immune components.
Physical Therapy: Exercises and assistive devices, like braces or walkers, restore mobility and strength.
Surgical Intervention: Recommended for nerve compression or tumor-related neuropathies.
Alternative Options
Acupuncture: Inserting fine needles at specific points may reduce symptoms after several sessions.
Herbal Remedies: Supplements such as evening primrose oil might ease pain, but consultation with a healthcare provider is advised.
Amino Acids: These may support nerve health, especially for diabetic or chemotherapy patients, though they can have side effects.
Home and Lifestyle Tips
Protect your feet with soft, loose socks and supportive footwear.
Engage in regular exercise like walking, yoga, or Tai Chi to improve strength and regulate blood sugar.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption to prevent nerve damage progression.
Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and proteins to support nerve repair.
Maintain blood sugar levels within the recommended range for optimal nerve health.
Proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan are essential for managing neuropathy effectively. Always consult a healthcare professional if symptoms appear.