Effective Strategies for Managing Persistent Pain
Discover effective strategies to manage and reduce chronic pain through lifestyle changes, physical therapies, and alternative treatments. Learn how exercises, acupuncture, heat/cold therapy, and psychological techniques can improve quality of life and alleviate persistent discomfort.
Sponsored
Occasional aches are common, often signaling injury. Pain transmits from the affected area via the spinal cord to your brain. Unlike temporary pain, chronic pain lingers beyond healing, making daily activities challenging. It persists for over 12 weeks and can feel sharp, dull, burning, or aching. It may be continuous or intermittent and often arises without clear cause, affecting any body part.
Examples include headaches, arthritis, post-surgical discomfort, lower back issues, post-trauma pain, nerve-related pain, and psychogenic pain. What starts as a minor injury can develop into long-term nerve damage, especially impacting older adults. Severity varies among individuals.
Proper pain management can help control but not always eliminate chronic pain. Here are some effective non-drug approaches:
Medications are helpful but not the sole solution. Alternative therapies can make a significant difference.
Regular exercise, tailored with professional guidance, improves overall health and reduces pain. Maintaining good posture, nutrition, and sleep support pain relief.
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese technique using fine needles at specific points, has gained global recognition for pain reduction.
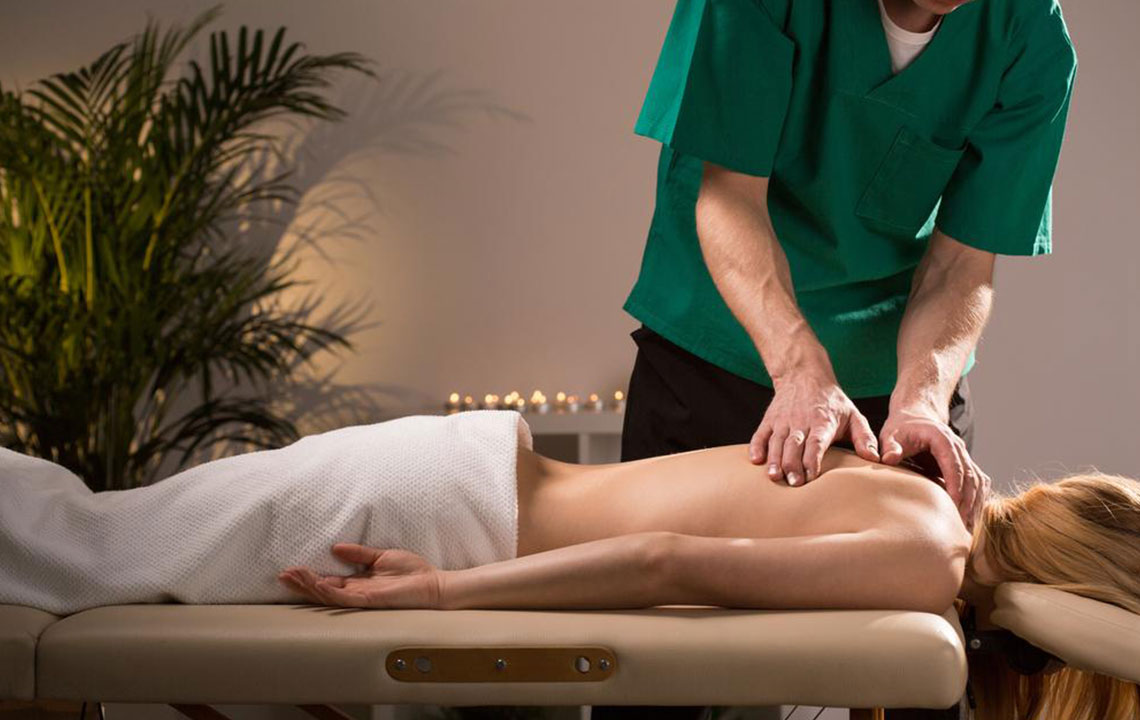
Massage therapy relaxes muscles and tissues, providing relief from chronic pain. When done correctly, it can alleviate lower back pain for months.
Physical therapy, guided by trained experts, teaches proper stretching and movements. It addresses underlying issues, encouraging long-term improvement. Water therapy, such as exercises in pools, is also beneficial.
Heat therapy increases blood flow and reduces inflammation; use hot packs or warm baths. Cold therapy constricts blood vessels and reduces swelling; apply ice packs or cold compresses.
Managing stress is crucial; psychological therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy help control emotional responses to pain. Techniques such as biofeedback and hypnosis can also assist.
TENS therapy uses electrical stimulation to interrupt pain signals via a small device attached to the skin, offering pain relief.
Engagement in hobbies or distraction techniques divert focus from pain. Visual imagery and immersive activities can lessen pain perception.






