Effective Strategies to Prevent and Manage Vasovagal Fainting
Explore comprehensive strategies and lifestyle modifications to effectively manage vasovagal syncope. Learn how to recognize symptoms early, prevent episodes with hydration, salt intake, and exercises, and when medical devices like pacemakers are necessary. Proper management can improve quality of life and minimize risks.
Sponsored

Vasovagal syncope is a condition where the body overreacts to certain triggers, such as emotional stress or the sight of blood. During an episode, blood pressure drops and heart rate slows, potentially reducing blood flow to the brain and causing fainting. Understanding the signs and implementing proper management techniques can help prevent serious injuries and improve quality of life.
Recognizing the Signs of a Vasovagal Episode
These episodes often occur suddenly and can be triggered by activities like straining during bowel movements, heat exposure, prolonged standing, or witnessing graphic scenes. They can happen while sitting or standing, with prodromal symptoms that include dizziness, yawning, sweating, pallor, and a slow pulse. As it progresses, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, twitching, brief unconsciousness, and pupil reversal, though breathing usually remains unaffected.
If you notice these signs, seek immediate medical attention. Steps to Alleviate Vasovagal Fainting and Its Effects
The following actions can help calm the body's automatic response and prevent future episodes:
Lie Down and Elevate Legs
During an episode, lying flat and raising your legs facilitates better blood flow to the brain. If lying down isn't possible, sitting and placing your head between your knees can help until symptoms improve.
Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can trigger fainting spells. Drink at least two liters of water daily and avoid caffeine-rich drinks. Check urine color—light yellow indicates proper hydration. Proper hydration maintains blood volume and reduces episode frequency.
Increase Salt Intake
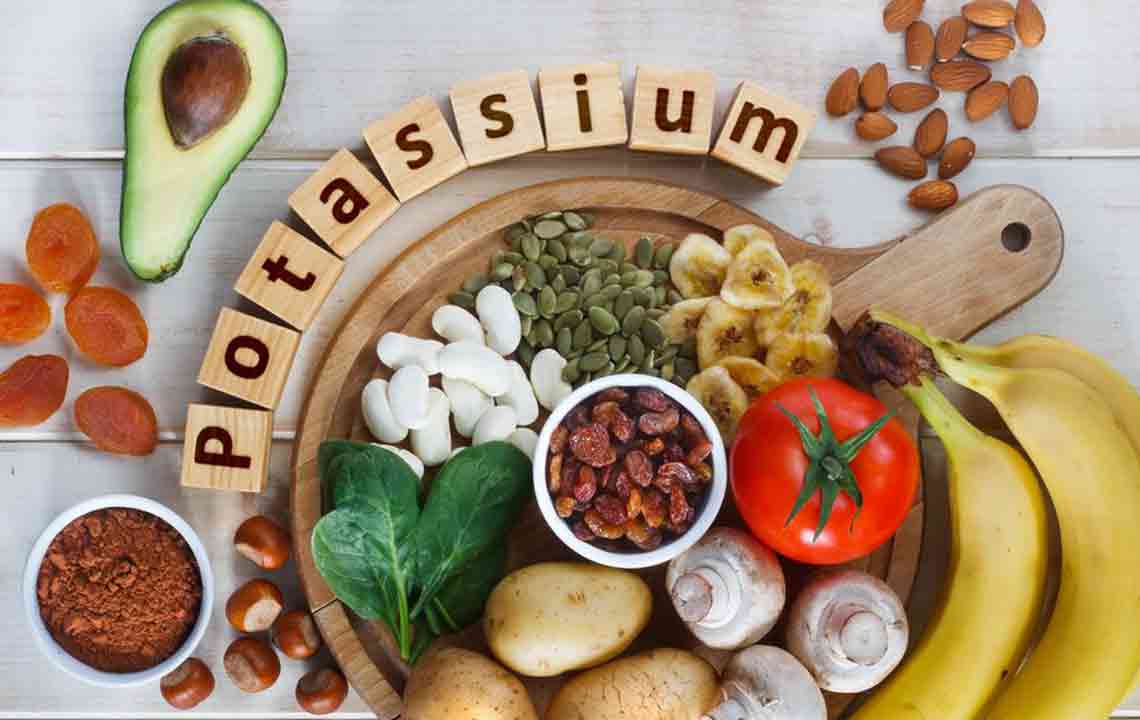
Adding salt can help manage vasovagal episodes by expanding blood plasma volume. Consult a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes to ensure safety and avoid potential health risks.
Avoid Known Triggers
Steer clear of situations that may provoke symptoms, such as blood, heat, stress, exhaustion, or seeing sharp objects. Recognizing and avoiding these can significantly reduce the likelihood of episodes.
Use Compression Stockings
Wearing compression stockings can improve blood circulation in the legs, preventing blood pooling that may lead to fainting during extended standing.
Perform Foot and Counter-Pressure Exercises
Exercises like leg crossings, arm tensing, and handgrip can help maintain blood flow during prolonged standing, especially in hot or crowded environments. Avoid standing still for long periods whenever possible.
Consider Biofeedback Techniques
Biofeedback can help control blood pressure and reduce fainting episodes through relaxation and self-regulation strategies.
Implant a Pacemaker
While vasovagal syncope is usually harmless, persistent or severe cases affecting daily life may require a pacemaker. This small device regulates heartbeat, especially when diagnostic tests reveal slow or irregular heart rhythms.
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids supports cardiovascular health. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are essential to develop personalized management plans tailored to individual needs and symptoms.