Understanding Foot Sole Discomfort: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pain on the sole of the foot. It highlights the significance of accurate diagnosis, including physical exams and imaging tests, and discusses therapies such as manual treatments, supportive devices, and exercises. Timely medical attention is emphasized for persistent discomfort or deformities. Proper management can significantly improve foot health, restore mobility, and prevent future issues. Understanding these aspects helps individuals seek appropriate care and maintain foot well-being effectively.
Sponsored
Experiencing pain on the underside of your foot can stem from various factors. It's essential to recognize that such discomfort doesn't always originate from toes or other parts of the foot. Sometimes, issues in the lower back or legs may contribute to this pain.
Signs of foot sole pain include limited mobility, numbness, and weakness. This may happen when nerve roots in the lower back become compressed, leading to radiating pain across the foot.
Symptoms of foot sole discomfort
Difficulty lifting the foot
Patients may struggle to move their foot forward or feel numbness.
This condition often results from nerve root compression in the lower back.
Weakness and heaviness in the foot
Pain radiates from nerve compression, traveling down over the top and bottom of the foot.
Difficulty walking on toes
Compressed sciatic nerve roots can cause weakness in calf muscles, making toe-walking and heel raising challenging. Mobility and balance may also be affected.
Causes of foot discomfort
Foot pain can arise from various conditions, including deformities, improper footwear, infections, and systemic diseases like gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus. Common foot deformities such as claw toes, tarsal coalitions, and calcaneal misalignment also contribute. Wearing high heels or tight shoes intensifies forefoot pain.
When to seek medical help
If foot pain hampers daily activities, causes deformity, swelling, skin or nail discoloration, or persistent tenderness, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Diagnosing foot pain
Accurate assessment involves physical examinations comparing both feet and grading pain levels from mild to severe. Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or bone scans help identify underlying issues not visible externally.
Evaluation procedures
Doctors assess both rested and active conditions, examining foot structure, muscle function, and nerve response. Movements against resistance, walking, and standing tests assist in pinpointing problems.
When physical exams are inconclusive, imaging studies are utilized to reveal hidden abnormalities or potential complications.
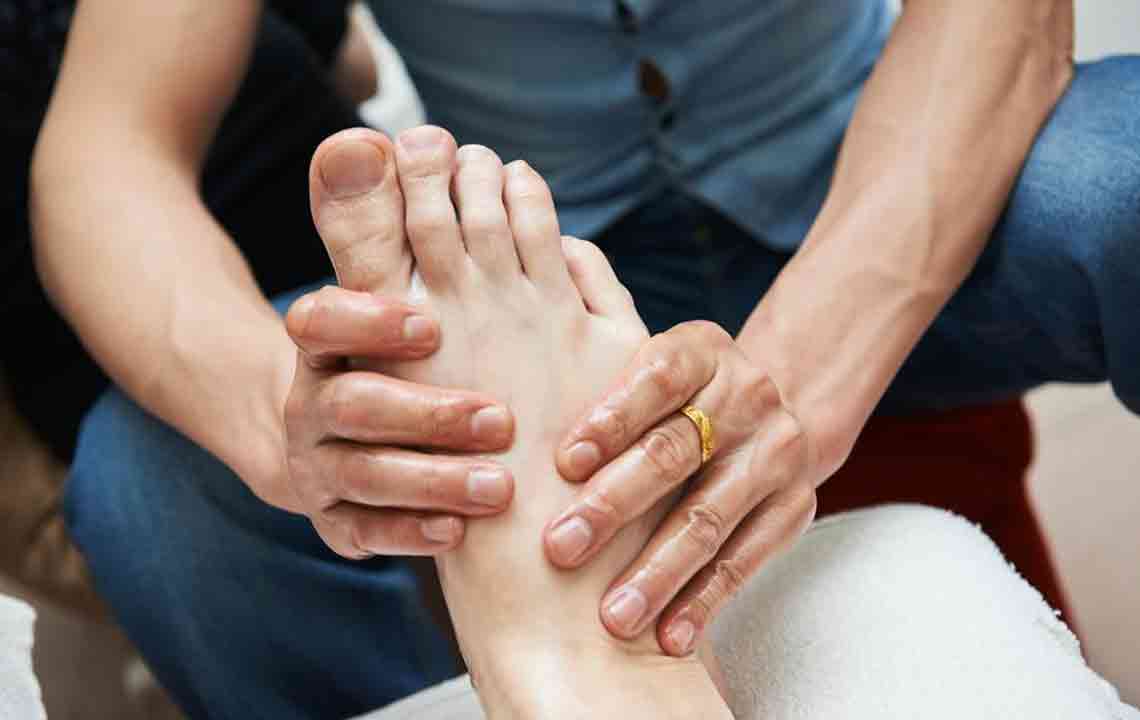
Managing foot sole discomfort
Treatment begins with identifying the root cause. Medical interventions may include ultrasound therapy, electrical stimulation, laser, or manual therapies to alleviate pain and improve circulation, promoting healing.
Supporting devices like heel pads, arch supports, or wedges are often recommended to enhance foot alignment and prevent further strain.
Strengthening exercises and stability routines can correct muscular imbalances, aiding recovery and preventing future issues.
Adherence to prescribed medications and ongoing care are vital. With time, proper management can restore comfort and mobility. Consistent follow-up and care are essential to ensure full recovery and prevent recurrence.