Comprehensive Guide to Cataract Management and Treatment Options
Learn about cataract causes, symptoms, and comprehensive treatment options including eye drops, laser surgery, and lifestyle changes. Discover how to prevent cataracts by managing risk factors like diabetes, UV exposure, and family history. Early detection and professional consultation are crucial to maintain healthy eyesight and avoid vision loss.
Sponsored

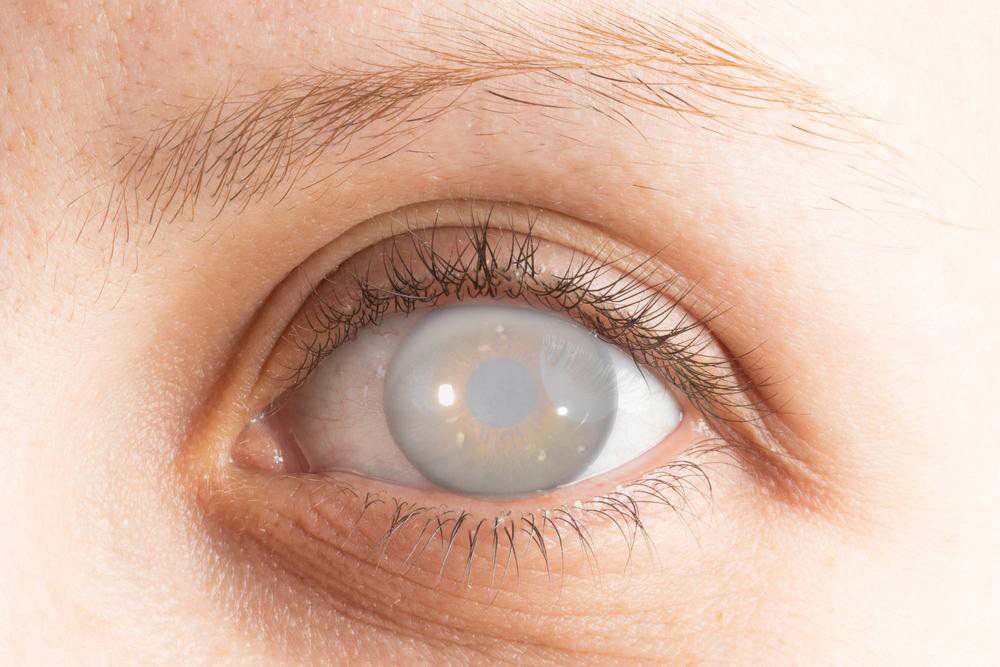
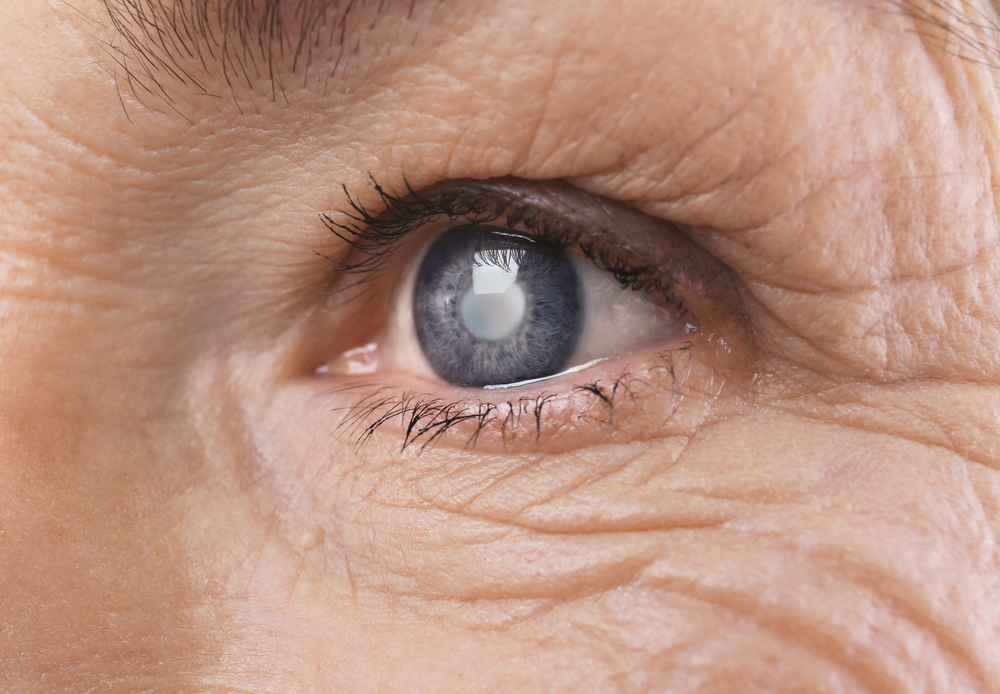
If you notice blurry vision, especially if you're in the senior age group, it could indicate cataracts. This common condition occurs when protein buildup clouds the eye's lens, leading to hazy sight. Left untreated in early stages, cataracts can worsen and cause significant vision loss. Over 22 million people worldwide suffer from this condition, and it's increasingly seen in children due to excessive exposure to screens.
Imagine viewing the world through a dusty window—that's how cataracts affect vision. Causes include age, trauma, genetics, or secondary conditions. Treatment varies from corrective eyewear to advanced surgical procedures.
Cataracts develop when the lens becomes cloudy, creating a blurred or foggy visual experience. They are classified into age-related, congenital, secondary, and traumatic categories. Management options include:
Eyewear and Contact Lenses
In early stages, medication such as eye drops, along with glasses or contact lenses, can improve vision. Consistent use as prescribed is crucial for effective control.
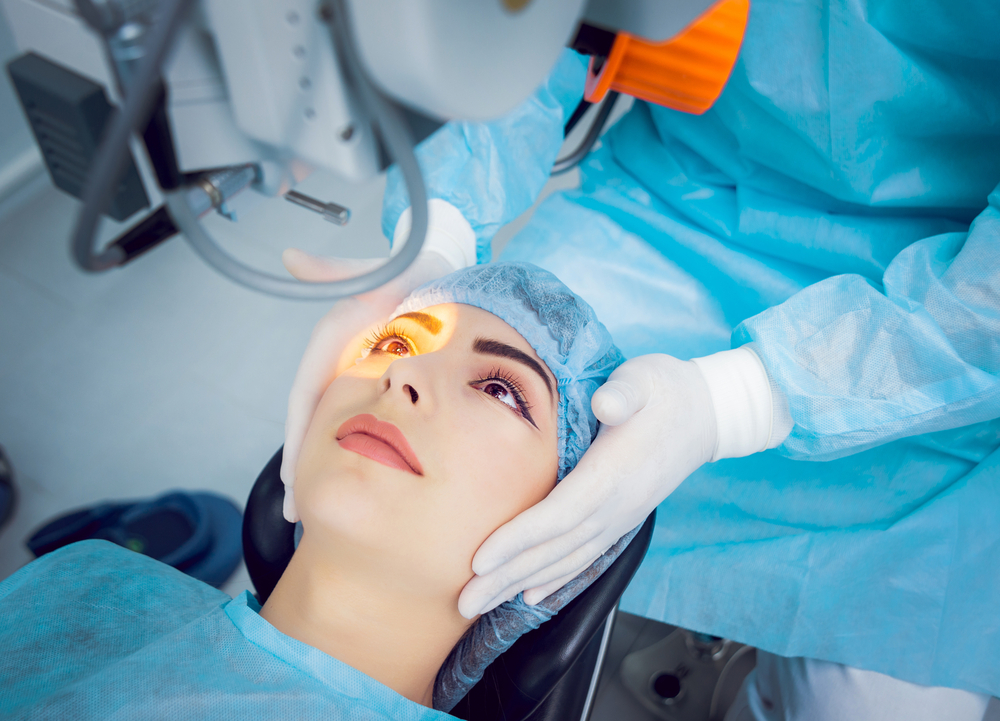
Recent technological advances make cataract surgery quick and minimally invasive. Laser procedures involve replacing the cloudy natural lens with an artificial one, often allowing same-day discharge. Patients generally experience sharper vision post-surgery. To prevent cataracts, lifestyle modifications are essential, especially for individuals at risk due to health conditions.
Risk Factors and Preventive Care
Diabetes: Diabetics, especially younger adults, are more prone. Managing blood sugar levels helps reduce risk.
Previous Eye Surgery or Injury: Past eye trauma or surgeries increase susceptibility, requiring careful monitoring.
Glaucoma and Medications: Treatments for glaucoma and certain drugs may elevate cataract risk. Consult your doctor for alternatives or precautions.
Obesity: Excess weight leads to diabetes, which can cause cataracts. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet is beneficial.
Sunlight and Artificial Light Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV rays damages eye lenses. Use sunglasses and take breaks from screens to protect your eyesight.
Tobacco and Alcohol: Nicotine and alcohol consumption damage eye tissues, increasing cataract likelihood. Abstaining supports overall eye health.
Family History: A genetic predisposition necessitates proactive monitoring and lifestyle adjustments. Regular checkups are recommended.
Adopting a nutritious diet and routine eye exams can significantly lower early-stage cataract development. If symptoms arise, seek prompt medical advice to explore suitable treatments rather than self-medicating. Early intervention ensures better preservation of vision.