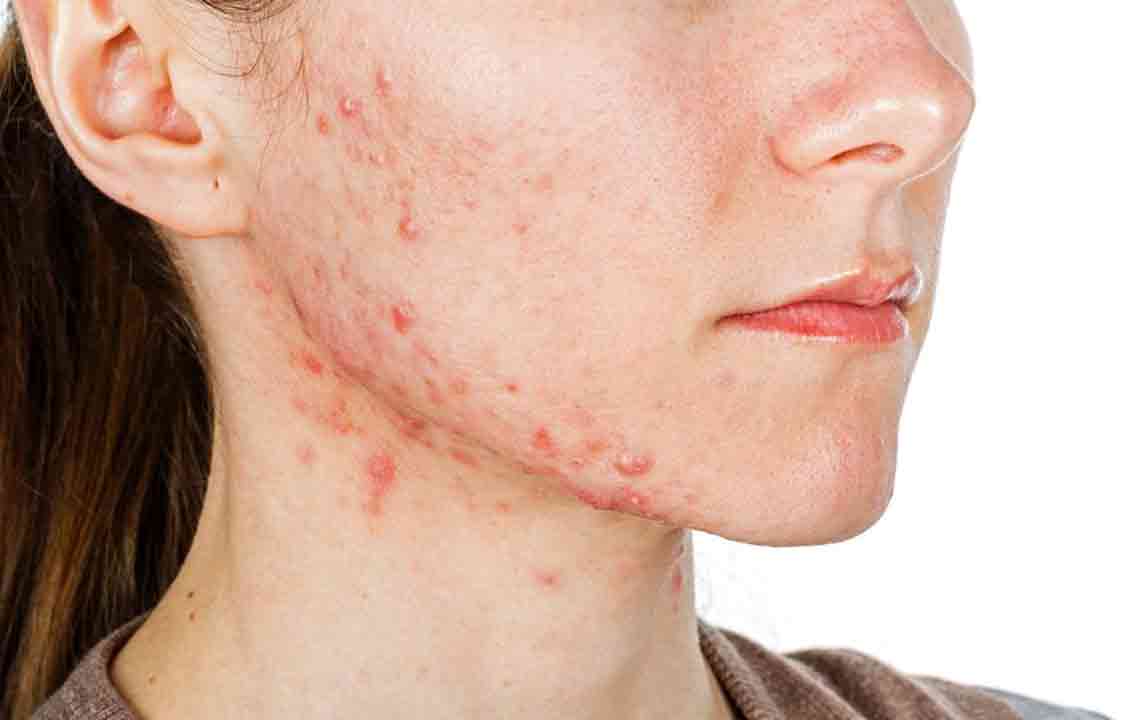
Understanding Lupus: Causes and Warning Signs
Lupus is an autoimmune disease marked by inflammation and skin rashes, with symptoms like fatigue, fever, hair loss, and joint pain. Causes include genetic and environmental factors, with triggers such as sun exposure, infections, and medications. Recognizing early signs and seeking prompt medical attention can lead to effective management of this complex condition, preventing serious health issues and improving patient outcomes.
Sponsored
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disorder that leads to inflammation and swelling in multiple body tissues. Its impact varies widely among individuals, with some experiencing intense symptoms while others have milder effects. Usually emerging in early adulthood, especially before age 30, lupus requires careful attention to its signs and triggers.
Factors Contributing to Lupus Skin Manifestations
The precise cause of lupus-related skin issues remains unknown. Scientific evidence suggests that genetic factors combined with environmental influences play significant roles. It’s important to note that lupus is not contagious and cannot be transmitted between individuals.
Potential triggers for lupus include:
Sun exposure: Excessive sunlight can provoke skin rashes in genetically predisposed individuals.
Infections: Certain infections may initiate or worsen lupus symptoms.
Medications: Drugs like blood-pressure medicines, antibiotics, and anti-seizure drugs can induce lupus flare-ups. Discontinuing these medications often improves symptoms.
Major Indicators of Lupus Skin Problems
Fatigue: Nearly 90% of lupus patients report persistent tiredness. An afternoon rest can help restore energy, but excessive sleep may cause insomnia. Staying active helps maintain vitality.
Unexplained Fever: A low-grade fever between 98.5°F and 101°F is common at early stages. Recurrent fevers warrant medical evaluation, as they could signal infections or lupus activity.
Hair Loss: Inflammation of the scalp and skin often results in hair thinning or shedding. This can affect eyebrows, eyelashes, and other body hair. Hair restoration usually occurs after effective treatment of lupus.
Lung Inflammation: Pulmonary involvement leads to lung swelling, chest pain during breathing, and in severe cases, shrinking of lung tissue, known as vanishing lung syndrome.
Kidney Issues: Nephritis, or kidney inflammation, may develop after several years of lupus. Symptoms include swelling in legs and feet, dark urine, blood in urine, frequent nighttime urination, and localized pain.
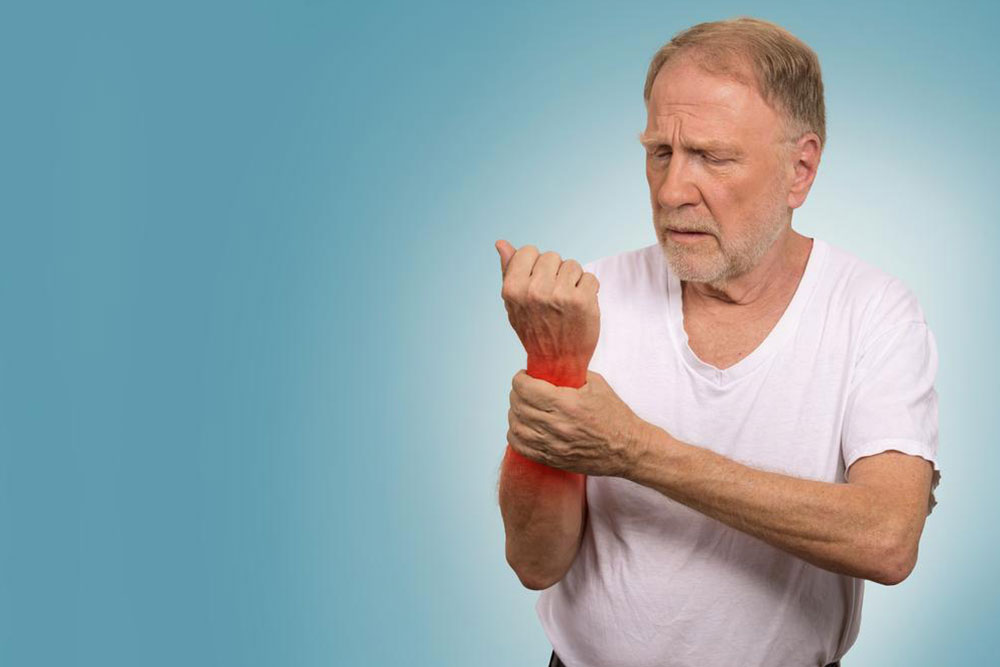
Joint Discomfort: Stiffness, swelling, and pain in joints are common. These symptoms fluctuate and may require medical management beyond over-the-counter remedies.
Thyroid Dysfunction: Many with lupus also develop thyroid disorders, affecting metabolism and causing weight fluctuations, along with impact on vital organs like the brain, liver, and heart.
If symptoms of lupus appear, prompt medical consultation is critical. Early diagnosis and treatment help prevent serious complications and improve quality of life.