Understanding Female Jock Itch: Causes and Variations
Discover the causes and types of female jock itch, a common fungal infection affecting the groin. Learn about risk factors, symptoms, and how to prevent the infection by maintaining good hygiene and avoiding shared clothing. Recognize different variations such as tinea cruris, eczema, inverse psoriasis, heat rash, and contact dermatitis to seek appropriate treatment. Consult a dermatologist if symptoms persist for effective management.
Sponsored

Female jock itch, medically known as tinea cruris, is a fungal skin infection affecting the groin region. It commonly develops in hot, humid environments where moisture and sweat are trapped in skin folds, creating ideal conditions for fungal growth.
Key causes of female jock itch include:
The warm, moist, and dark nature of the groin area encourages fungal proliferation.
Frequent workouts lead to moist clothing, increasing infection risk. Public pools and shared gym lockers can also facilitate transmission.
Sharing contaminated clothing can spread the infection among uninfected women. To prevent this, wear cotton underwear, shower regularly, and change workout or swimwear promptly after use.
Types of female jock itch to be aware of include:
Tinea cruris
Also called jock itch or crotch rot, this fungal infection results from the factors mentioned above.
Atopic dermatitis
Often known as eczema, it causes rashes due to skin hypersensitivity.
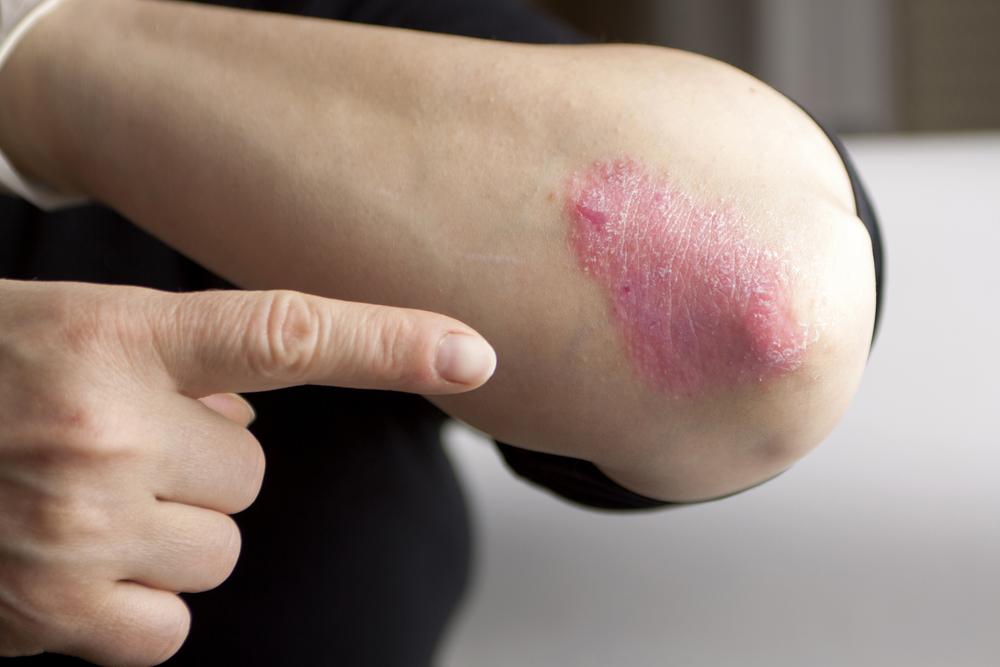
Inverse psoriasis
A chronic condition producing bright red, shiny, and smooth skin plaques resulting from overgrowth and inflammation.
Heat rash
Caused by blocked sweat glands, leading to sweat accumulation under the skin and resulting in heat rash.
Contact dermatitis
Triggered by allergic reactions to fabrics, chemicals, soaps, or topical products applied to the groin, causing itching, rashes, and sometimes blisters.
If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a dermatologist is recommended for proper diagnosis and treatment.