Understanding Lower Back Cramping: Causes, Symptoms, and Remedies
Lower back muscle spasms are common and manageable conditions caused by injuries, strain, or underlying health issues. Treatments include ice and heat therapy, medications, physical therapy, and natural remedies like hydration and exercise. Prevention strategies focus on maintaining good posture, weight, and muscle strength. Early medical consultation is recommended for severe or persistent symptoms. With proper care, most back spasms can be effectively relieved, improving mobility and quality of life without surgical intervention.
Sponsored

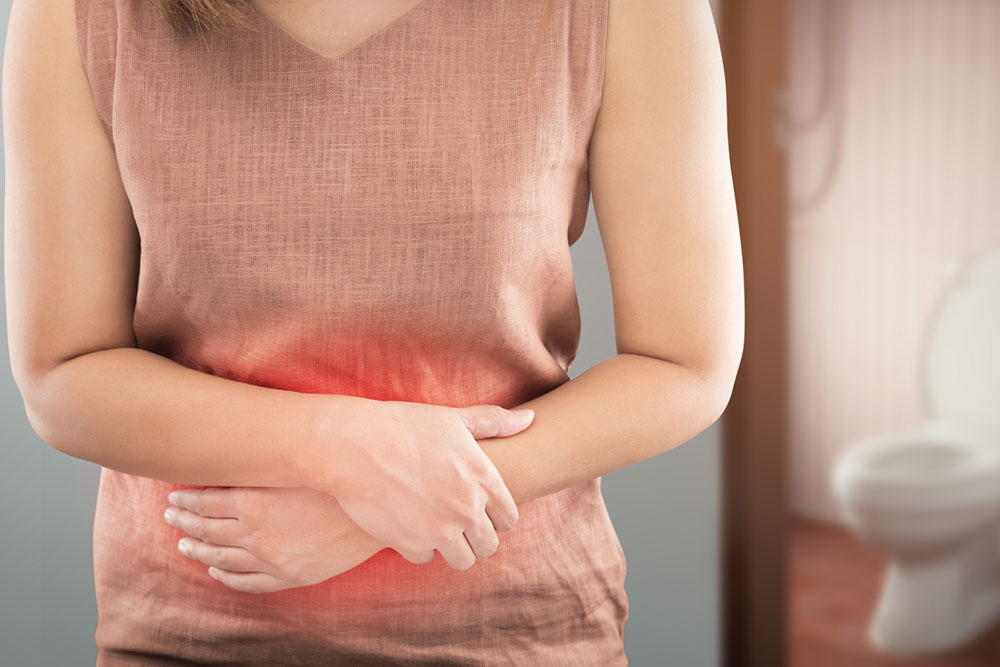
Back muscle spasms are common discomforts experienced by many individuals, especially in the lower back. These involuntary muscle contractions can occur unexpectedly, ranging from mild soreness to intense pain that hampers movement.
Thankfully, most back spasms can be managed without surgical intervention. However, if nerve issues in the spine contribute to the pain, professional medical treatment becomes necessary.
Factors Leading to Lower Back Spasms
Several factors can trigger lower back spasms, including muscle, ligament, or tendon injuries, as well as underlying health issues like arthritis or herniated discs.
Heavy lifting, sudden movements, or strenuous activities can also cause spasms. Athletes involved in sports like football and golf often experience this due to intense training regimes. Conditions such as arthritis or spinal disc damage further increase risk.
Diagnosis typically involves X-rays to detect fractures or arthritis, while MRI or CT scans provide detailed images of soft tissues when necessary.
During consultation, doctors assess the pain's severity and duration to determine the best treatment approach. Prompt attention to spasms usually results in relief, but severe symptoms require medical intervention.
Treatment Options for Lower Back Spasms
Initial treatment includes applying ice and heat—ice reduces inflammation, while heat promotes blood flow and relieves pain. Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants may also be prescribed.
Injections might be recommended for inflammation, but these should only be administered under medical supervision to avoid side effects. Physical therapy focusing on strengthening back and core muscles can also prevent future spasms.
Natural Remedies for Back Spasm Relief
Natural strategies include staying well-hydrated, as water helps eliminate toxins and keeps muscles healthy. Maintaining adequate magnesium levels supports muscle function, reducing cramping episodes.
Engaging in daily gentle exercises, like stretching or yoga, can improve flexibility and prevent spasms. Regular activity is beneficial in maintaining back health and reducing discomfort.
Preventive Tips for Back Spasms
Protecting your back involves proper posture, weight management, and wearing supportive footwear. Strengthening core and back muscles through targeted exercises also decreases risk. Consulting a healthcare professional is advisable if spasms persist or worsen. Combining medication, exercise, and healthy habits offers effective relief and enhances back resilience. Remember, back spasms are generally manageable and not life-threatening when treated early.