Understanding Anxiety Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
This article explores anxiety disorders, highlighting their causes, key symptoms, and treatment methods. It emphasizes recognizing early signs and seeking appropriate medical or therapeutic intervention to manage anxiety effectively. Understanding the triggers and symptoms helps individuals seek timely help to improve their quality of life.
Sponsored
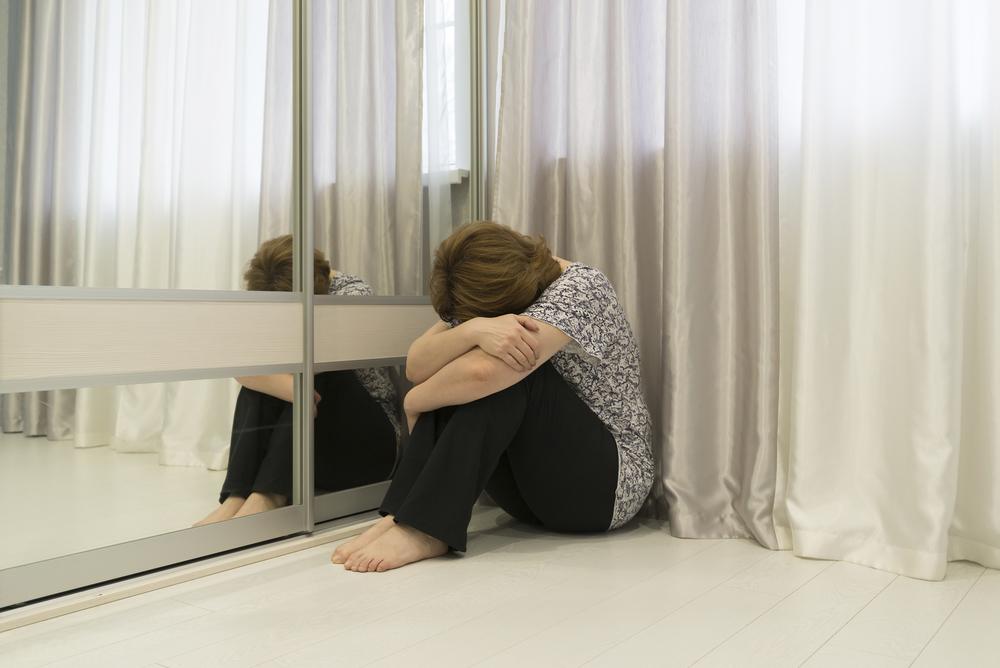

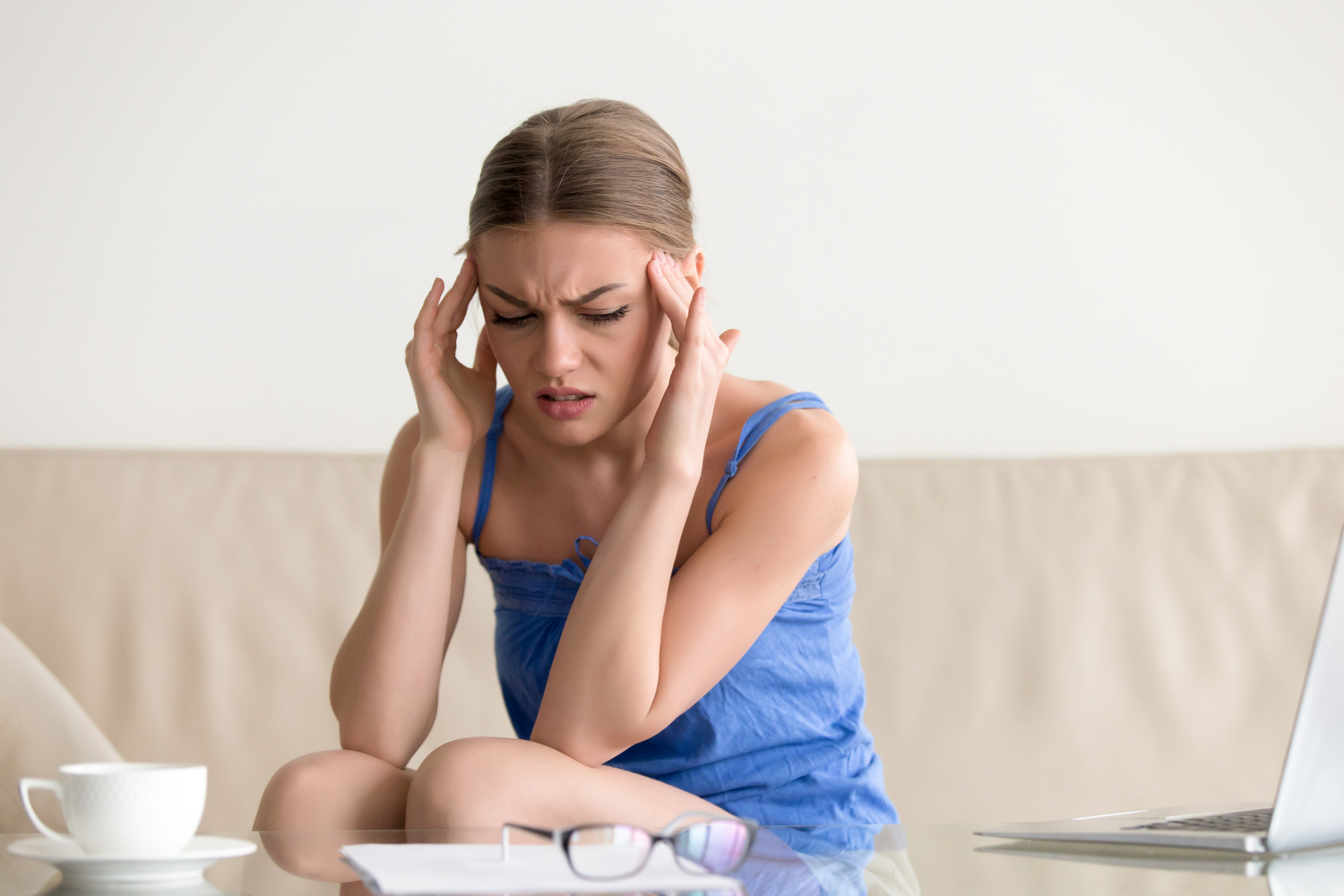
Anxiety can strike at any moment—whether at work, during exams, or when facing important choices. For some individuals, anxiety becomes persistent, interfering with everyday life. These disorders include conditions like phobias and panic attacks. Someone with anxiety may experience heightened fears lasting over six months, significantly impacting their routine.
Panic episodes
People with panic disorder may experience sudden attacks characterized by intense fear, shortness of breath, sweating, and a sense of impending danger.
Those suffering from panic attacks often anticipate future episodes, leading them to avoid specific situations and environments.
Phobic conditions
Phobias involve an irrational fear of particular objects or scenarios. Affected individuals might avoid situations they perceive as threatening, even if others see them as harmless.
What triggers anxiety?
Research indicates both genetic and environmental factors contribute to anxiety development.
Imbalances in brain chemistry can initiate feelings of fear or anxiety. Common causes include:
Family history of mental health issues increases vulnerability.
Childhood traits such as shyness or inhibition can predispose individuals.
Excessive caffeine intake may cause restlessness and heart palpitations.
Preexisting health problems like heart conditions can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
External influences also play a role, including:
Financial hardships
Medication side effects
Emotional trauma such as loss of loved ones
Intense work-related stress
Substance misuse
Relationship issues
Post-illness depression
Recognizing symptoms of anxiety
Symptoms can develop during adolescence and worsen over time. Awareness of signs is crucial for seeking effective treatment.
Persistent worry and inability to control fears
Restlessness and concentration difficulties
Physical issues like headaches, muscle pain, and stomach discomfort
Irritability and mood disturbances
Sleep disturbances such as insomnia
Excessive concern over minor matters
Seeking proper treatment for anxiety
Management options include medication, psychotherapy, or both, tailored to individual needs.
Psychotherapy, especially cognitive-behavioral therapy, helps individuals challenge and reduce fearful thoughts and behaviors.
Medications like antidepressants and beta-blockers can help alleviate symptoms.
Benzodiazepines are also effective, providing quick relief compared to other medications.