Understanding Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Explore comprehensive insights into type 1 diabetes, including its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. Learn how insulin therapy and lifestyle changes can help maintain health. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential for avoiding complications like kidney damage and vision problems, ensuring a better quality of life for those affected.
Sponsored

Type 1 diabetes, often called juvenile diabetes, occurs when the pancreas produces minimal or no insulin. The immune system mistakenly destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, disrupting glucose regulation in the body.
Importance of Insulin
Insulin is vital for transporting glucose into body cells, providing energy. Without enough insulin, glucose cannot enter cells and accumulates in the bloodstream, starving cells of energy.
This buildup causes high blood sugar, leading to various health issues such as:
Dehydration
Excess sugar causes increased urination, resulting in water loss and dehydration.
Weight Loss
The loss of glucose through urination leads to calorie loss, causing unexplained weight reduction.
High blood sugar also damages nerves and blood vessels in the eyes, kidneys, and heart, increasing risks of strokes and heart attacks.
Type 1 diabetes is relatively rare, affecting about 5% of the population, typically appearing around age 20, equally affecting men and women.
What Causes It?
The exact cause remains unknown, but genetics play a significant role. It may also be associated with other autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo.
Symptoms
Early signs include excessive thirst, increased hunger, dry mouth, stomach pain, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, blurred vision, and skin infections. Emergency signs include confusion, shaking, rapid breathing, severe abdominal pain, and rare loss of consciousness.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure glucose levels and urine tests for sugar. Currently, there is no way to prevent type 1 diabetes.
Management
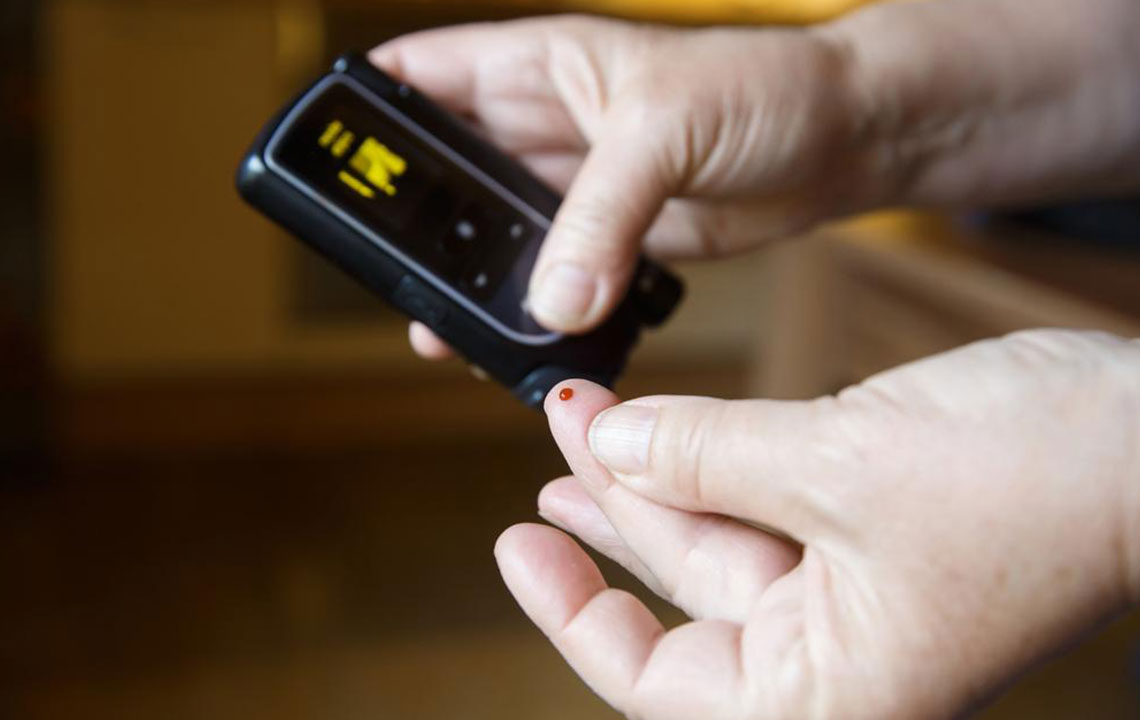
People with type 1 diabetes can lead healthy lives by monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. Treatment primarily involves insulin injections, with attention to three phases: onset, peak, and duration. Lifestyle modifications, especially exercise, are crucial; blood sugar should be checked before and after activities, ideally under a dietitian’s guidance.
Potential Complications
If uncontrolled, type 1 diabetes can cause retinopathy (eye problems), nephropathy (kidney damage), and poor blood circulation, increasing risks of serious health issues such as heart disease and kidney failure.