Selecting the Perfect Digital Hearing Device
Discover the key factors in choosing the ideal digital hearing aid. From discreet models to powerful behind-the-ear options, this guide covers the main types, benefits, and considerations to help you find the best match for your hearing needs and lifestyle. Understand features, costs, and customization options to make an informed decision and improve your daily hearing experience.
Sponsored
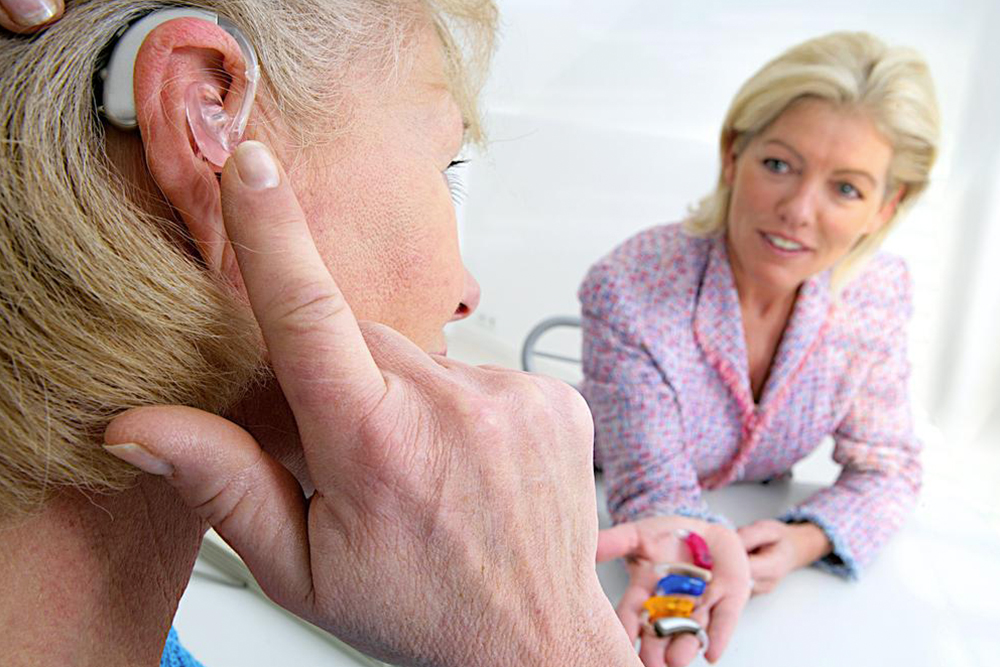

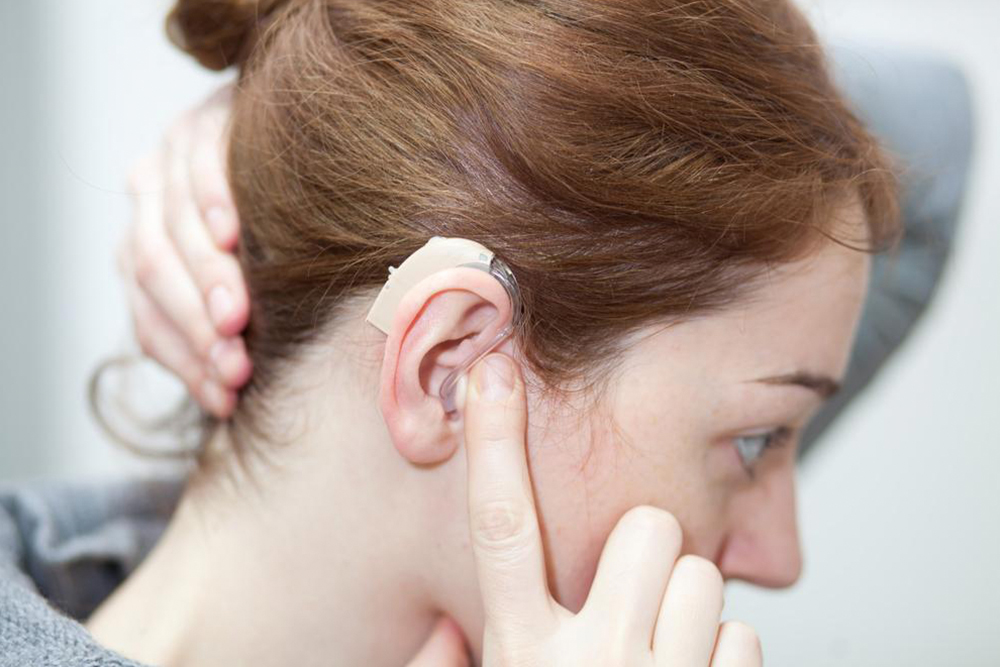
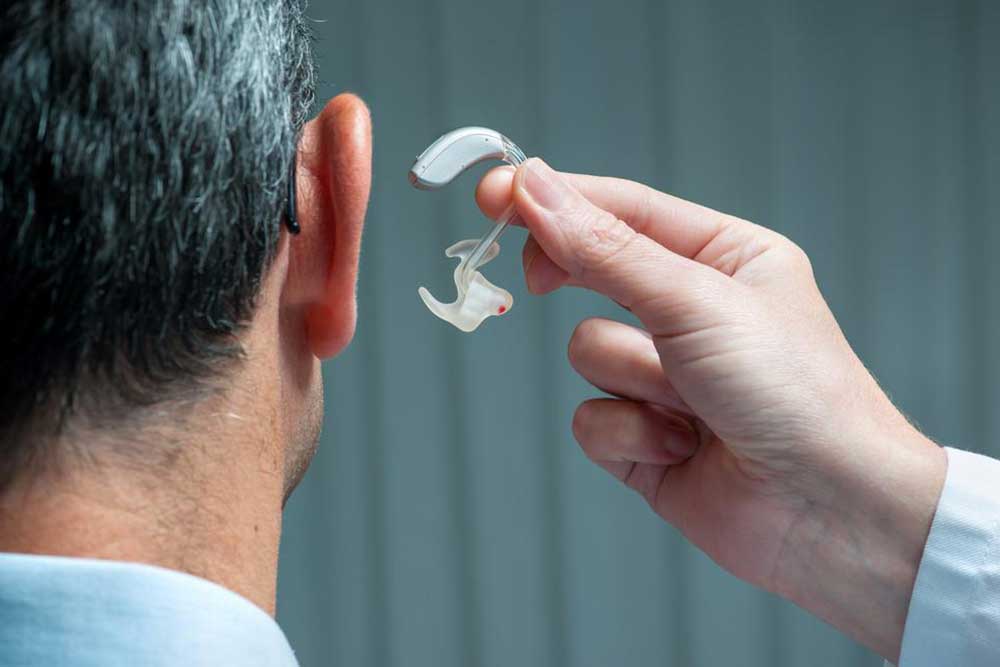
If you find yourself repeatedly asking "what!" throughout the day, it might be time to consider a hearing aid. While hearing aids don't cure deafness, they amplify sounds to make them clearer. A typical digital hearing device features a microchip with an amplifier that converts sounds into digital signals, adjusts amplification based on your hearing loss and environment, then converts them back into sound waves for your ears. Customization to fit your ear and lifestyle is essential when choosing a device.
There are six primary types of digital hearing aids to consider:
In-the-ear (ITE) Hearing Aids: These are crafted to fit inside your ear and are nearly invisible. Suitable for mild to moderate hearing impairment.
Pros:
Discrete and compact design
Minimizes background noise interference
Cons:
Prone to earwax clogging
Lacks additional controls like volume adjustment
Uses small batteries with limited lifespan
In-the-canal (ITC) Hearing Aids: Slightly larger, molded to fit within the ear canal. Ideal for mild to moderate loss.
Pros:
More manageable size
Easy to put on and remove
Cons:
Clogging risk from earwax
Button controls may be harder to operate due to size
Full-shell or Half-shell In-the-ear Aids: Full shell covers most of the outer ear; half shell covers the lower half.
Pros:
Good handling and maintenance access
Accept larger batteries with longer use
Cons:
More visible
May pick up more background noise
Susceptible to earwax buildup
Behind-the-ear (BTE) Hearing Aids: Consist of a component behind the ear connected via a tube or wire to the earpiece. Versatile for various hearing levels.
Pros:
High amplification capability
Easy to handle and adjust
Cons:
More noticeable visually
Can pick up background noise
Receiver-in-canal (RIC) Hearing Aids: Similar to BTEs but use a thin wire instead of a tube, making them less visible.
Pricing for digital hearing aids typically starts around $1500, increasing with added features, accessories, professional services, warranties, battery life, and noise reduction capabilities. It's recommended to try devices before making a final decision to ensure the best fit and performance.