Understanding Chronic Bronchitis: Symptoms, Triggers, and Management Strategies
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term lung condition characterized by persistent cough, mucus production, and airway inflammation. Causes include infections, smoking, and exposure to irritants. Treatment involves lifestyle changes, medications, breathing exercises, and vaccinations to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Regular exercise and pulmonary rehab programs are beneficial for improving lung function. Recognizing symptoms early and avoiding triggers can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.
Sponsored

Chronic bronchitis involves long-term inflammation or irritation of the bronchial tubes within the lungs. These airways, responsible for directing airflow, become inflamed and produce excess mucus, leading to obstruction of airflow. Persistent coughing, mucus production, and chest tightness are common signs. The condition is characterized by symptoms lasting over three months and often occurs with emphysema, collectively forming chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This article highlights symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options for chronic bronchitis.
Exposure to viruses, particularly those causing colds, frequently triggers inflammation of the bronchial lining. These infections can be contagious, spreading through breathing or contact. Smoking significantly worsens the condition by irritating airways and promoting mucus buildup. Long-term exposure to chemical fumes also increases risk.
Management includes home remedies such as staying well-hydrated, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, ensuring adequate rest, and using humidifiers. Over-the-counter medications like pain relievers and cough suppressants can alleviate symptoms. Quitting smoking and avoiding irritants are essential preventive measures.
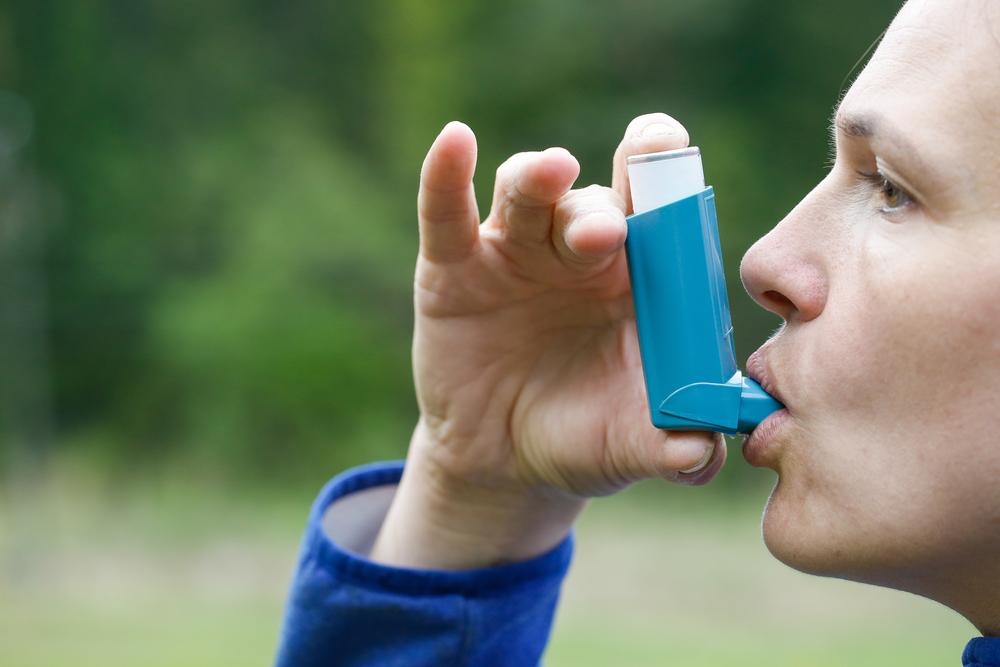
Persistent cases may require medical treatment, including bronchodilators to open airway passages, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and combination therapies. Regular exercise and pulmonary rehab programs strengthen respiratory muscles and improve breathing. Breathing techniques like pursed-lip breathing can slow rapid breathing. Severe cases may benefit from supplemental oxygen therapy. Vaccinations like the flu shot and pneumococcal vaccine are recommended to prevent lung infections associated with chronic bronchitis.