Understanding Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
This article explores the various causes, common symptoms, and different types of arthritis. It highlights the importance of early diagnosis and management, including medication and lifestyle changes, to reduce pain and prevent joint damage. Recognizing symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, and swelling is crucial for timely treatment. The article details specific arthritis forms like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and more, providing a comprehensive overview for those affected or seeking to learn about this widespread condition.
Sponsored

Arthritis is a condition characterized by joint inflammation that causes significant pain. This broad term encompasses over 200 different diseases, categorized into seven primary groups based on their nature and effects. These include degenerative, inflammatory, soft tissue, back pain, infectious, connective tissue, and metabolic arthritis.
The causes of arthritis are varied and often involve multiple factors. Family history can predispose individuals to osteoarthritis. Autoimmune issues may trigger rheumatoid arthritis or lupus. Metabolic irregularities can lead to gout. Injuries or infections also contribute to different arthritis forms.
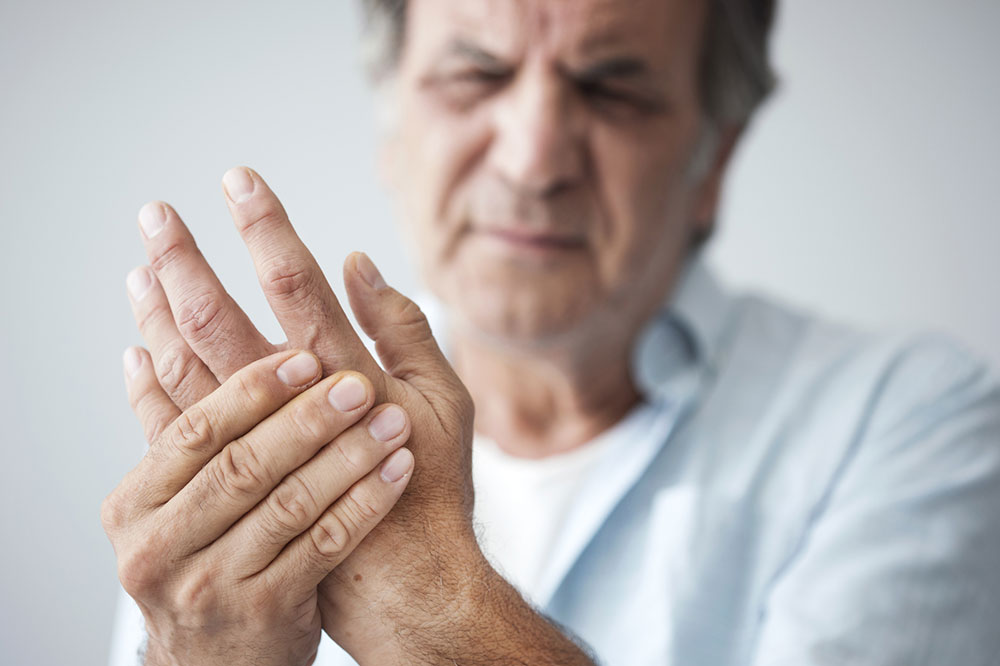
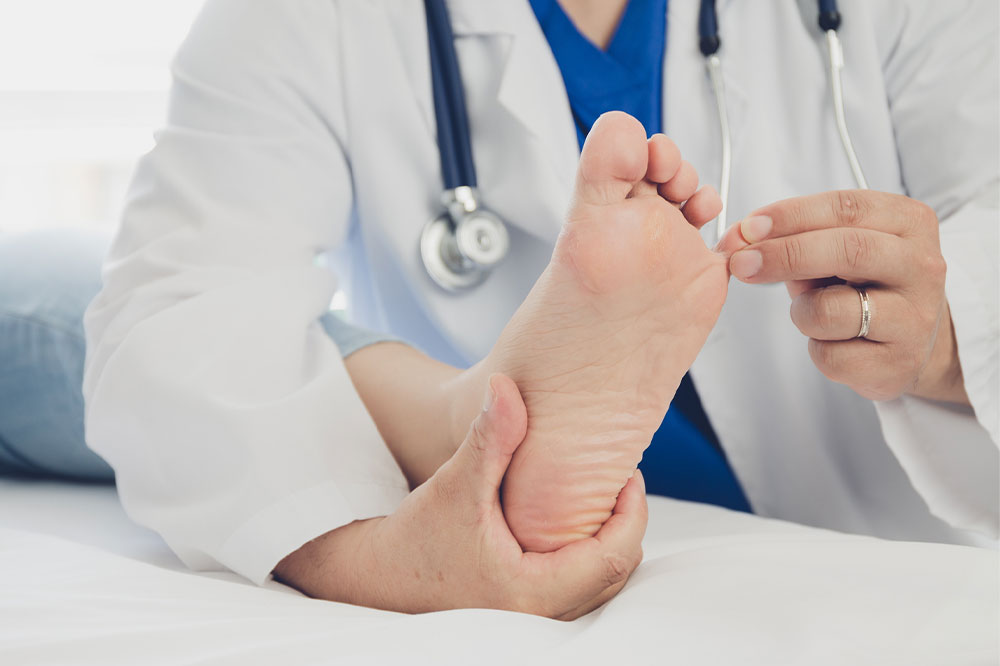
Common symptoms of arthritis often include persistent joint pain, stiffness especially after waking, swelling, and difficulty moving affected joints. The severity and type of symptoms depend on the specific arthritis variant. Recognizing these signs early helps in effective management and prevents progression.
Joint discomfort - Pain in joints such as knees, hips, shoulders, or elbows, which may be continuous or episodic.
Stiffness - Usually occurs after inactivity or waking up and may persist in some cases.
Swelling - Affected joints may become tender, red, warm, and swollen.
Mobility challenges - Difficulty in moving joints or performing routine tasks, signaling potential arthritis issues.
If these symptoms appear, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for diagnosis and treatment to slow disease progression. Different types of arthritis exhibit unique painful features:
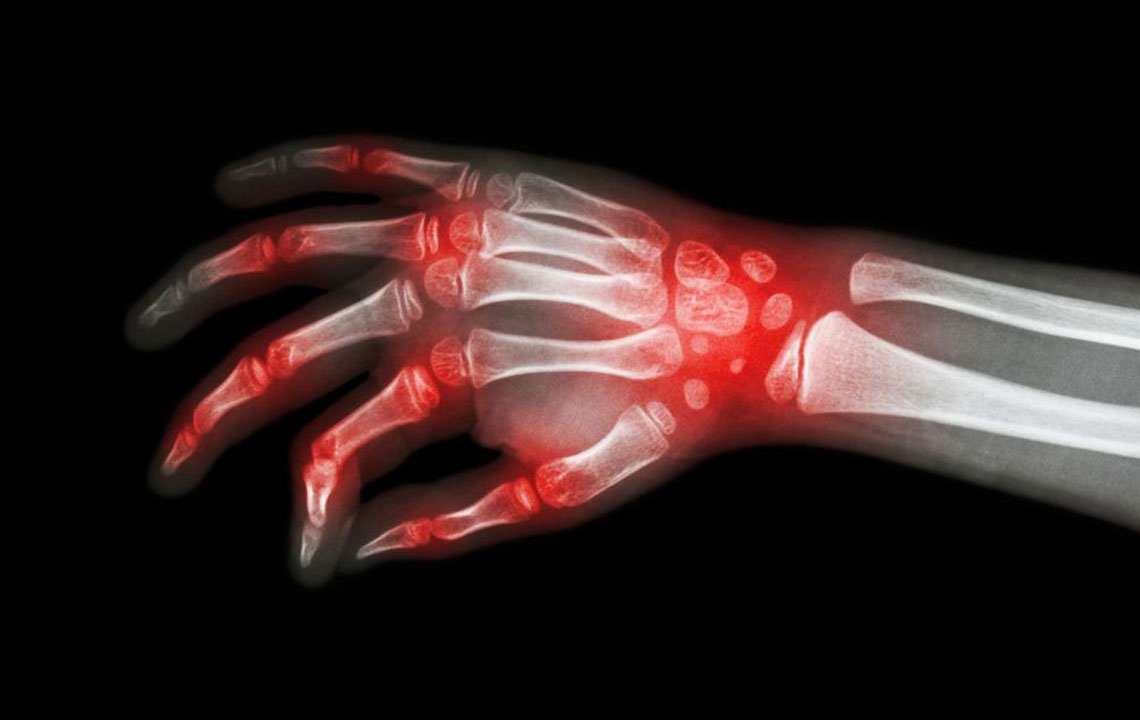
Osteoarthritis - Cartilage breakdown leads to bone-on-bone contact, causing severe pain during joint movement.
Rheumatoid arthritis - An overactive immune response damages joint lining and surrounding tissues, resulting in persistent pain and potential deformities.
Psoriatic arthritis - Immune system attacks connective tissues and joints, often accompanying psoriasis.
Gout - Uric acid build-up crystallizes in joints, especially the big toe, leading to sudden and intense pain episodes.
Fibromyalgia - Causes widespread, chronic pain along with fatigue, sleep disturbances, and mood issues.
Lupus - An autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs with joint pain, fatigue, and skin rashes.
Managing arthritis involves medications, physical therapy, regular exercise, and a balanced diet to alleviate pain and prevent joint deterioration.