Effective Strategies for Preventing and Managing Whooping Cough
This article covers essential preventive measures and treatments for whooping cough, including vaccinations like Tdap and DTaP, antibiotic therapy, and home care strategies. It emphasizes early intervention and vaccination to effectively manage and prevent Pertussis infections across all age groups.
Sponsored

Strategies for Prevention and Management of Whooping Cough
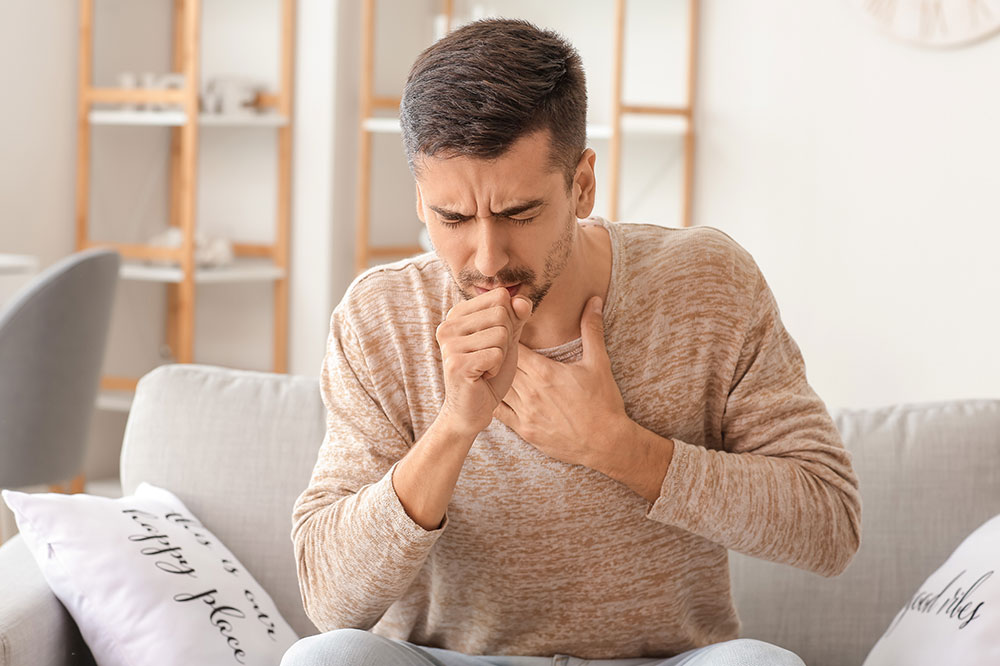
Whooping cough, medically known as Pertussis, causes a severe, uncontrollable cough that can impair breathing. It is caused by the Bordetella pertussis bacteria and can affect anyone from infants to adults. The disease is treatable with prompt medical care, making prevention crucial. This article outlines essential preventive tactics and treatment options for whooping cough.
Prevention Tips for Whooping Cough
Since the disease is highly contagious, vaccination is key to protection. The Tdap vaccine is administered to teenagers and adults, while children receive the DTaP shot as part of their routine immunizations.
Pregnant women are recommended to get the vaccine between 27 and 36 weeks of pregnancy, enabling antibody transfer to the baby. Combining vaccination with antibiotics during treatment can protect both children and adults from this illness.
Standard Treatment Options
Antibiotics
As Pertussis is bacterial, antibiotics are used to control its progression. Additionally, IV fluids are administered to prevent dehydration. Even vaccinated children may need antibiotics to prevent infection spread.
It’s important to note that antibiotics manage the bacterial infection but do not cure Pertussis itself. Treatment duration typically spans a few weeks, after which health professionals review symptoms.
Home Care and Monitoring
Infants and young children may take longer to recover, and symptoms can reappear weeks after treatment. Close observation by family and caregivers is essential, and emergency medical attention should be sought if cough intensity increases. Using humidifiers can help soothe irritated airways and ease coughing discomfort.
In addition to treatment, booster doses of Tdap are recommended in adolescence to sustain immunity and reduce transmission risks.